English II 2020
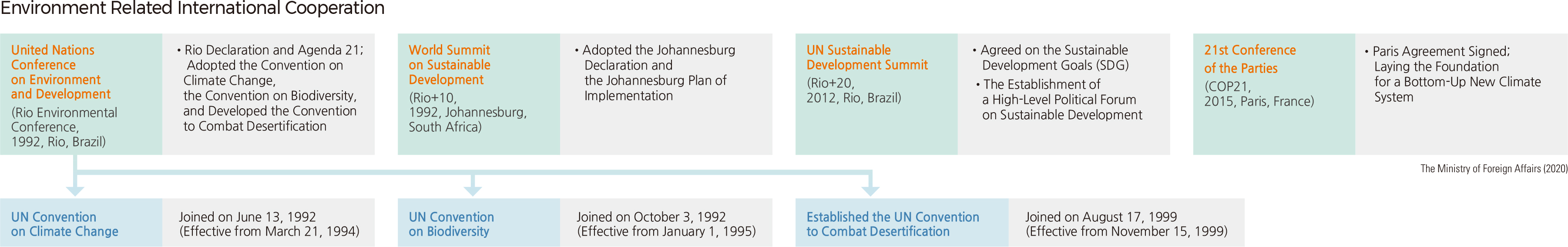
Sustainable development is the most frequently cited term at international conferences in the 21st century. Humanity and the global ecosystem have suffered many difficulties due to environmental destruction caused by excessive economic development after the Industrial Revolution. To mitigate these impacts, global leaders, governmental representatives, international organizations, and NGOs gathered together under the supervision of the United Nations to discuss sustainable development, which means to continue development without damaging the global environment. The starting point was the Earth Summit (United Nations Conference on Environment and Development) held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, in 1992. In this meeting, leaders around the world jointly adopted the Rio Declaration on Environment and Development and Agenda 21.
Subsequently, at the 21st Annual Conference of Parties (COP) in 2015, the Paris Agreement was adopted. Its goal is to limit global warming, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius. In this trend, South Korea is striving to implement sustainable development through national laws and policies such as the Framework Act on Sustainable Development and Framework Act on Low Carbon Green Growth. It is also flexibly responding to changes in international discussions through opportunities such as the subsequent Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) and the High- Level-Political Forum (HLPF).
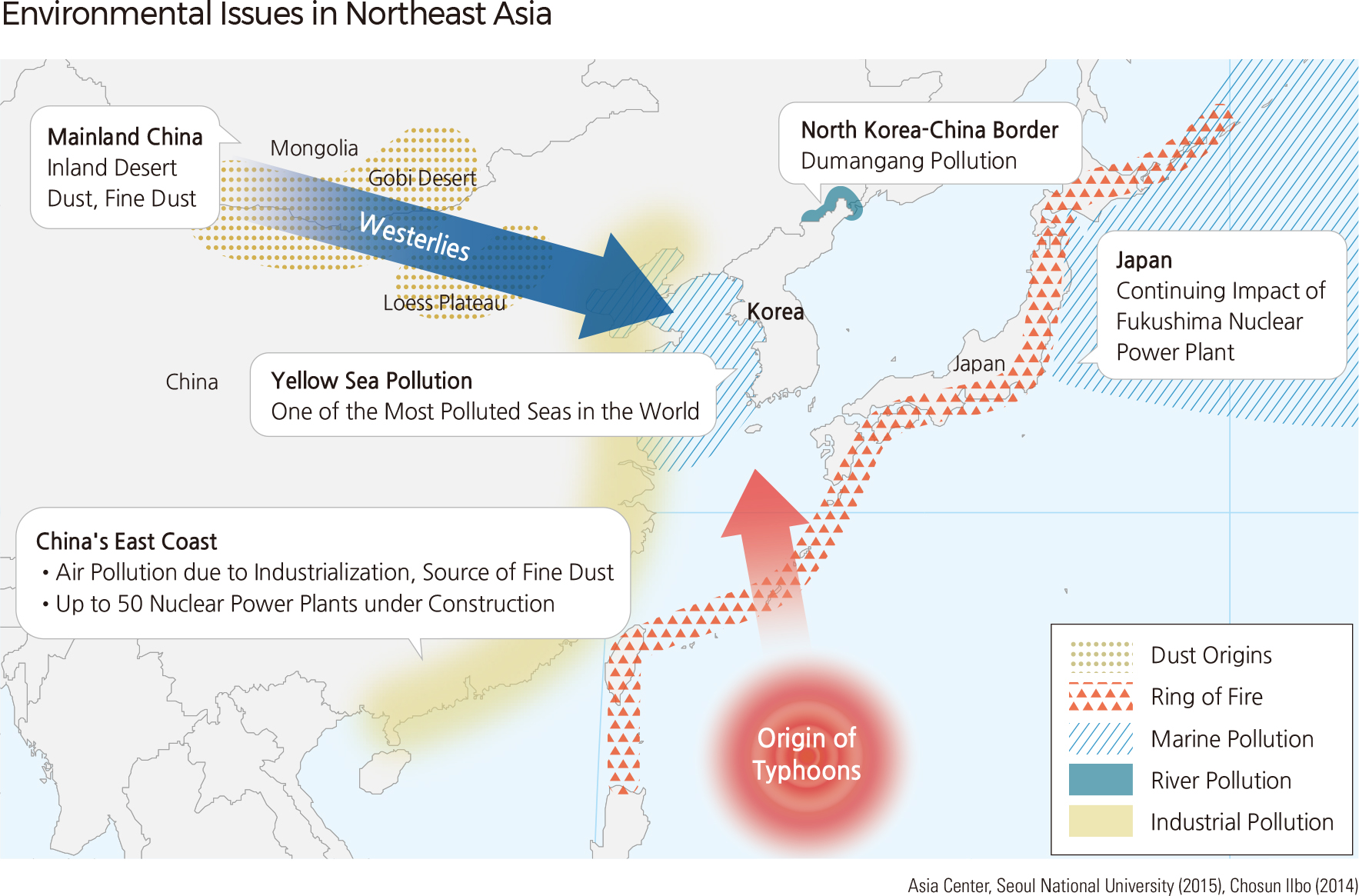
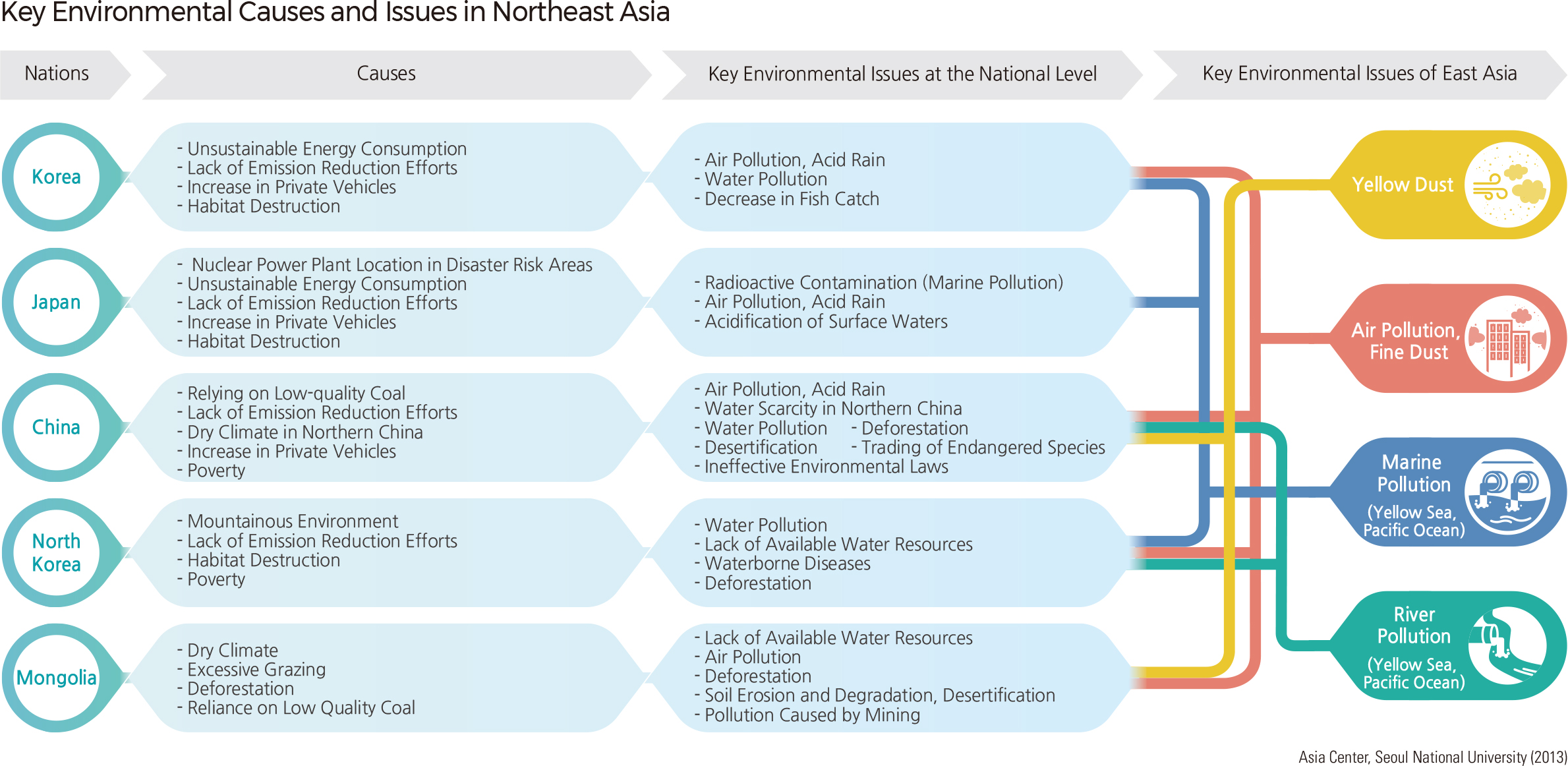
Every country in Northeast Asia faces different environmental challenges because of their different natural environmental conditions and distinct socio-economic situation. South Korea and Japan share environmental problems that can generally be seen in developed countries; their advanced industrial structures have led to increases in energy consumption and the number of private vehicles. North Korea and Mongolia experience environmental damage problems that are brought about by poverty. North Korea is undergoing serious environmental damage as a consequence of forest degradation due to food and energy shortages. Mongolia and western China are affected by desertification, while recent rapid industrial development in the eastern part of China has caused serious air and water pollution.
Such environmental problems in Northeast Asia also affect neighboring countries. For instance, yellow dust originating from the Gobi Desert and the Loess Plateau picks up pollutants such as fine dust and nitrogenous compounds as it crosses the rapidly industrialized east coast of China. It then reaches Korea and Japan. The pollution of international seas and streams such as the Yellow Sea and Dumangang is also being discussed as one of the most important environmental issues in this region. Radioactive water from the Fukushima nuclear power plant in Japan is leaking into the waters, increasing international concern about pollution in the North Pacific. In the future, such transboundary disasters will be frequent in Northeast Asia. Not only are the nations of Northeast Asia located on the same plate boundary, but they are also affected by various disasters through westerly winds, currents, and typhoons. Many nuclear power plants are being built even though they are located close to the boundary of the plate, so there is a risk of large-scale disasters.
Environmental Cooperation with Europe and North America
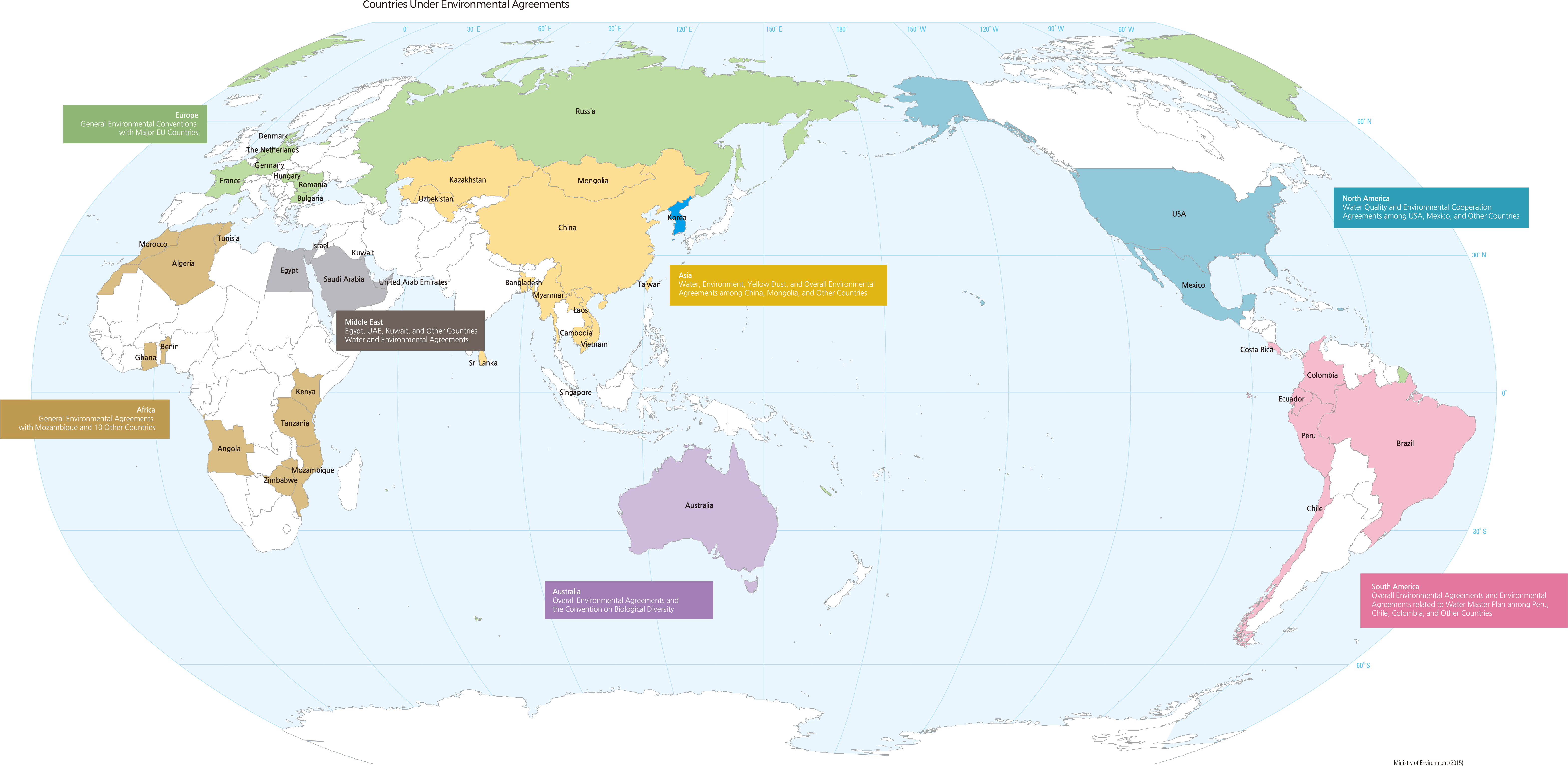
To improve the national environmental status, South Korea has been promoting cooperation with advanced western countries such as the United States, France, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Germany to adopt advanced environmental policy and technology, based on the memorandum of understanding for environmental cooperation between countries. South Korea is actively promoting cooperation projects, such as activating expert exchange and holding joint seminars. Meanwhile, in 2013, per the "US-ROK Environmental Cooperation Agreement" effective in 2012, the US-ROK Environmental Affairs Council and Environmental Cooperation Commission held its first meeting in the United States. At this meeting, they discussed ways to jointly approach international environmental issues such as air quality pollution investigation and marine waste management. In 2019, at the third meeting, the two countries promised close cooperation regarding the investigation of the cause of fine dust, the development of sustainable marine fisheries, and the conversion of renewable energy.
Environmental Cooperation with Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is also experiencing serious environmental problems due to rapid industrialization and urbanization. South Korea maintains a cooperative relationship with countries in the region. It provides practical help in improving the environment of Southeast Asian countries while also pursuing practical aspects by supporting smooth advancement of Korea's environmental industry into Southeast Asia.
Aiming for sustainable development in Asia, South Korea has been discussing sustainable development and environmental matters through the ASEAN+3 Environment Ministers Meeting, the Tripartite Environment Ministers Meeting among Korea, China, and Japan, and other cooperation initiatives with Vietnam, Cambodia, and Indonesia. At the 2019 ASEAN-ROK Commemorative Summit in Myanmar, the government of South Korea agreed to build the Korea-Mekong Biodiversity Center (Mekong-ROK Biodiversity Center) (to be completed in 2025). Also, by signing a memorandum of understanding for environmental cooperation with Myanmar, both governments promised to cooperate to resolve environmental issues such as climate change, air pollution, and the use of waste resources.
Tripartite Environment Ministers Meeting among Korea, China, and Japan
In 1999, the first Tripartite Environment Ministers Meeting among Korea, China, and Japan (TEMM) was held in Seoul of South Korea. Each country has annually hosted a meeting of the Environment Ministers in turn. Its objective is to devise cooperative measures to tackle East Asian environmental issues such as yellow dust, acid rain, atmospheric pollution, and hazardous waste management, and to raise a sense of environmental community among the three countries. This meeting is the only minister-level conference in the East Asian region and has served as the highest-level coordination mechanism on environmental cooperation. A total of 21 meetings have been held as of November 2019.
Northeast Asian International Cooperation for Yellow and Fine Dust
Responding to yellow dust and fine dust is an important environmental task for not only the nation but also the entire Northeast Asian region. Because it is one of the major environmental cooperation tasks in Northeast Asia, South Korea has actively pushed for a collective response to this issue, regarding it as a major agenda in national summit meetings, Korea-China-Japan ministerial meetings, and Northeast Asian environmental cooperation channels, and has demanded joint responses. In 2013 and 2014, three countries' yellow dust experts jointly investigated the Hulunbuir area of Inner Mongolia, China. The three countries plan to use this area as a base for the ecological restoration of desertified areas. In 2019, ROK-China Joint Committee on Environmental Cooperation and ROK-China Director-General-Level Meeting on Environmental Cooperation took place in South Korea. In the meetings, the two countries have coordinated their opinions to solve the fine dust problem by jointly establishing an early warning system for fine dust.
Environmental Cooperation with Africa
In Africa, recent environmental pollution is considered a major factor impeding economic development. Accordingly, people accept that the key to resolving regional poverty-related issues is to curtail economic growth to control environmental destruction. The Ministry of Environment of Korea has been holding the Korea-Africa Environmental Cooperation Forum every year since the groundwork for discussions on environmental cooperation between the two countries was laid in 2010.
In 2014, South Korea hosted a joint workshop with Tunisia along with the 5th Korea-Africa Forum, in which the vice-minister and director of the Tunisian Ministry of Environment, officials from Nigeria and Côte d'Ivoire, and Water and Sanitation for Africa discussed ways to share environmental policy and technology for atmospheric and waste management sectors. In 2017, South Korea also held the Middle East-Africa Environment Forum 2017. As of May 2015, the Korean government has signed MOUs on environmental cooperation with 11 African countries. |