English II 2020
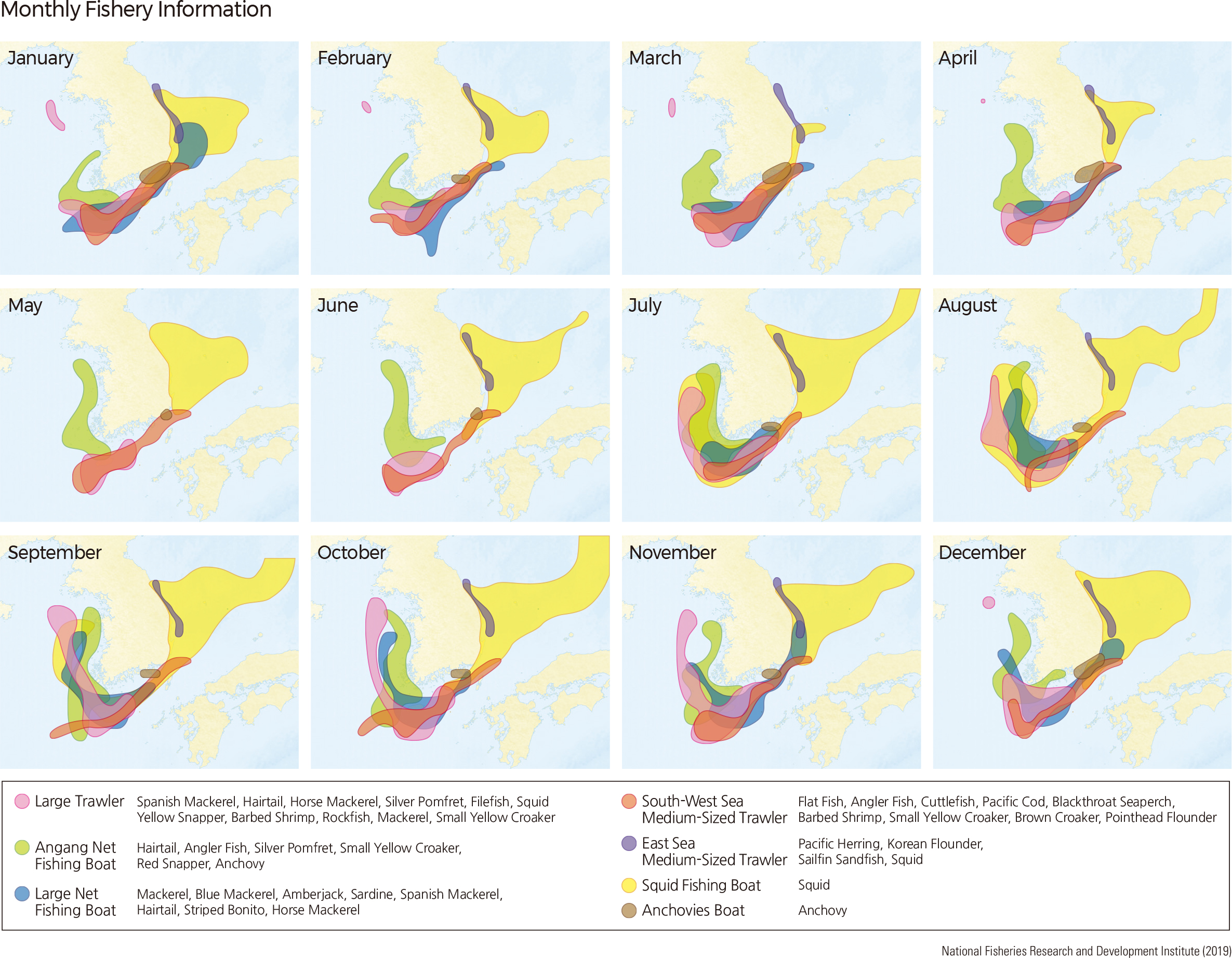
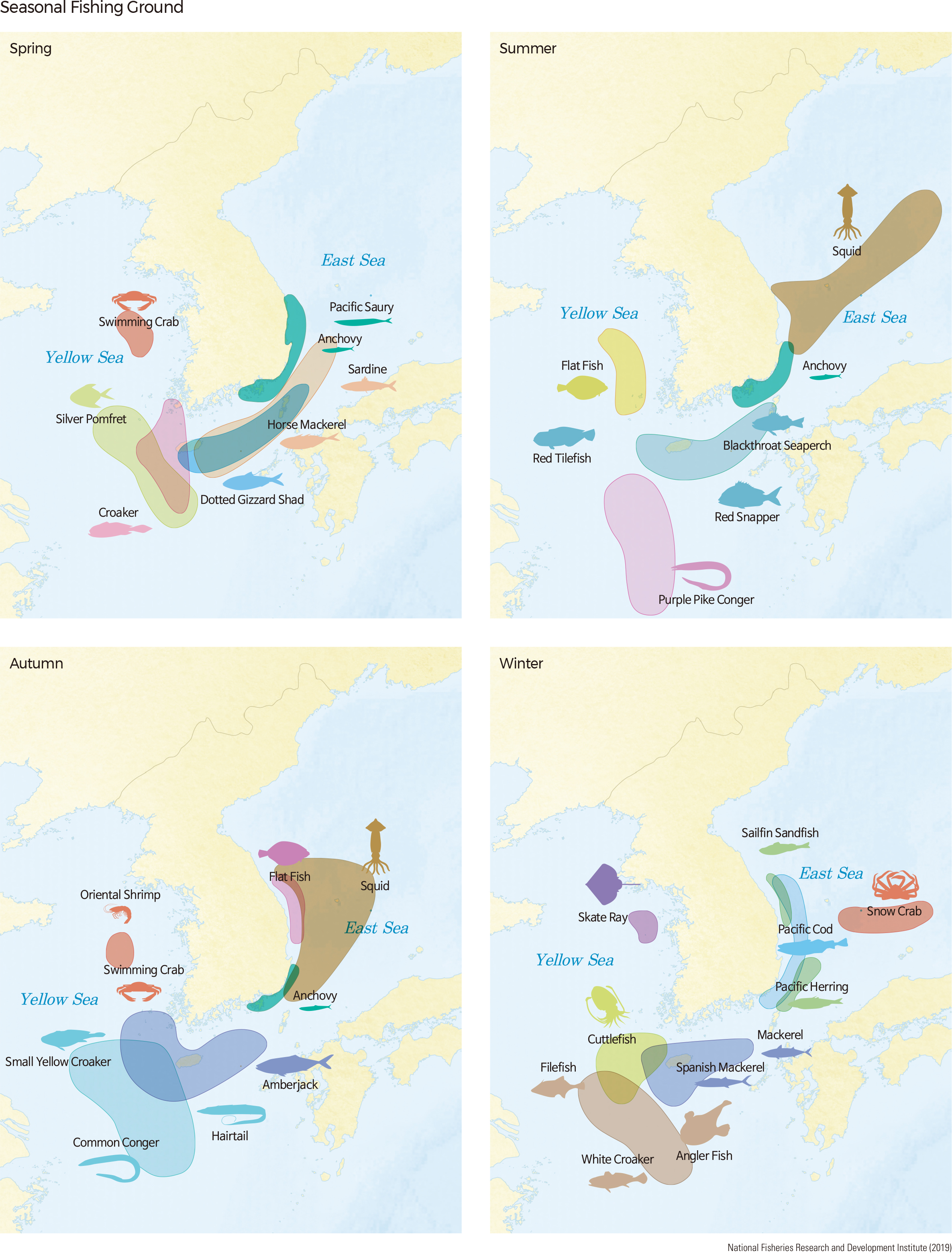
As of 2019, stow nets on anchors or trawl nets are used to catch largehead hairtail and Japanese Spanish mackerel on the Yellow Sea. The large purse seine fishery catches mackerel and Japanese amberjack on the South Sea and expands to the East Sea and the Yellow Sea after autumn. The fishing area is the widest during the fall-winter period. In July-October, when squid is mainly caught, the fishing area is expanded to the eastern end of the East Sea. Fishing methods such as large trawls and trawls, which capture large amounts of fishery products, are prohibited in some areas. Fishing activities take place within the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) and provisional waters.
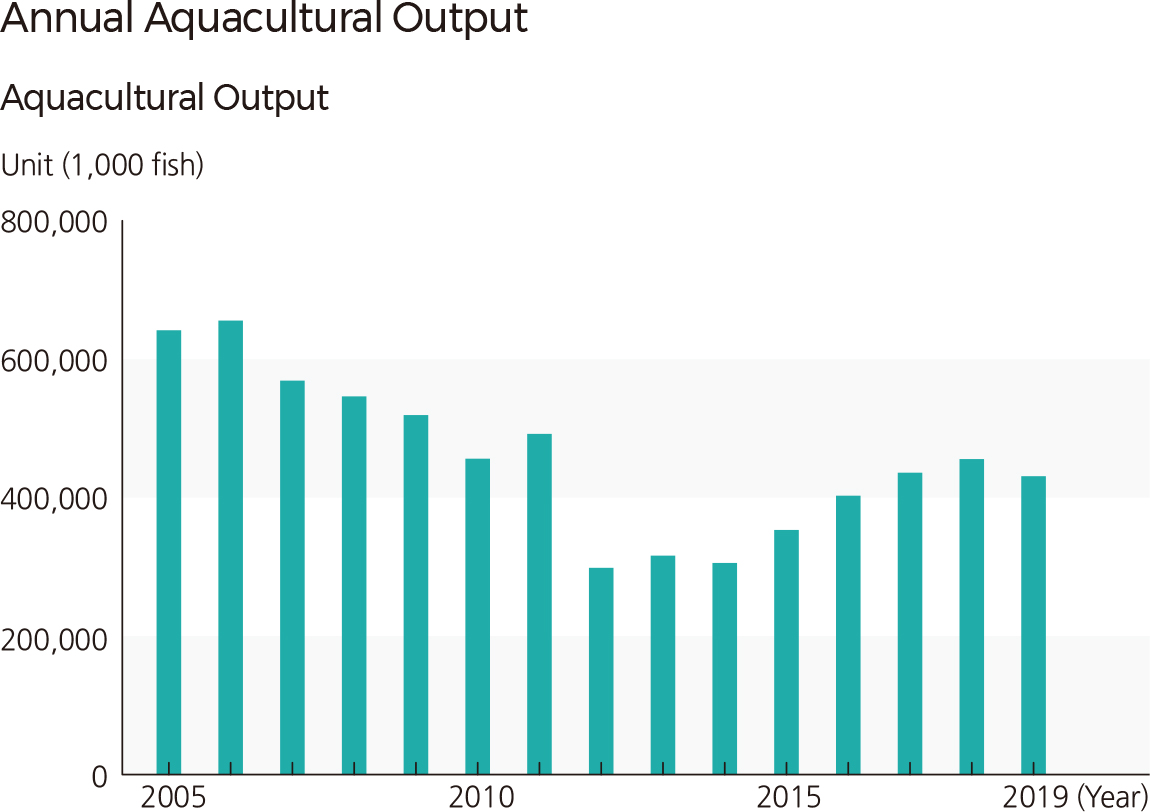
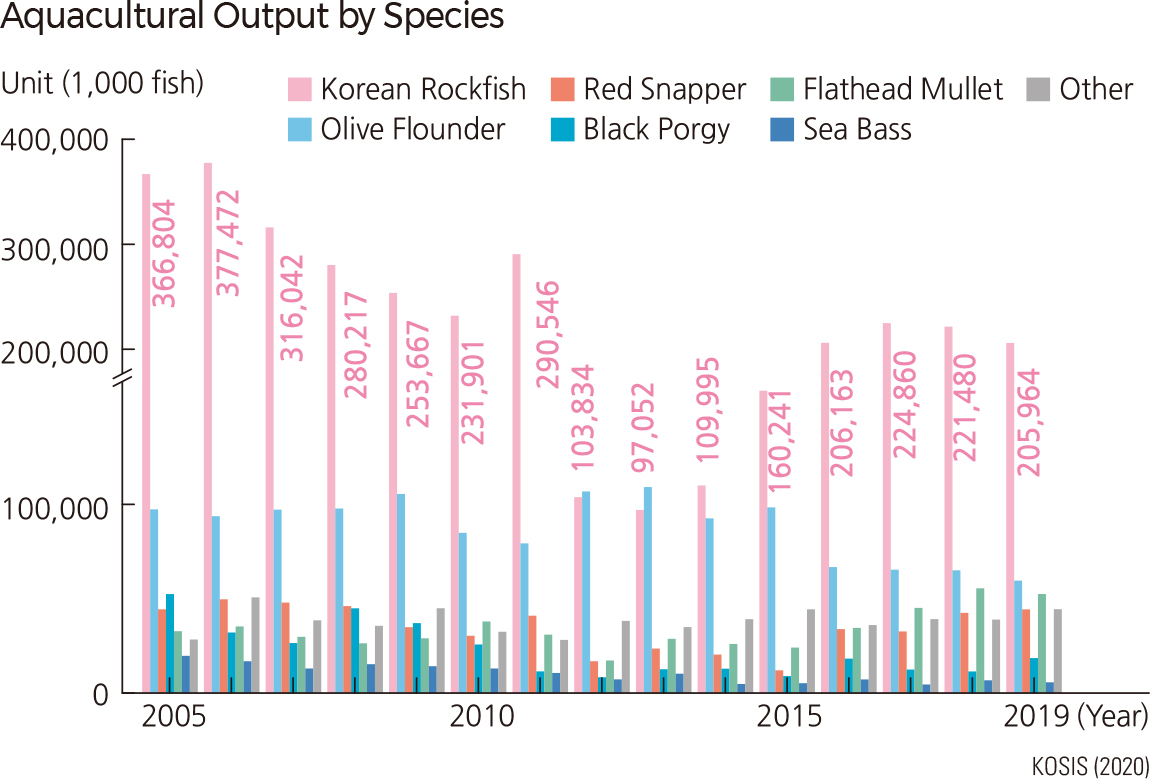
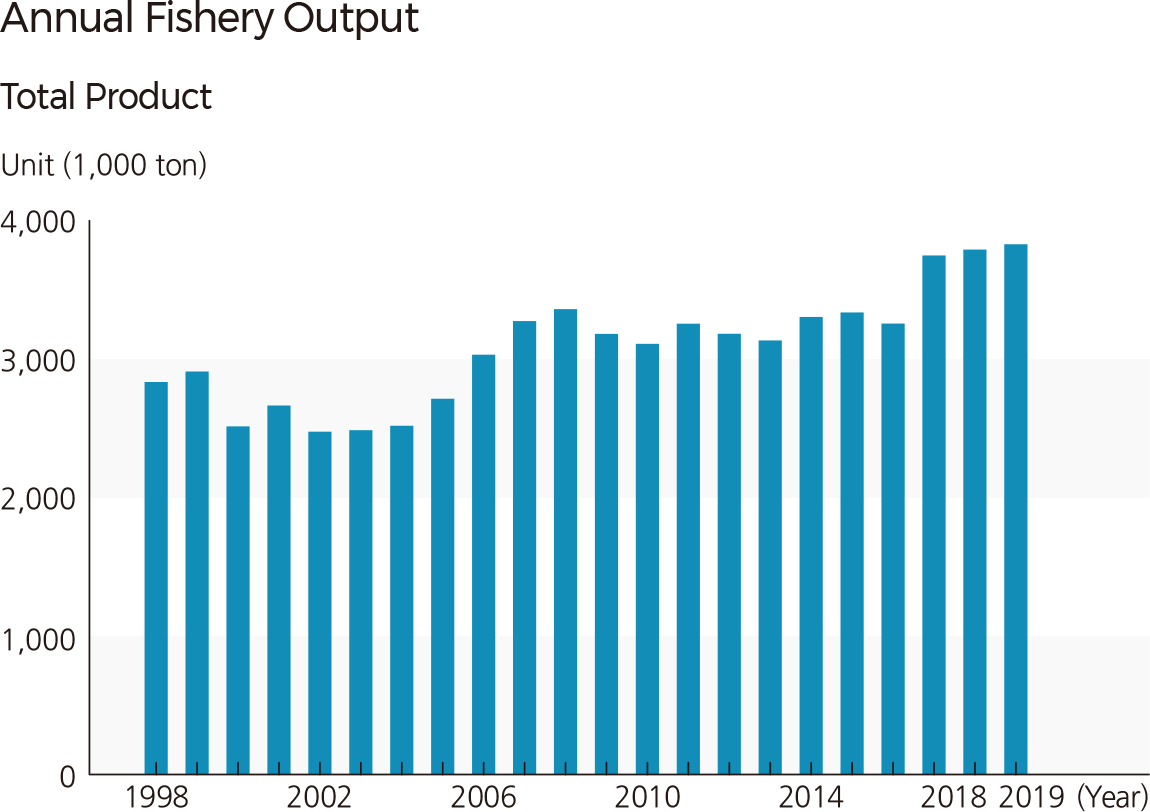
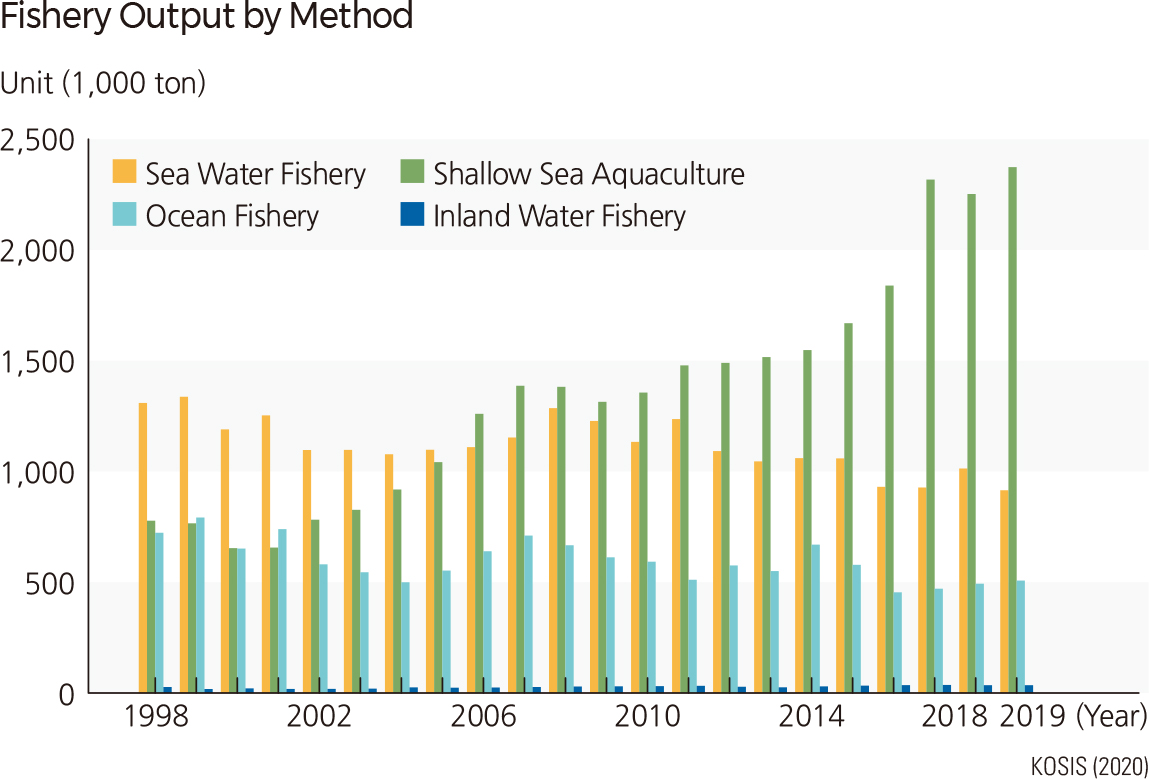
The fishery output has been on the rise since 1998, and it reached a maximum of 2,835,000 tons in 2019. If the fisheries output is categorized by fishery method, ocean fishery, excluding aquaculture, deep-sea fishery, and inland water fishery, accounted for the largest amount (40%) from the 1990s to the early 2000s. Since 2006, the output by shallow sea farming increased sharply. In 2019, shallow sea farming produced about 60 percent of fishery output. Deep-sea fisheries accounted for about 25 percent of fishery output in 1998 but continued to decline, reaching about 13 percent in 2019. Based on the fishery output, the major fish species of the aquaculture industry is rockfish, followed by flounder, red sea bream, and blackhead sea bream. The output of shallow-sea farming continued to increase. The output of fish farming repeated fluctuations, and in 2012, the output recorded its minimum of about 300 million fish. |