English II 2020
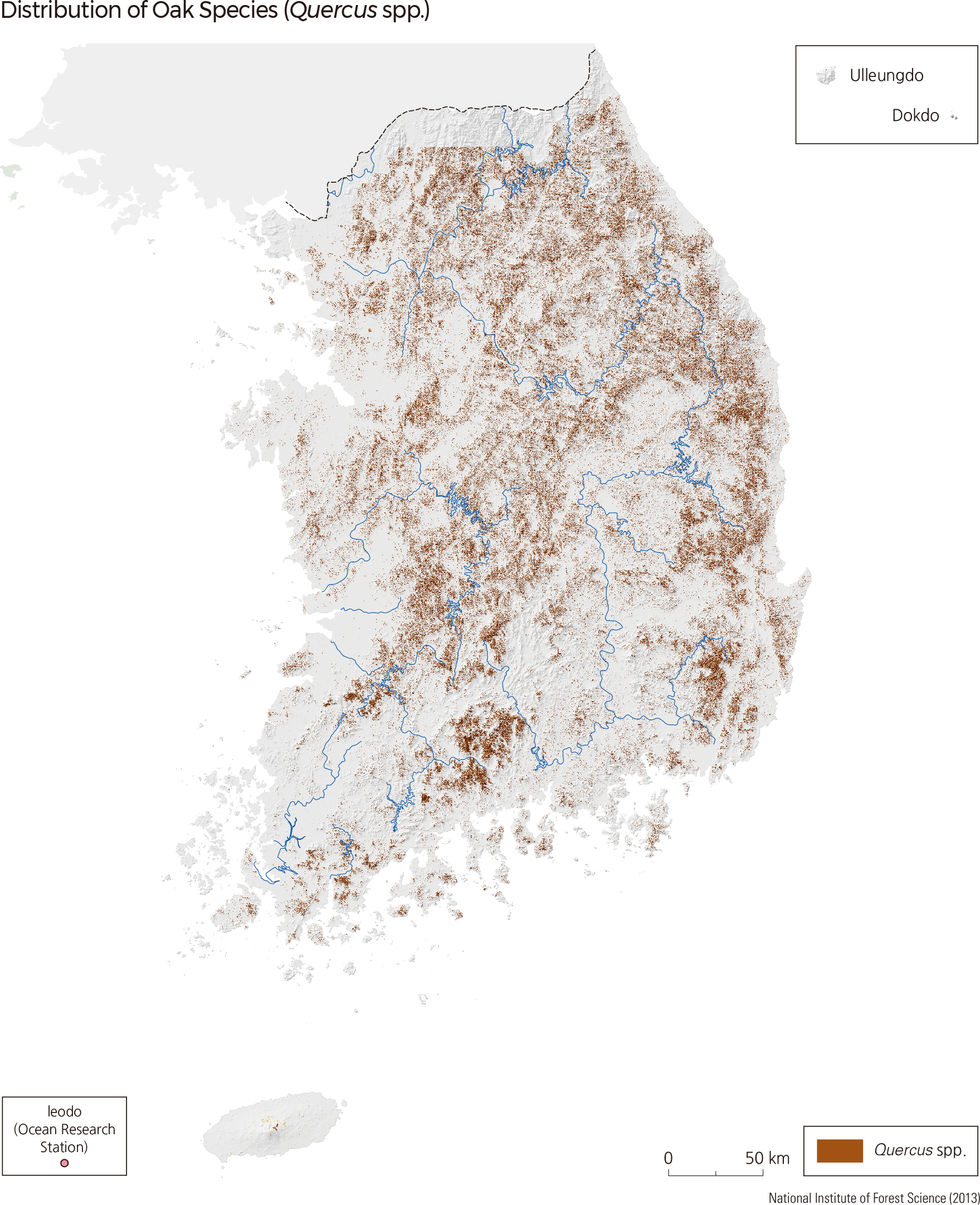
The major tree species distribution map shows the distribution of tree species that can be easily found in the forests of South Korea. Loose-flower Hornbeam (Carpinus laxiflora) forests are native to Korean forests. But today, much of the native forest has been destroyed and replaced by oak species such as Mongolian Oak (Quercus mongolica), Sawtooth Oak (Quercus acutissima), Oriental Cork Oak (Quercus variabilis), and Jolcham Oak (Quercus serrata). Other species, including Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia), East Asian Alder (Alnus japonica), Sargent's Cherry (Prunus sargentii), and Snowbell Tree (Styrax japonicus) can be easily found in Korean forests.
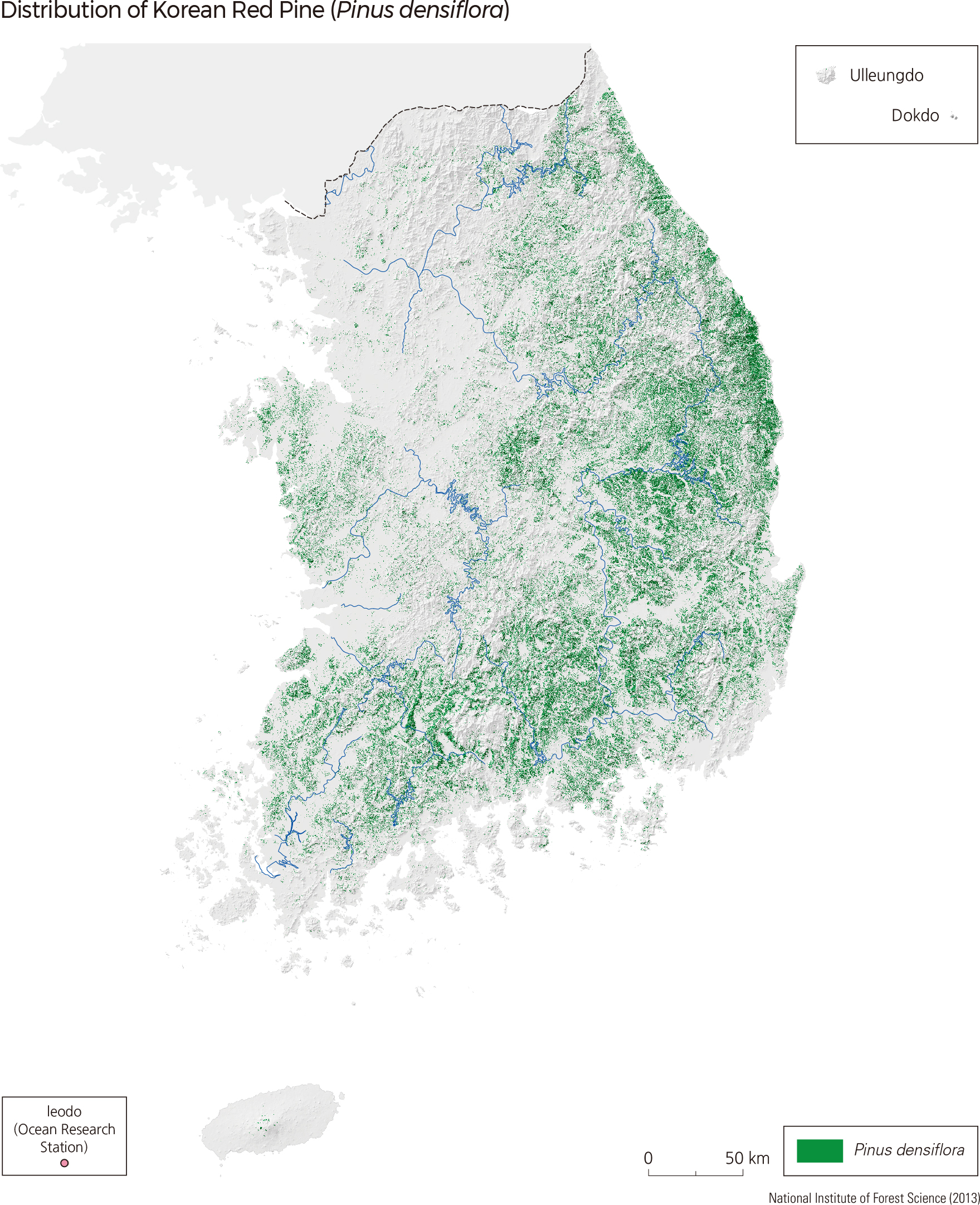
The largest forest consisting of one species is a Korean Red Pine (Pinus densiflora) forest. The species has been protected under governmental policy, and lumbering has been prohibited. It is widely distributed in the entire country as it has a high tolerance for nutrient-poor soil conditions. Recently, however, the area covered by Korean Red Pine is decreasing because of wildfire, diseases such as pine wilt, and insects such as Thecodiplosis japonensis.
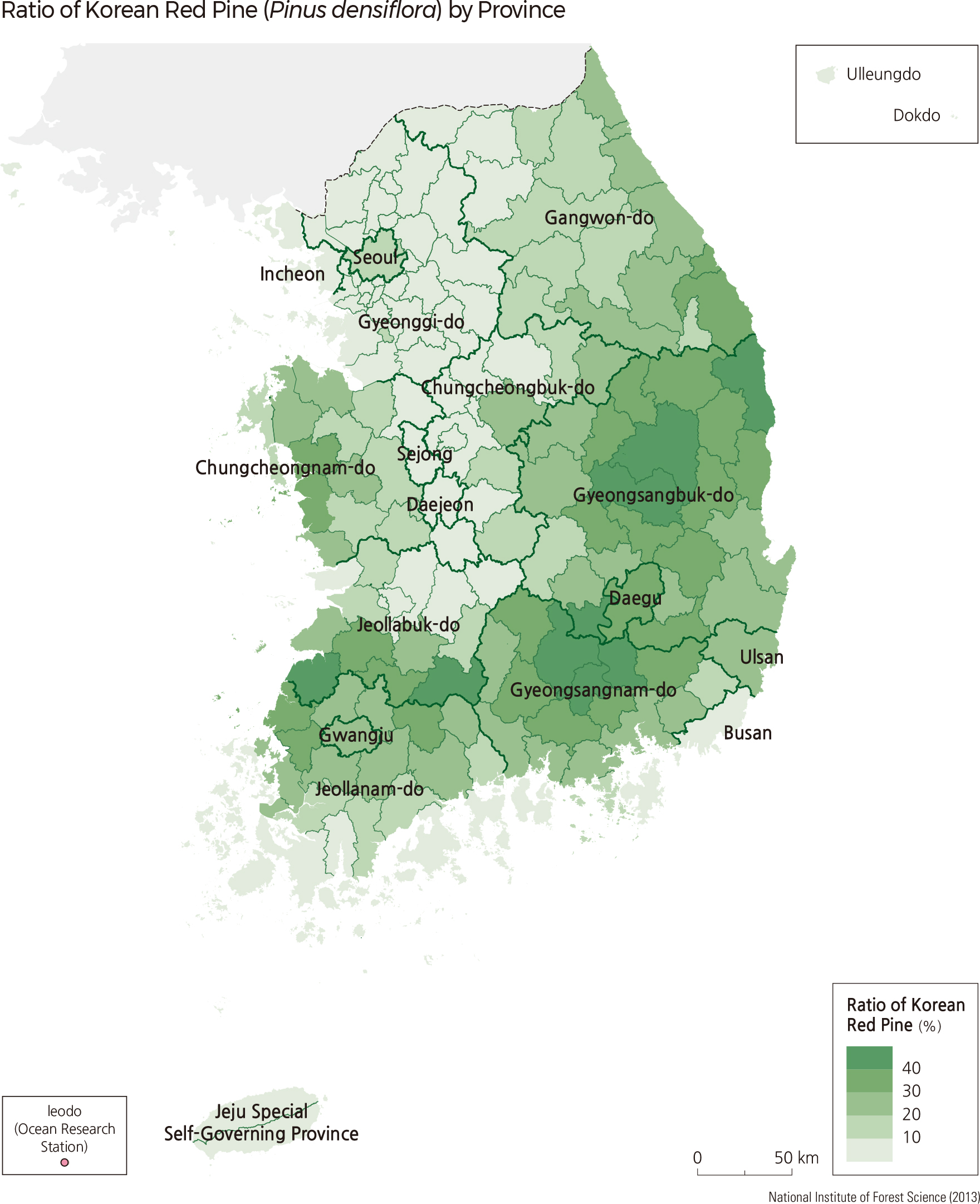
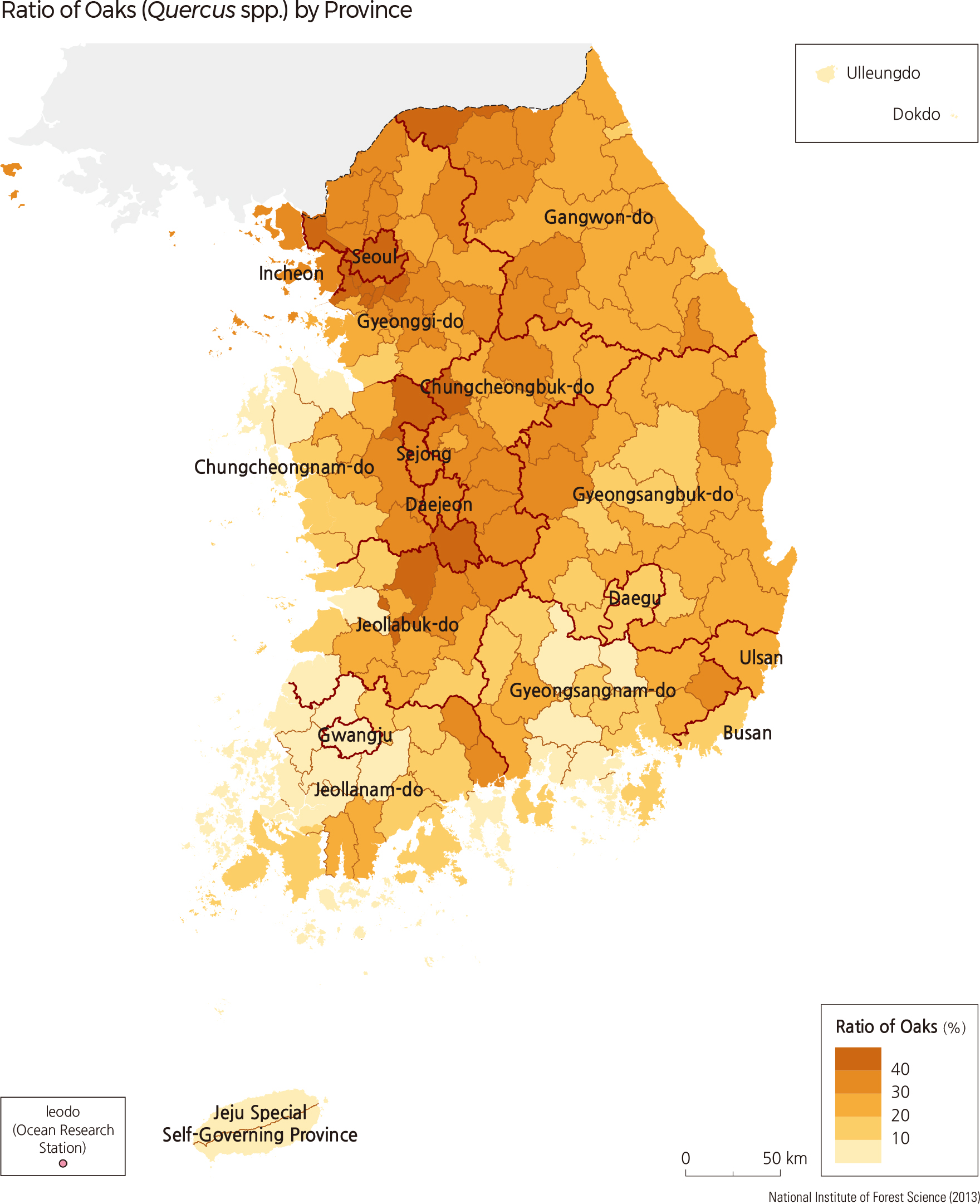
The Korean Red Pine (Pinus densiflora) accounts for 21.9% of the total forests in South Korea. Although evenly distributed across the nation, they are most dominant in Gangwon-do and the eastern coasts of Gyeongsangbuk-do. In Andong-si and Uljin-gun of Gyeongsangbuk-do, the proportion of Korean Pine dominance is 49.9%. Changnyeong-gun of Gyeongsangnam-do shows the highest distribution rate among all cities of Korean Red Pine trees at 52.9%. Oak species are the major broadleaf tree species in South Korea, including Jolcham Oak (Quercus serrata), Galcham Oak (Quercus aliena), Oriental Cork Oak (Quercus variabilis), Mongolian Oak (Quercus mongolica), and Japanese Emperor Oak (Quercus dentata). Oak covers 24.2% of the total forest area, which is higher than that of pines. Oak distribution is the greatest in Hongcheon-gun of Gangwon-do, followed by Inje-gun and Chuncheon-si. In Gimpo-si of Gyeonggi-do, 52.9% of forests are composed of oak species, which is the highest distribution rate among all South Korean cities.
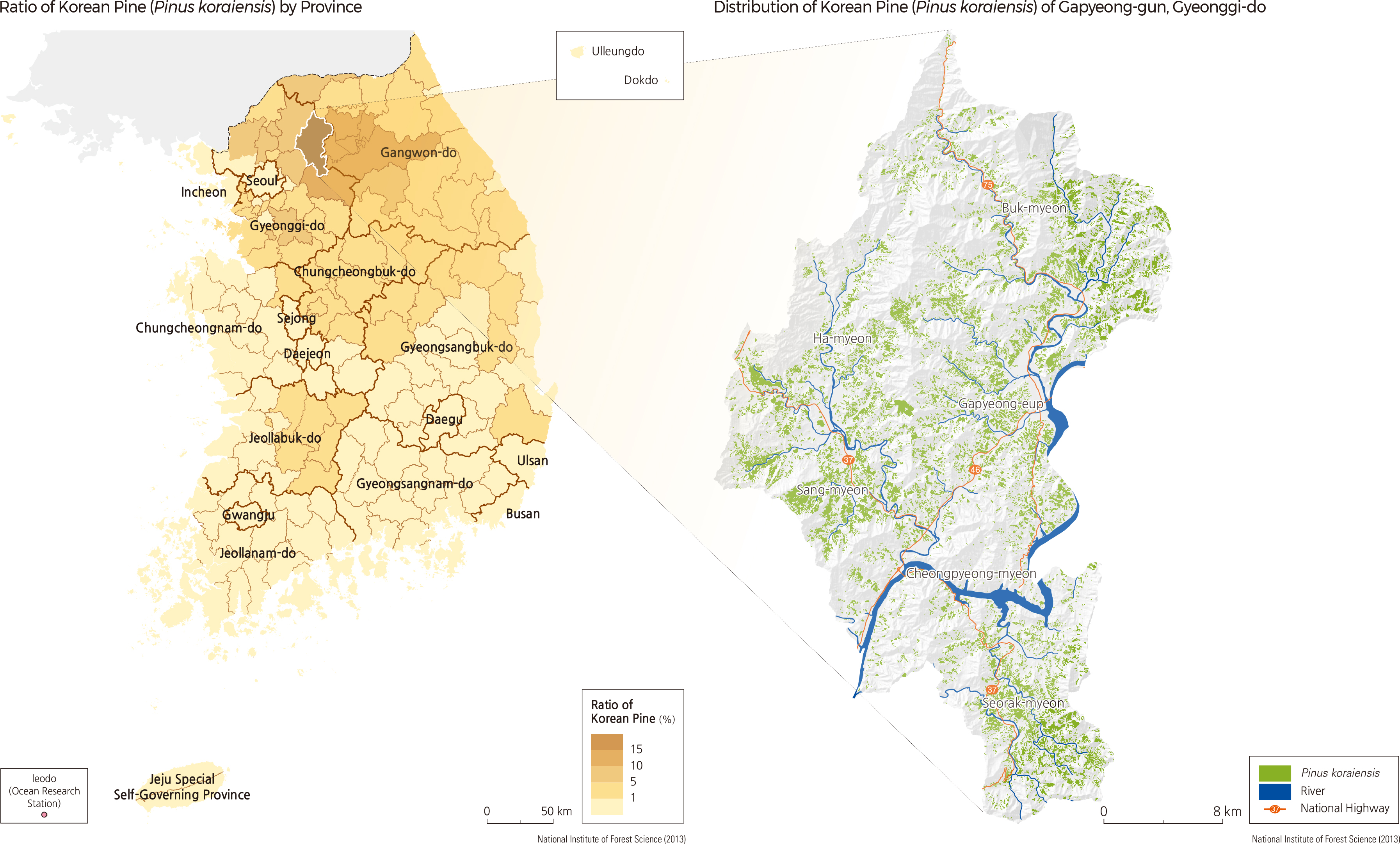
Korean Pine (Pinus koraiensis) is an evergreen coniferous tree species and one of the oldest trees associated with Korean history, along with the Korean Red Pine (Pinus densiflora). It is distributed across the Korean Peninsula, Japan, China, and Siberia. Korean Pine is a species that adapts well to the cold, so its distribution is largely in mountainous and alpine regions. Its major habitats in Korea include Gapyeong-gun and Yangju-si of Gyeonggi-do and Hongcheon-gun of Gangwon-do. Korean Pine covers 2.4% of the total national forest area. With 20.0% of its forests composed of this species, Gapyeong-gun of Gyeonggi-do has the highest distribution of Korean Pine among all regions.
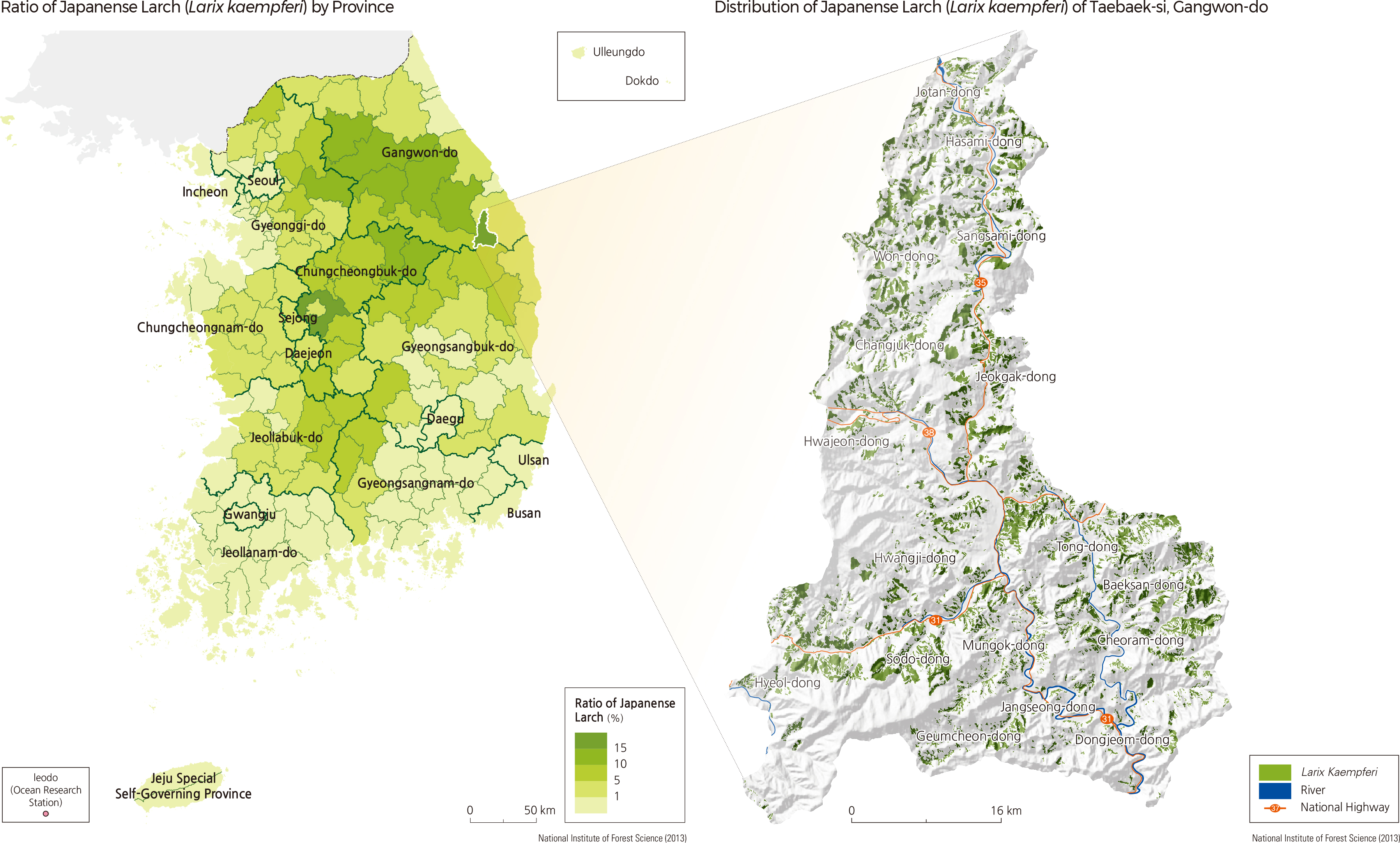
Japanese Larch (Larix kaempferi) is a deciduous conifer. It is called deciduous pine because it belongs to Pinaceae, but it sheds its leaves annually. The species comprises 4.5% of the entire national forest. Hongcheon-gun, Pyeongchang-gun, and Jeongseon-gun have the highest Japanese larch population. With 19.1% of its forest comprised by this species, Taebaek-si of Gangwon-do displays the highest distribution rate of Japanese larch. |