English II 2020
Biological diversity means the variability among living organisms from all sources, including terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are part; this includes diversity within species, between species, and of ecosystems and genetic resources. The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) was adopted on May 22, 1992, for the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity at the global level, and entered into force on 29 December 1993 as an International Convention on Biodiversity.
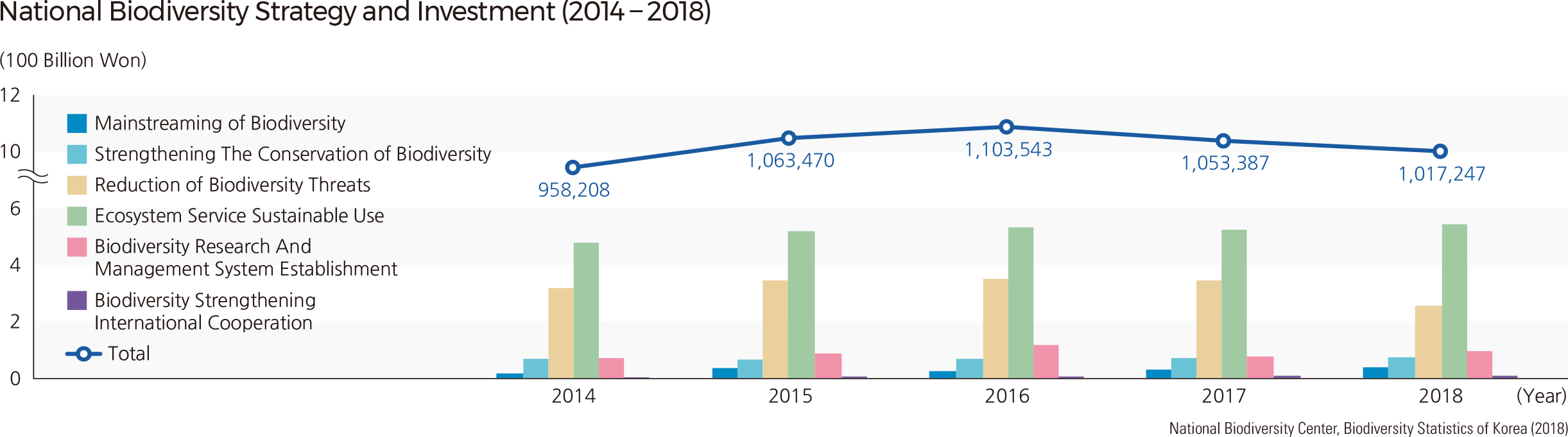
Biodiversity provides various ecosystem services and affects human wellbeing and the overall sustainability of the Earth ecosystems. Therefore, a national strategy is required for systematic conservation and sustainable use of nature. Korea manifested the National Biodiversity Strategy and the action plan to abide by the CBD, and established the Biodiversity Act to formulate and implement the National Biodiversity Strategy every five years in terms of the central administrative agreement.
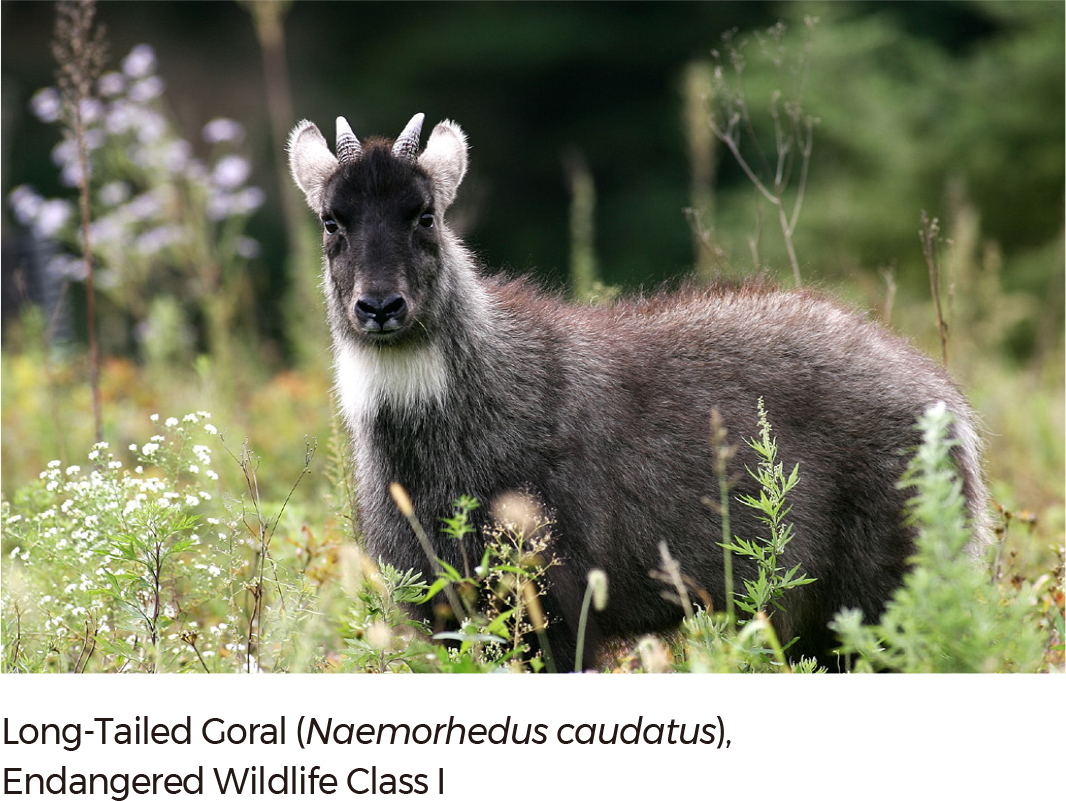
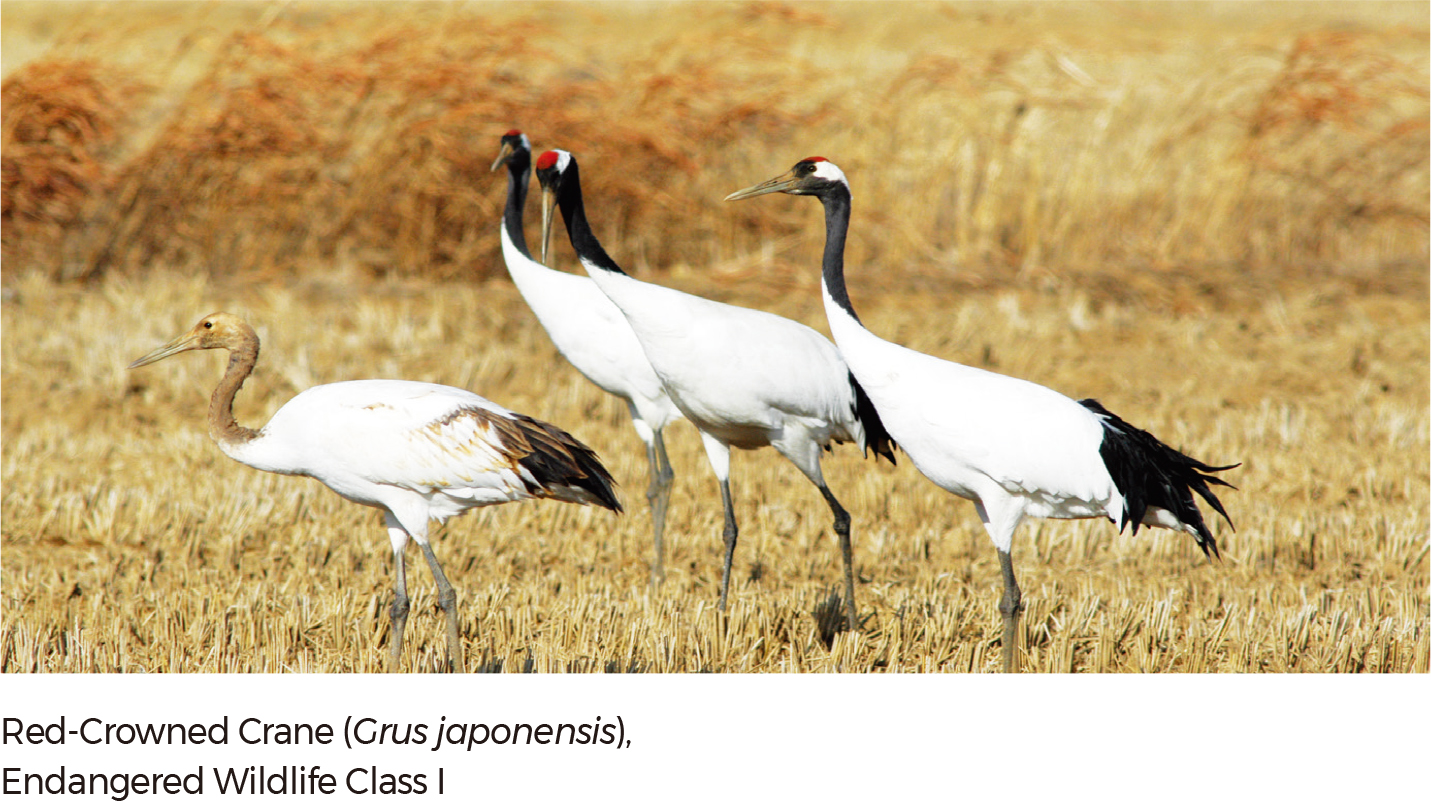
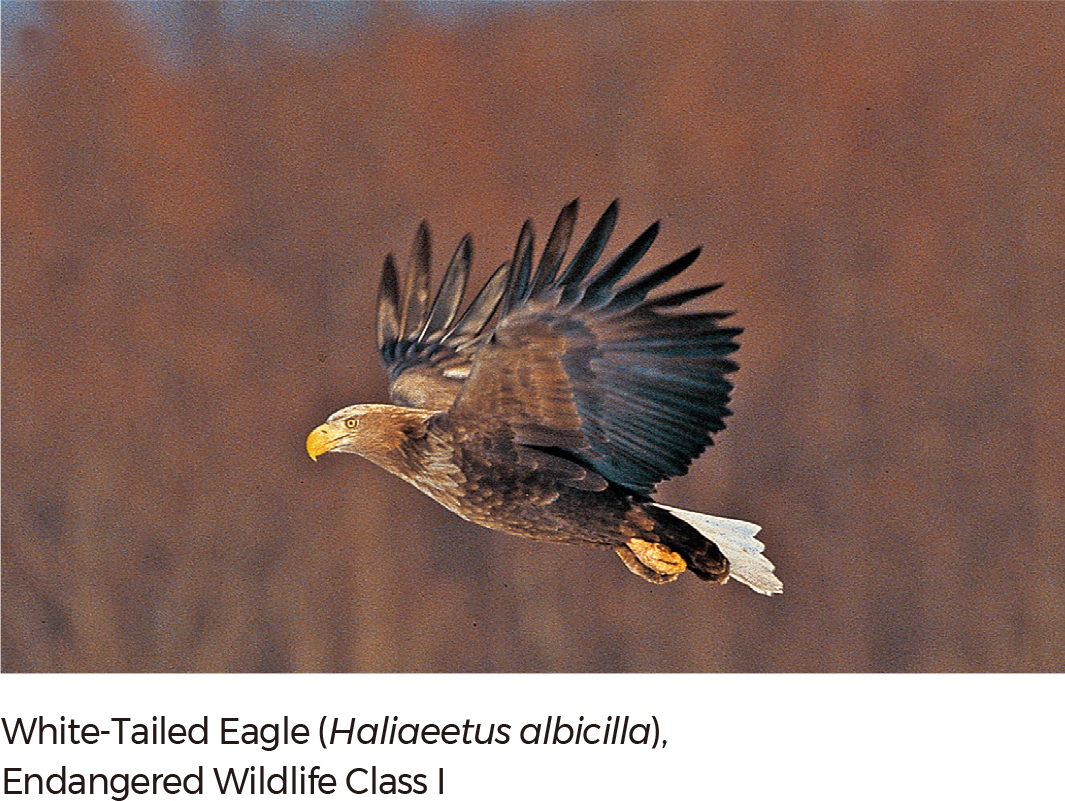
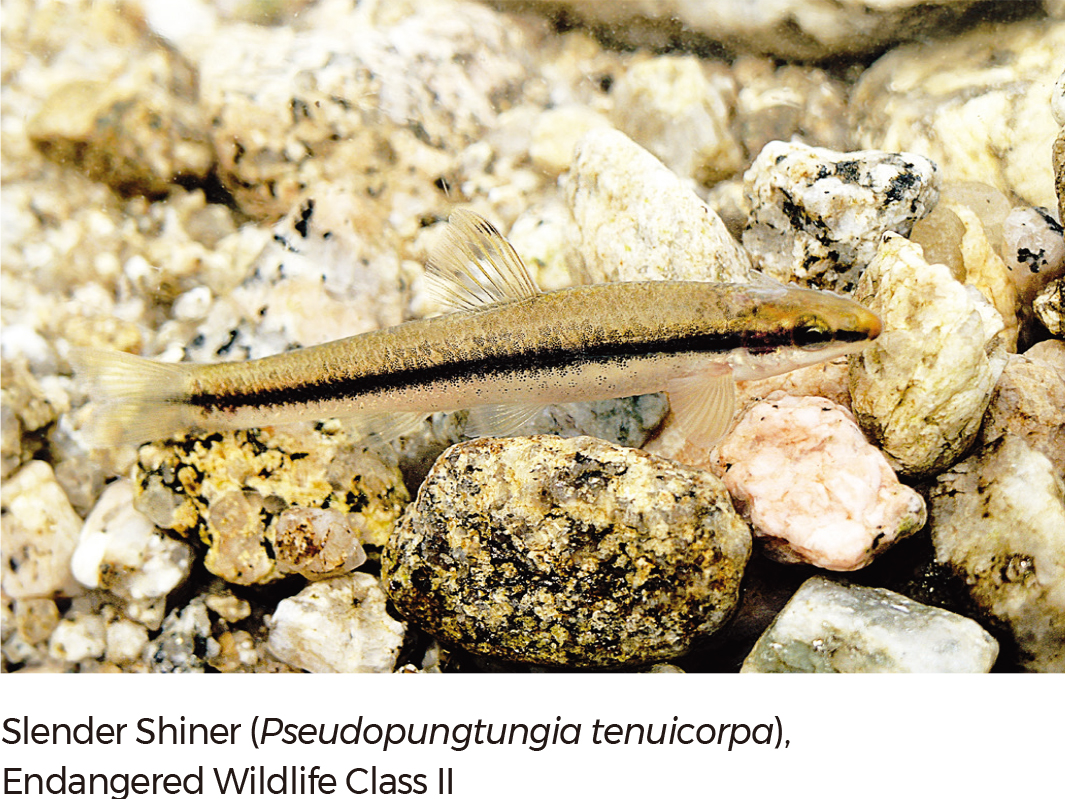
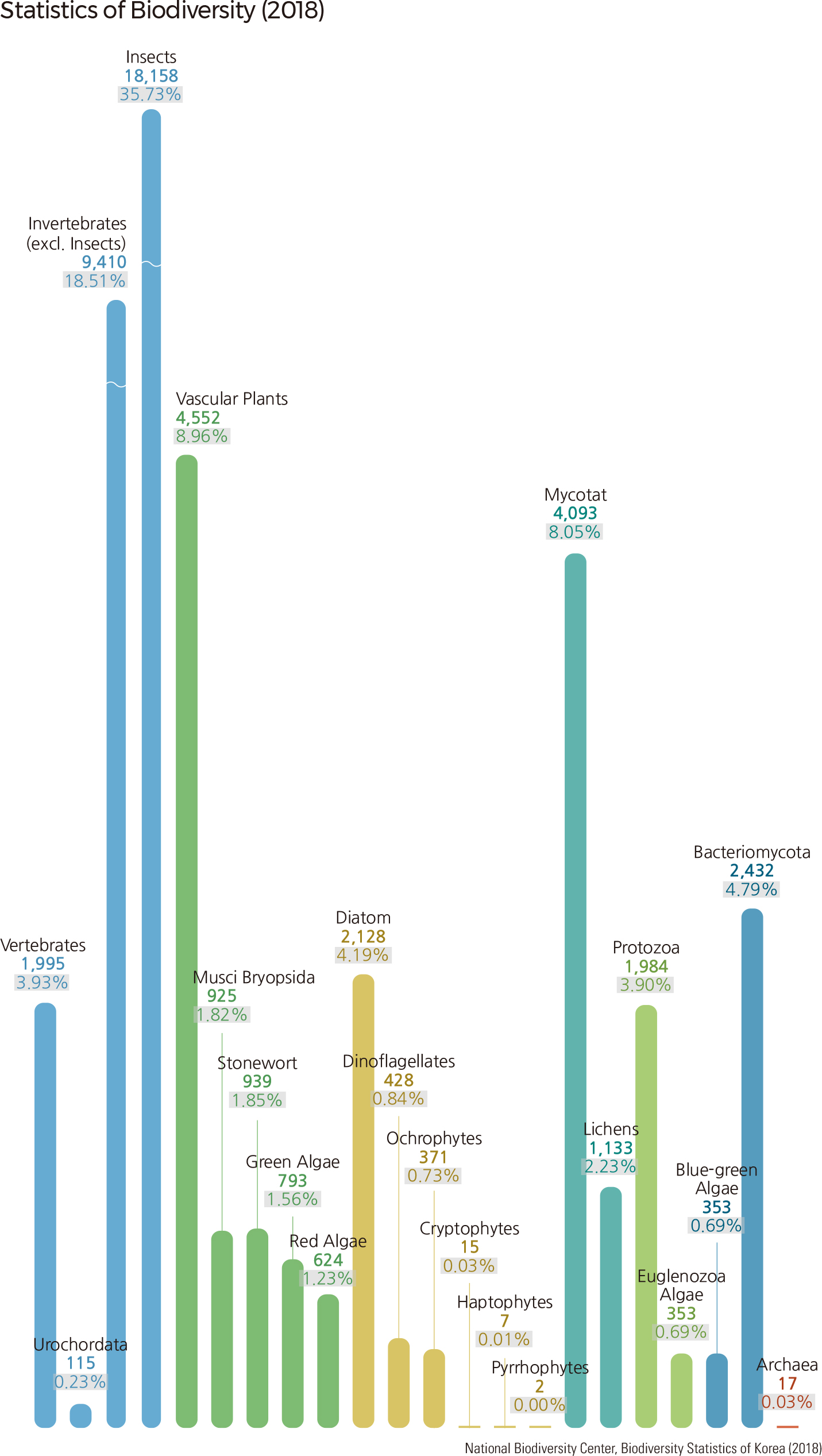
As of 2018, according to the Ministry of Environment and the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR), a total of 50,827 species inhabit the Republic of Korea. Among the species, 29,678 species are in the Animalia Kingdom, followed by Plantae (7,833 species), Fungi (5,226 species), Chromista (2,951 species), Bacteria (2,785 species), Protozoa (2,337 species), and Archaea (17 species). |