English II 2020
Korea invented the world's first rainfall gauge and has a long history of recording weather events and natural disasters. According to historical records, natural disasters occurred 40,000 times in Korea from the Three Kingdoms period to the Joseon dynasty. Some natural disasters were inevitable. However, people have tried to manage these kinds of disasters by strengthening prediction, prevention, and preparedness strategies.
In ancient times, Koreans conducted irrigation projects and used charms or incantations to overcome nature's challenges, reduce damage from droughts and floods, and bring good harvests. Since the Agricultural Age, agricultural productivity has been constantly influenced by droughts and floods. When floods occurred during the Three Kingdoms period, they were described in detail by recording Daesu (big water) and Daewu (big rainfall). There were about 40 events, including DaeSu, Daewu, and rainfalls causing water-related damages, according to Samgug sagi (the History of the Three Kingdoms). Records of natural disasters from the Three Kingdoms history focused on the capital. Even though the historical disaster records from the Goryeo dynasty focused on the capital as well, there were more records about natural disasters than from the Three Kingdoms period. Thus, the central government implemented strong policies to mitigate the damage caused by natural disasters during the Goryeo dynasty.
During the Joseon dynasty, both the Seungjeongwon ilgi (the Diaries of the Royal Secretariat) and the Joseon wangjo silrok (the Annals of the Joseon Dynasty) recorded floods that occurred in Seoul for 450 years. Water levels of the Hangang and streams in Seoul also appear in the documents recording ritual ceremonies for rain and sun held during the Joseon dynasty. According to these documents, there were 176 floods around Seoul in this period.
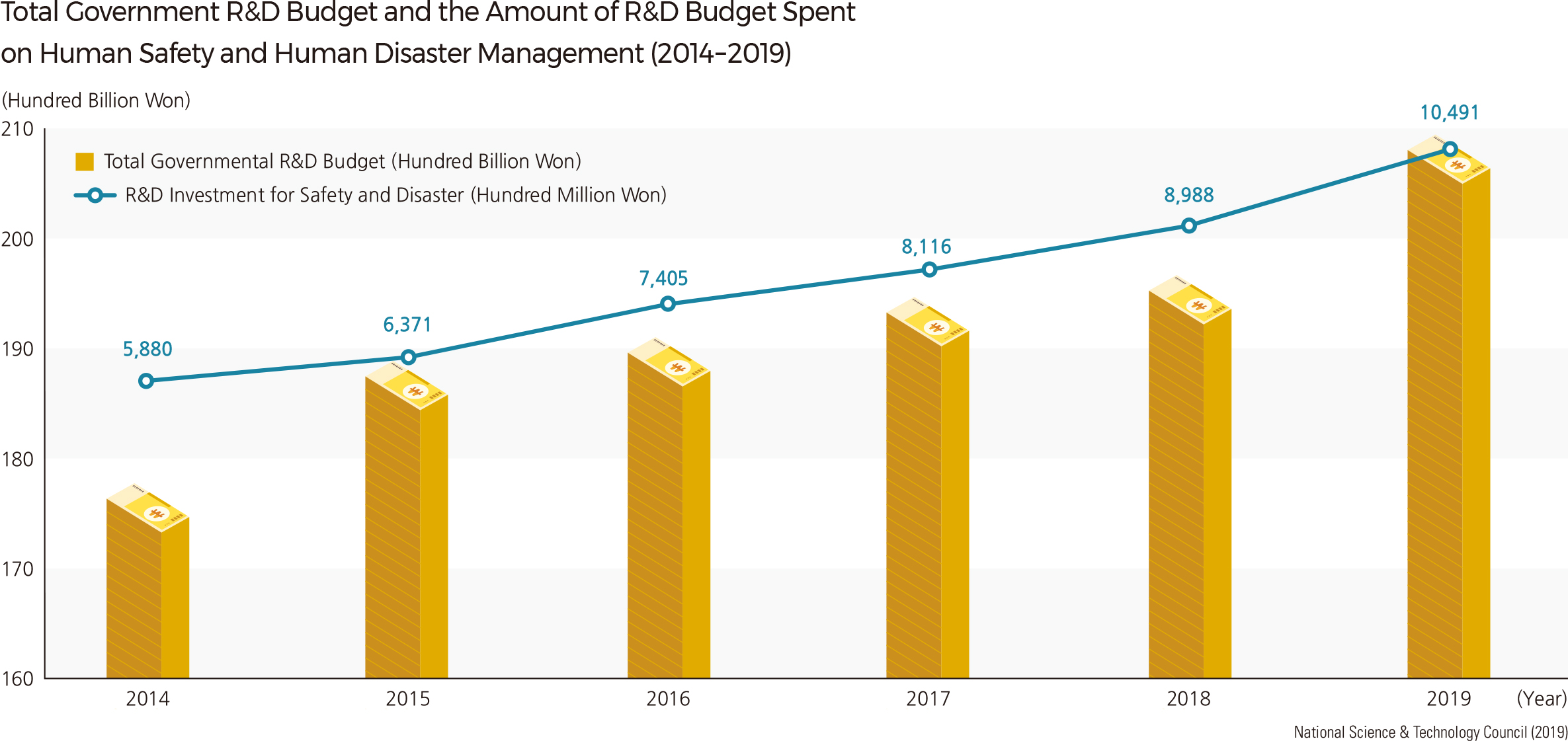
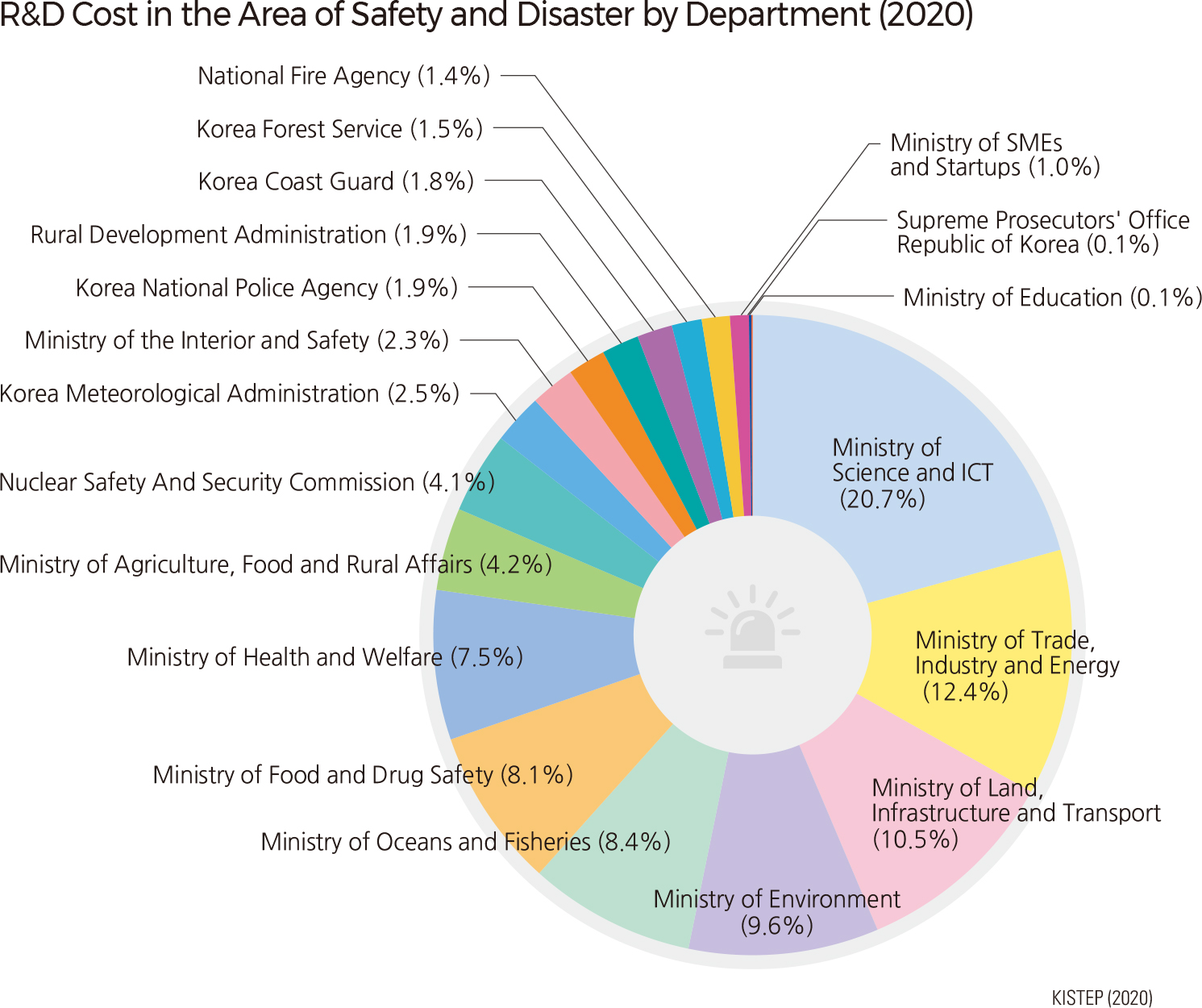
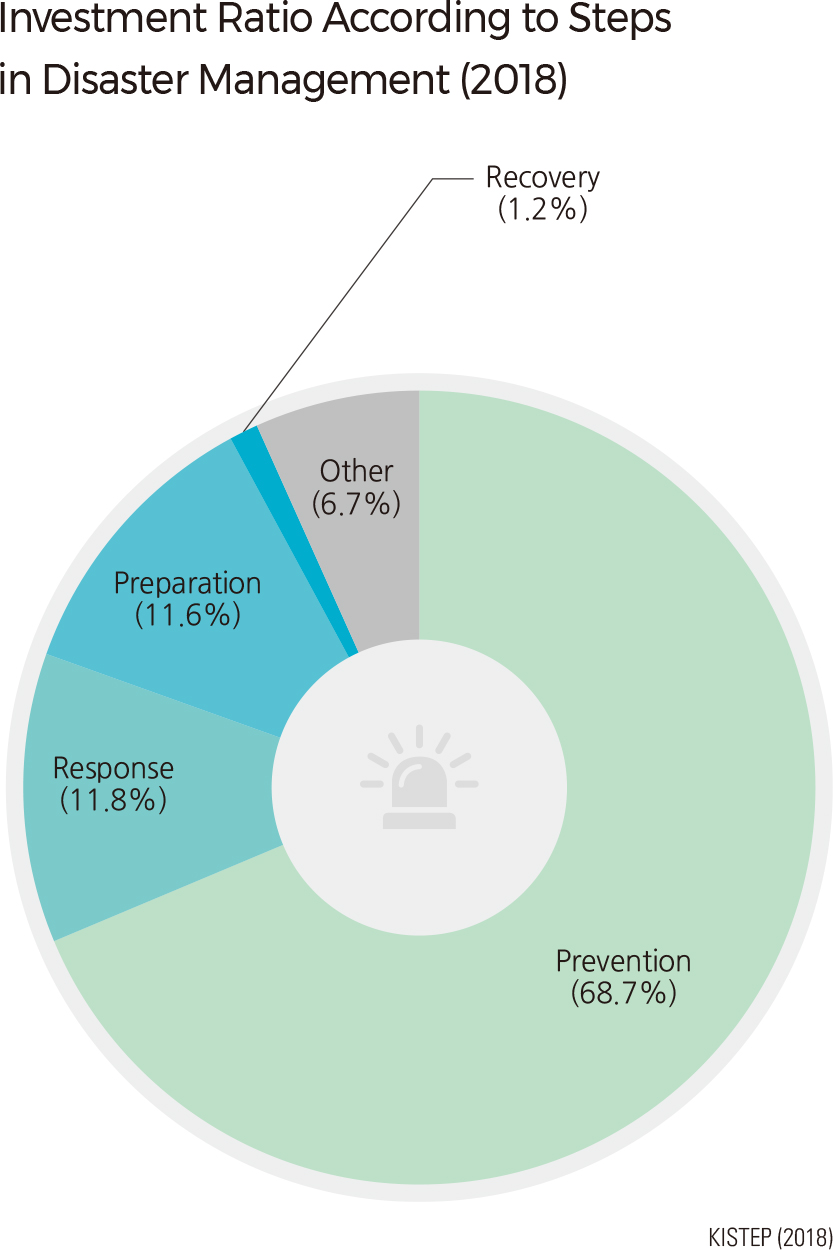
Most natural disasters in recent years were caused by localized heavy rains, typhoons, and tsunamis. However, the type and extent of damage caused by natural disasters have diversified and are increasing. Expanding cities, industrial areas, and decreasing reservoirs have caused a significant increase in the amount of runoff, resulting in greater damages. The central government conducts various nation-wide prevention measures to mitigate damage from natural disasters, such as by applying earthquake resistant design codes to new buildings and by building erosion control dams.
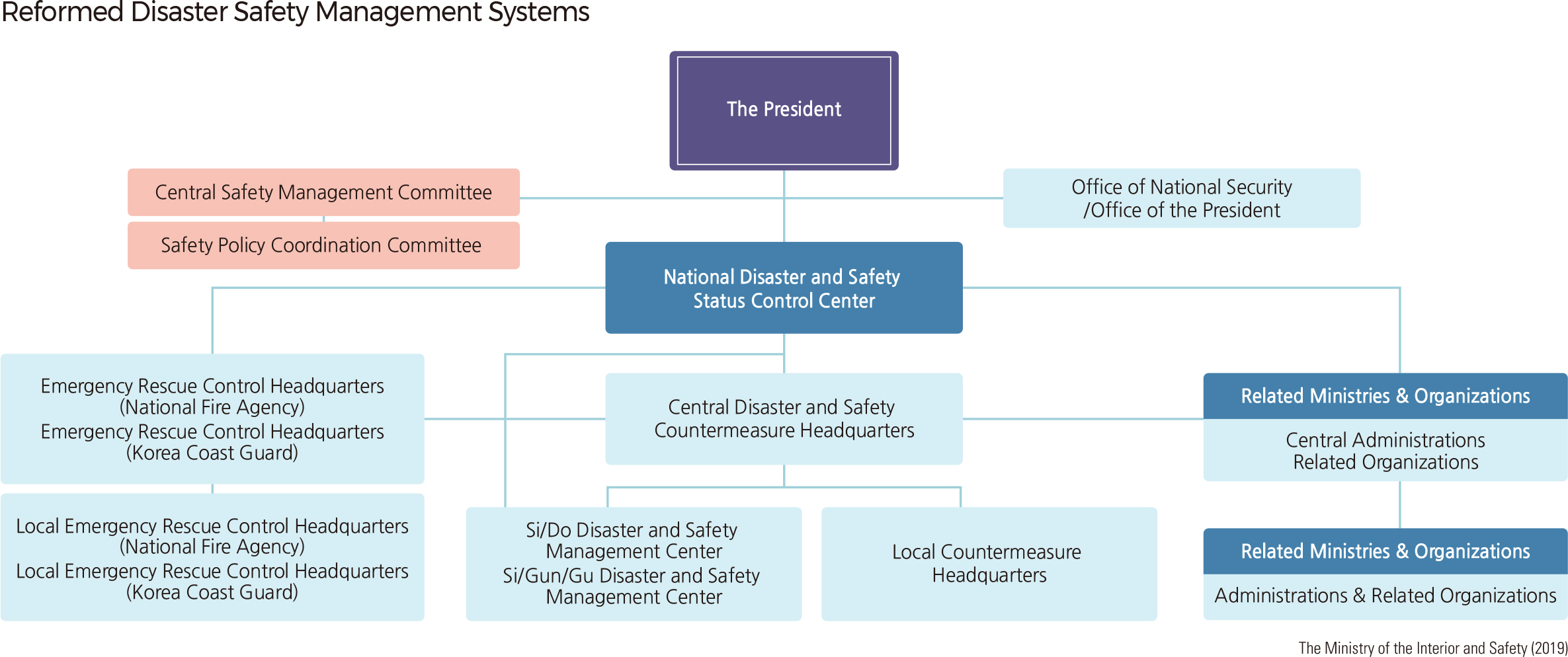
The Ministry of Public Safety and Security, which was launched by integrating disaster prevention and response functions, was incorporated into the Ministry of Interior and Safety in July 2017. The Ministry of Interior and Safety is responsible for overseeing and coordinating disaster and safety management tasks conducted by the state and local governments. |