English II 2020
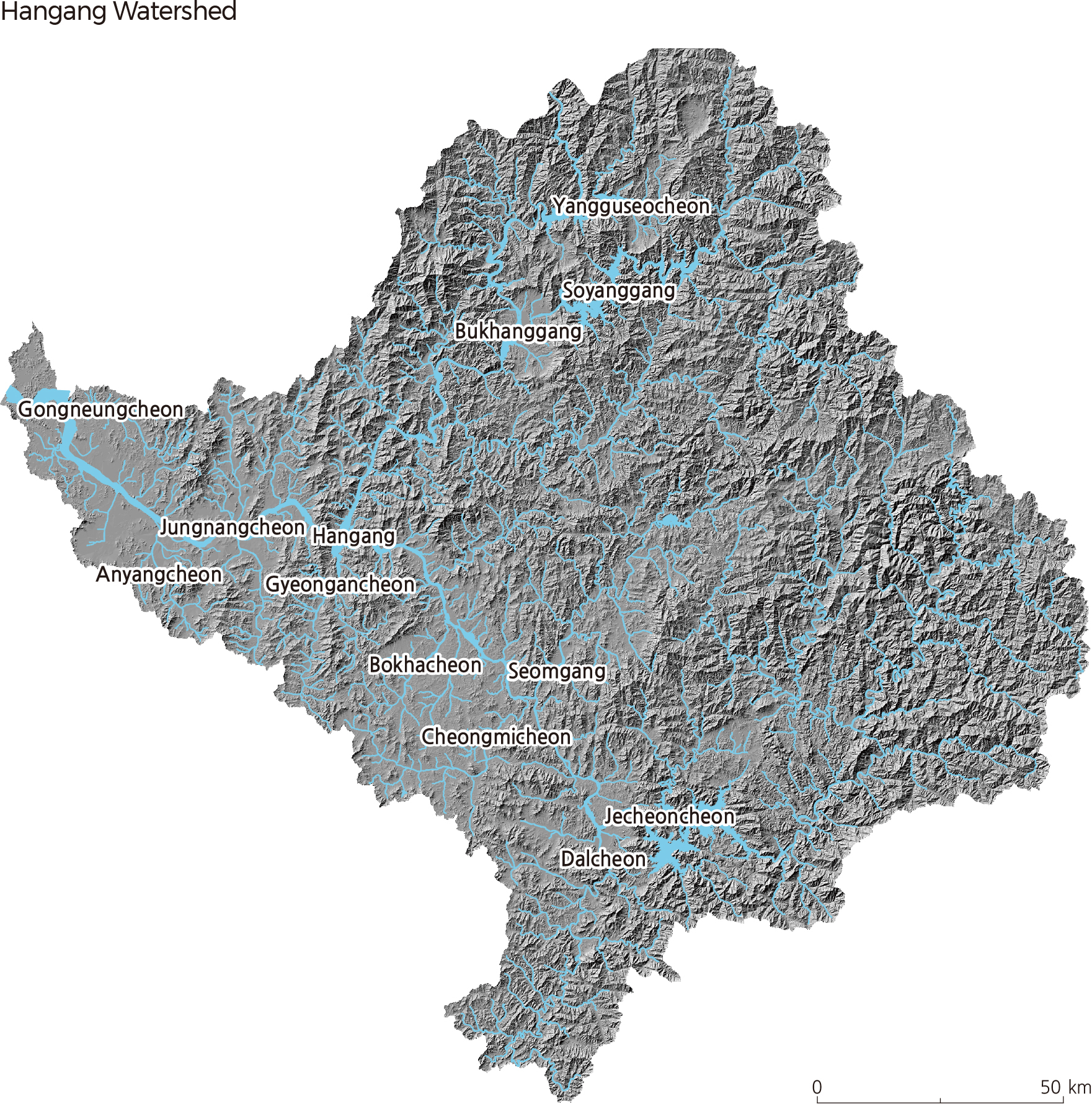
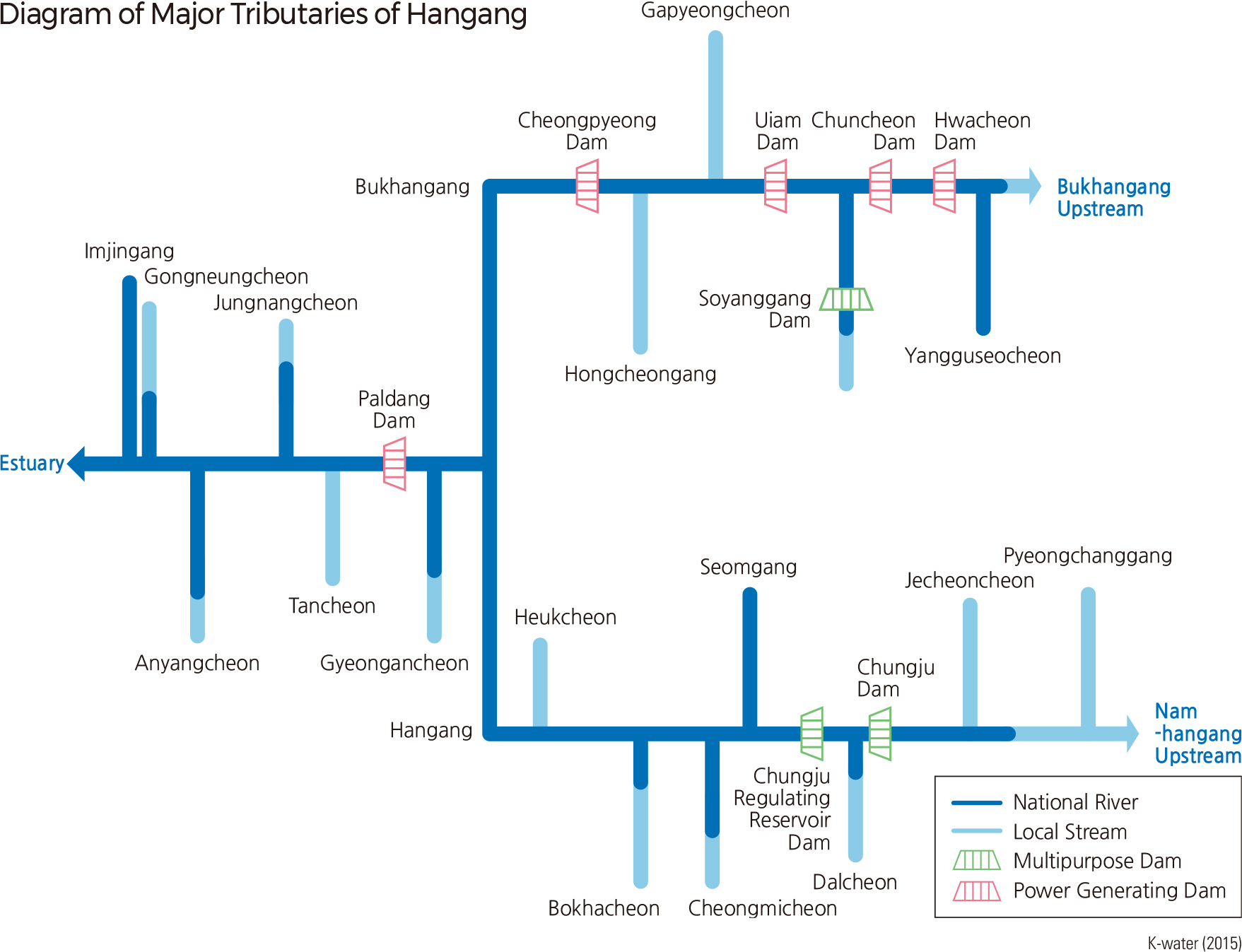
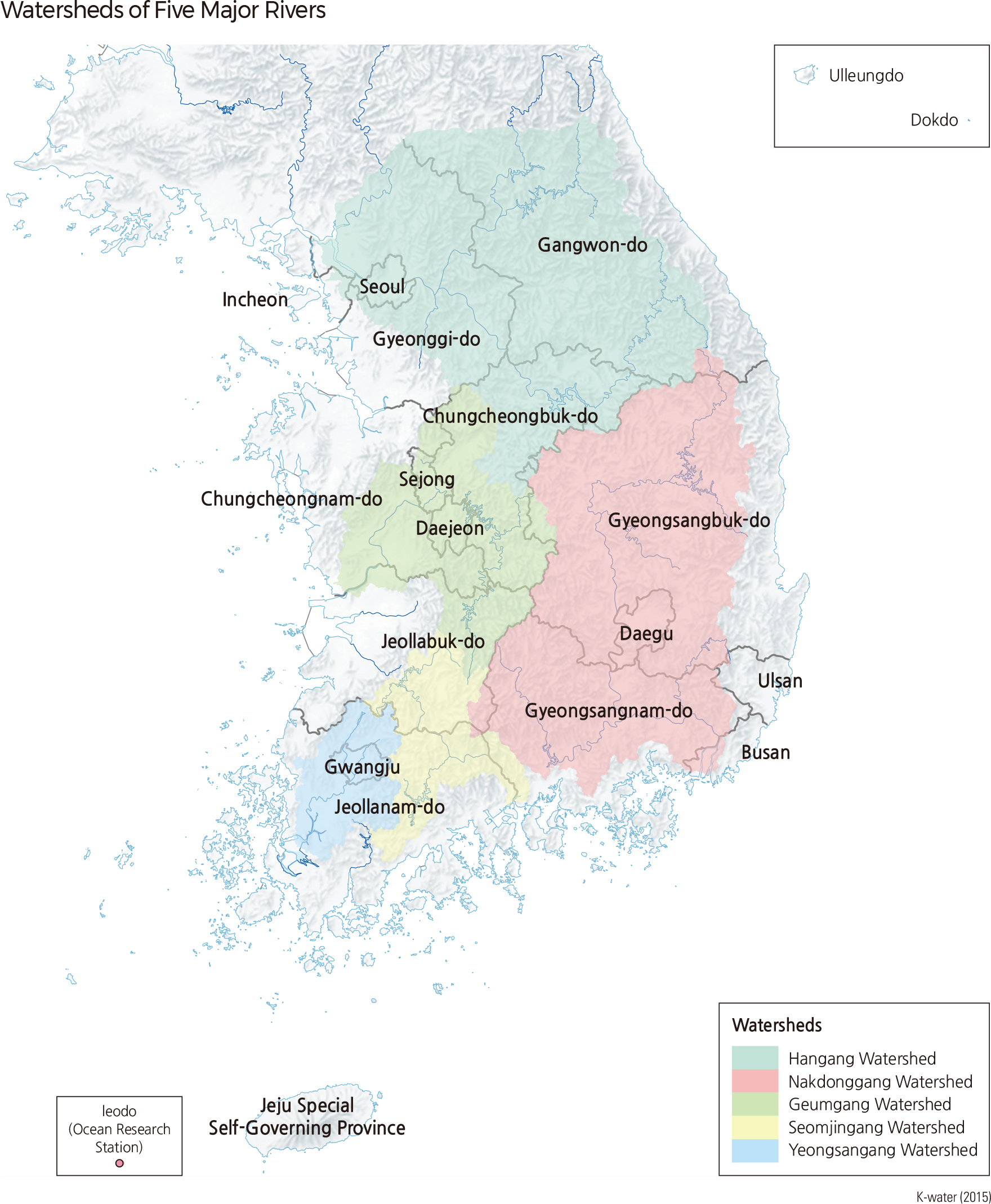
Hangang is a river that flows horizontally across the midsection of the Korean Peninsula. It is 494.4 km long and has a drainage area of 25,953 ㎢, or 35,770 ㎢ including the section in North Korea. Lying mainly in Gangwon-do and Gyeonggido, the Hangang watershed extends into Seoul, Incheon, Chungcheongnam-do, and Chungcheongbuk-do. Hangang is largely divided into Bukhangang (North Hangang) and Namhangang (South Hangang). The two rivers join at Yangsuri, Yangseo-myeon, Yangpyeong-gun, Gyeonggi-do, flow through Seoul, and finally drain into the Yellow Sea at Bogugot-ri, Wolgotmyoen, Gimpo-si. Namhangang, the main stream of Hangang, originates in Geomryongso of Geumdaebong (1,418 m) in Changjuk-dong, Taebaek-si, Gangwon-do. Dalcheon, Sumgang, Cheongmicheon, and Bokhacheon are some of the streams that flow into Namhangang. Bukhangang, which is the largest branch of Hangang, originates in Danbalryeong (1,241 m), Geumgang-gun, Gangwon-do, and is joined by Yangguseocheon and Soyangang.
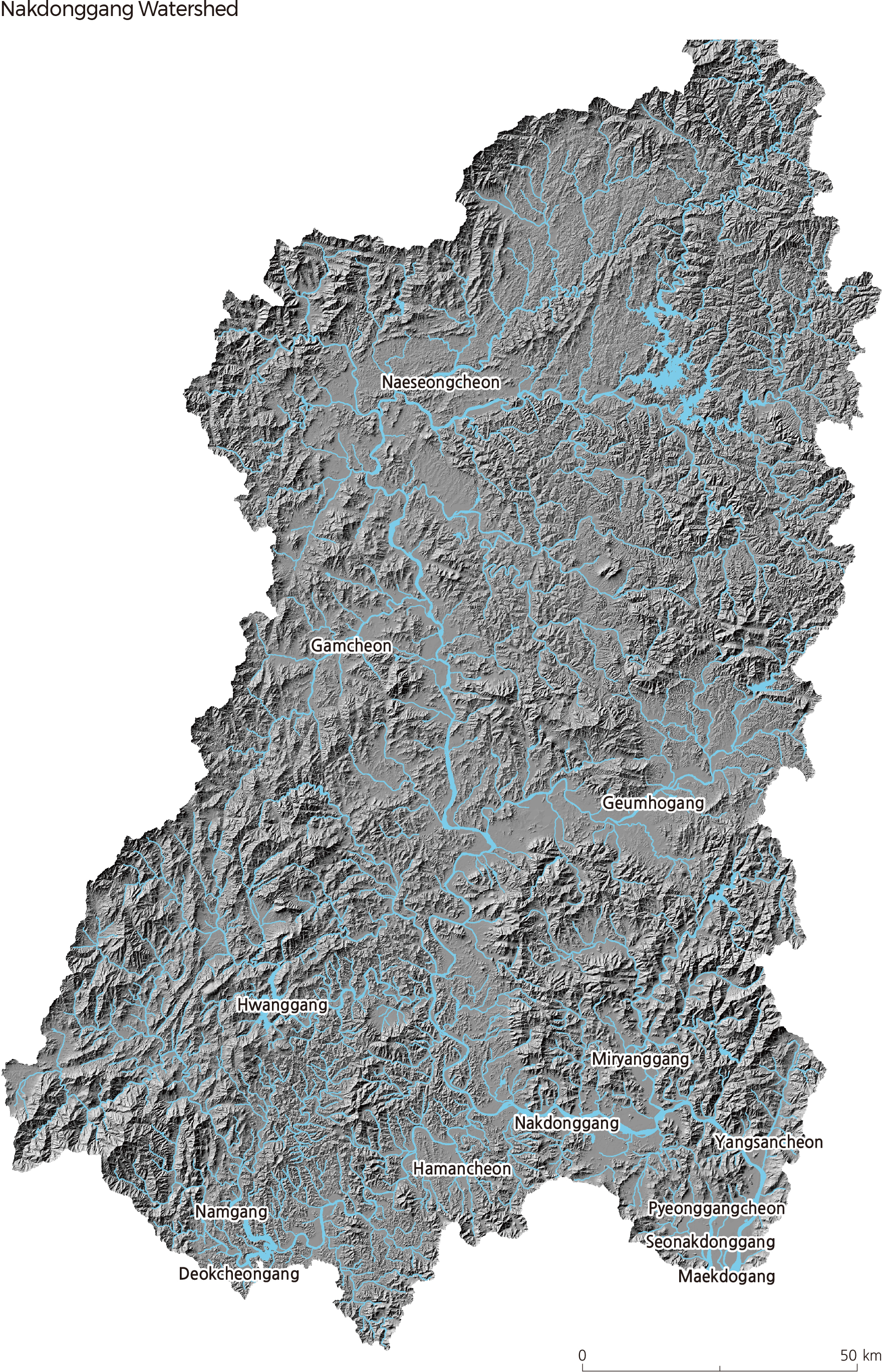
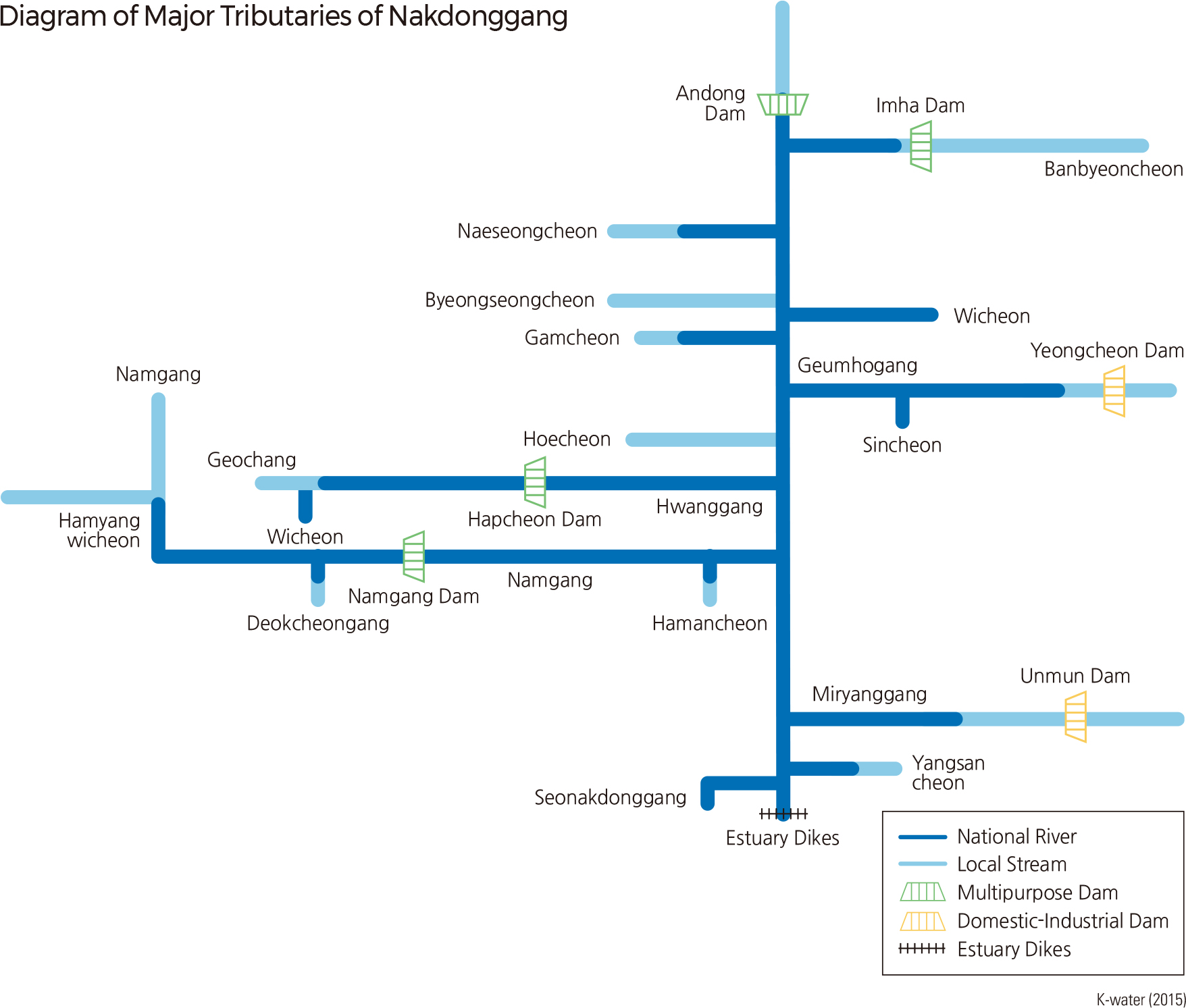
Nakdonggang, which flows south through the southeastern part of the Korean Peninsula, is 510.3 km long and has a drainage area of 23,384 ㎢. The Nakdonggang watershed is located across Busan, Daegu, Gangwon-do, Gyeongsangnam-do, and Gyeongsangbukdo, and also lies along the boundaries of Jeollanam-do, Jeollabukdo, and Chungcheongbuk-do. Nakdonggang stems from Hwangji Pond on the eastern side of Hambaeksan in Taebaek-si, Gangwondo and discharges into the South Sea through an estuary dike and delta in Busan. Seonakdonggang branches off at the delta located at the river mouth of Nakdonggang.
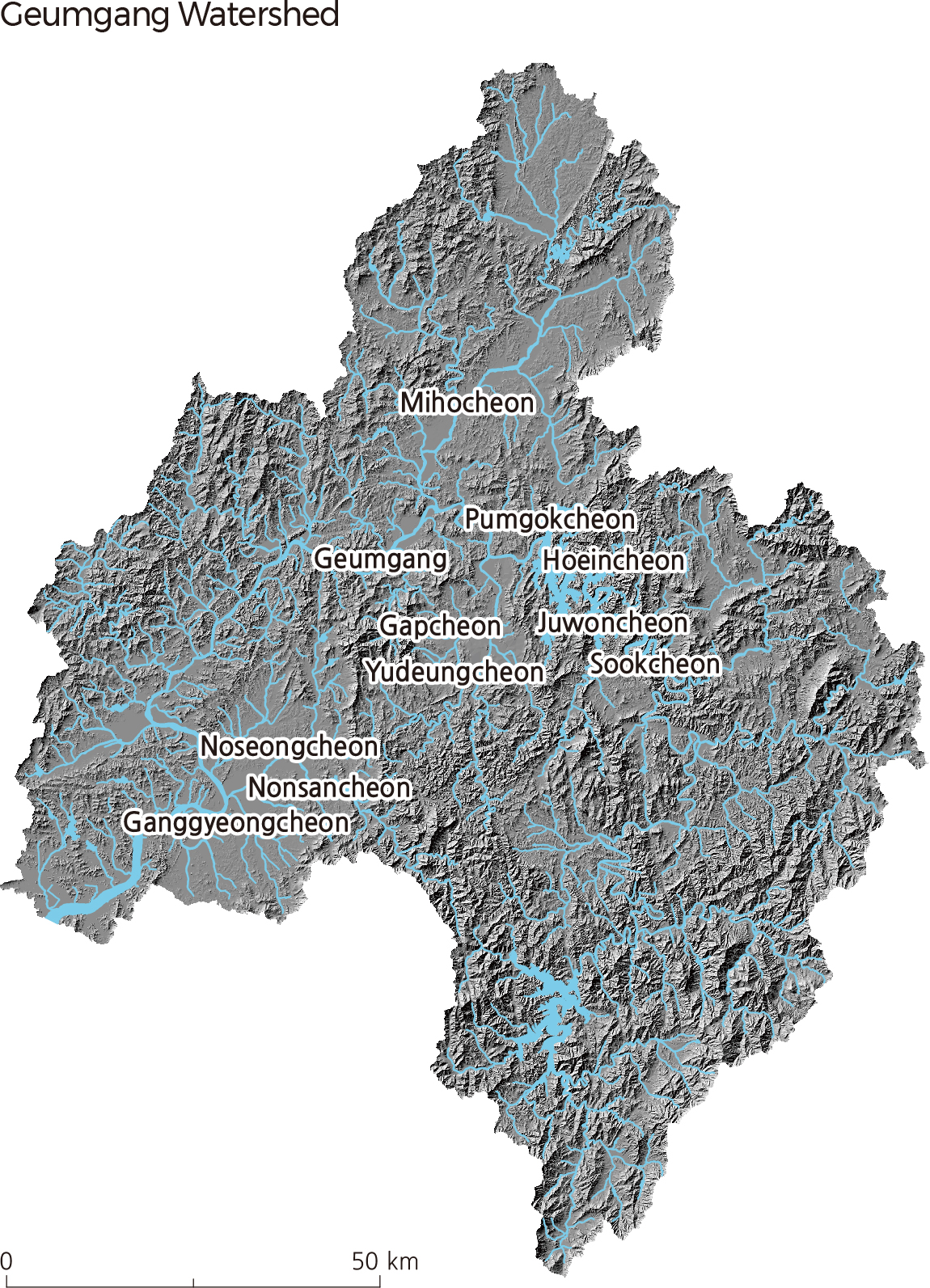
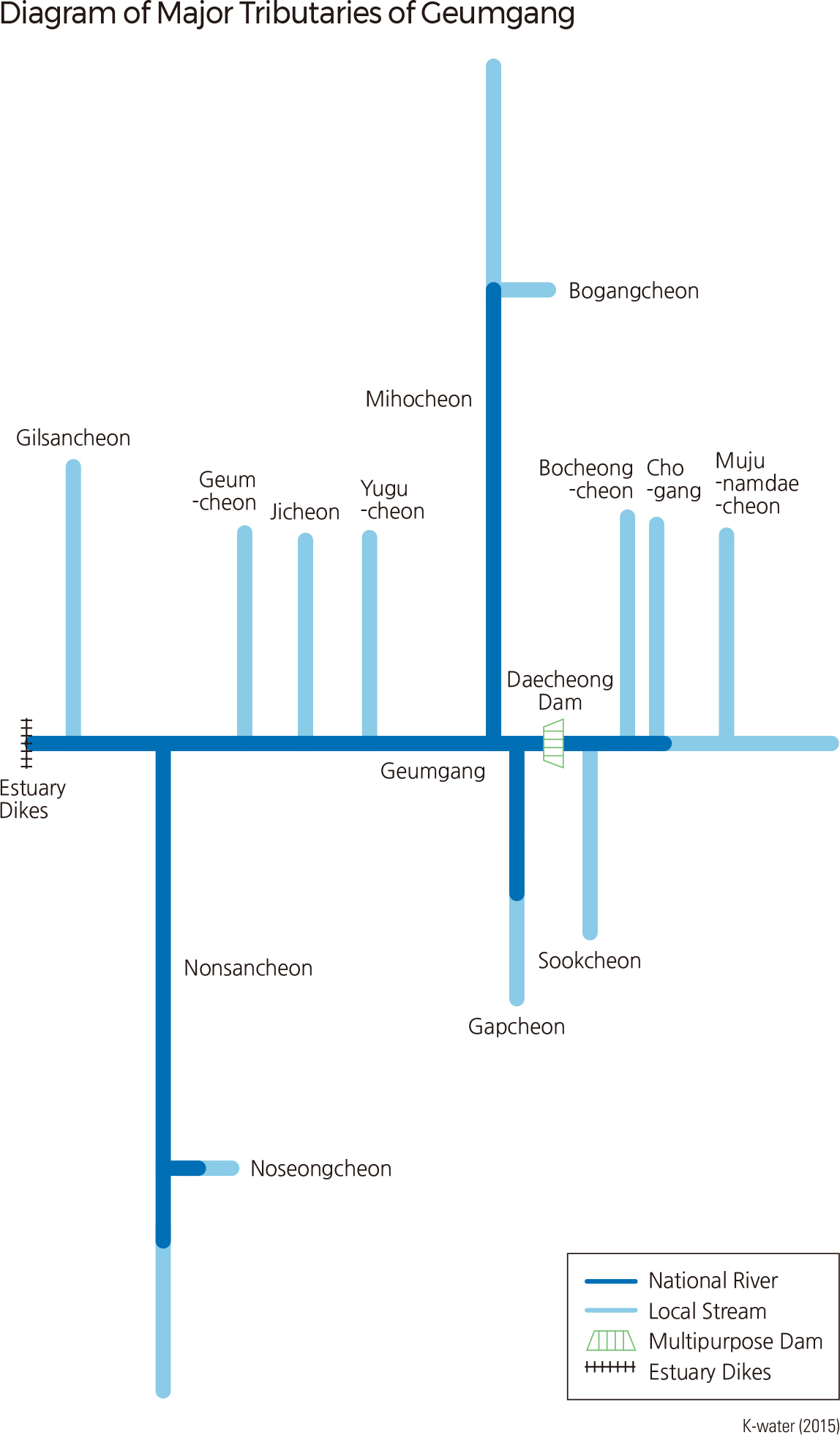
Geumgang starts in the center of the Korean Peninsula and flows northwest and southwest. It is 397.8 km long with a drainage area of 9,912 ㎢, and its watershed lies mainly in Sejongsi, Daejeon, Chungcheongnam-do, Chungcheongbuk-do, and Jeollabuk-do. Originating in Tteunbongsaem Spring of Sinmusan (896.8 m), Subun-ri, Jangsu-eup, Jangsu-gun in Jeollabukdo, Geumgang flows northwest through Daejeon, Daecheong reservoir, and Sejong, and then flows southwest through Gongju and Buyeo before finally discharging into the Yellow Sea. Until the completion of the Geumgang Estuary Dike in 1990, high tide seawater would flow upstream as far as Ganggyeong-eup, Nonsansi Chungcheongnam-do.
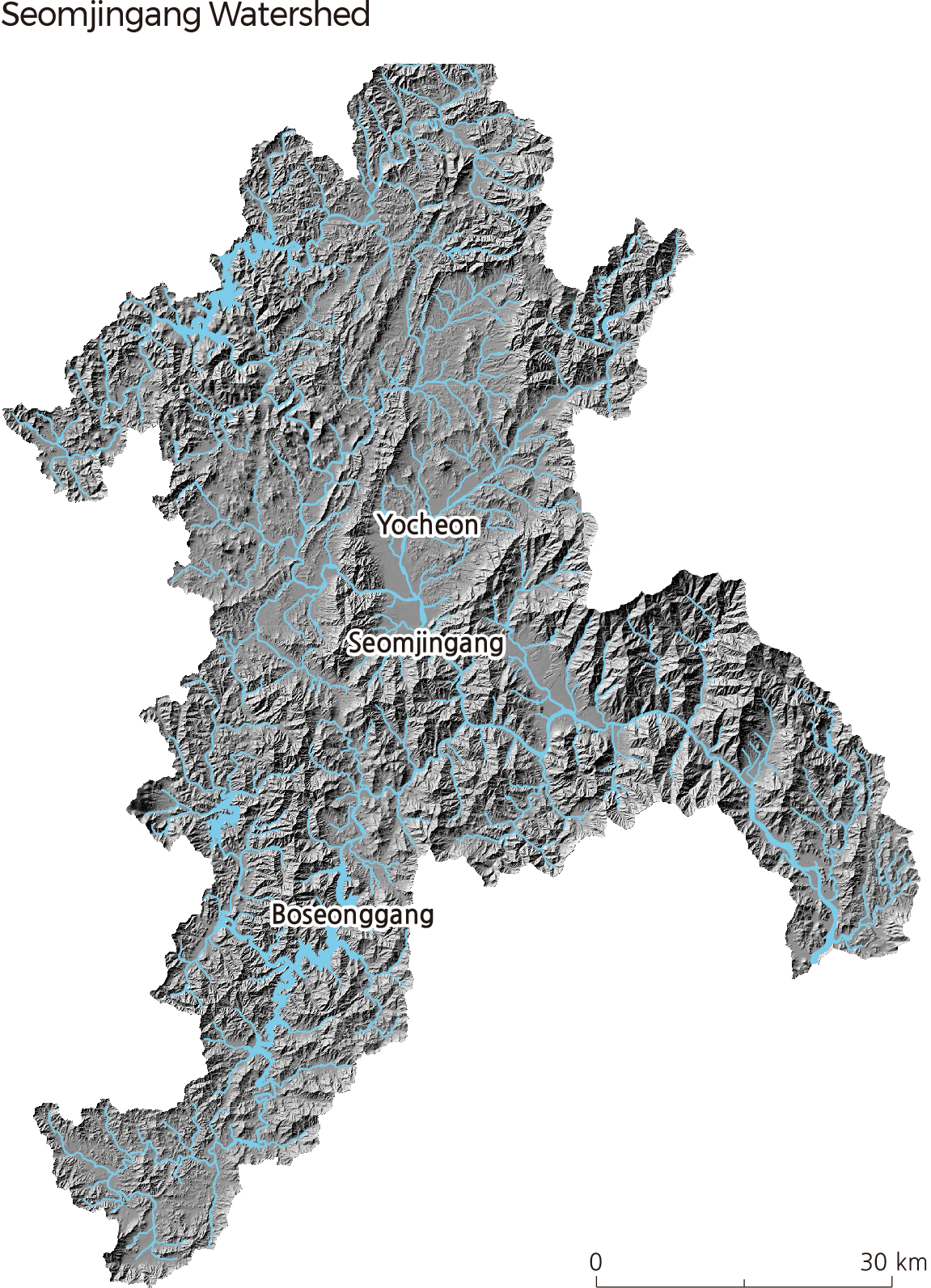
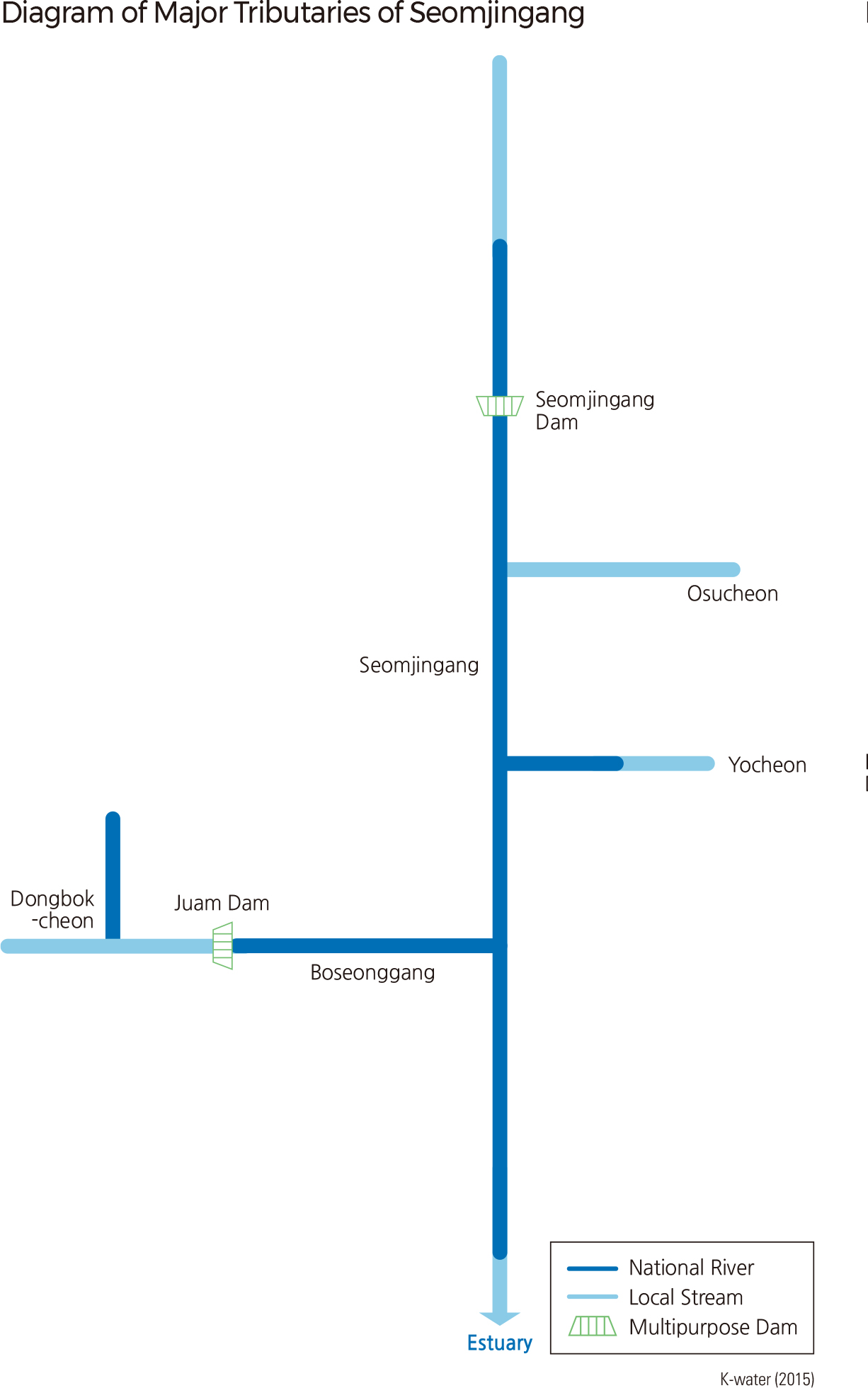
Seomjingang, flowing south in the southern part of the Korean Peninsula, is 223.9 ㎢ long with a drainage area of 4,911 ㎢. It has a watershed that is located across Jeollanam-do, Jeollabuk-do, and Gyeongsangnam-do. Starting at Demisaem Spring on Palgongsan (located at the boundary of Jinan-gun and Jangsu-gun, Jeollabuk-do), Seomjingang flows through Jeollanam-do and Gyeongsangnam-do and discharges into the Gwangyang Bay in the South Sea.
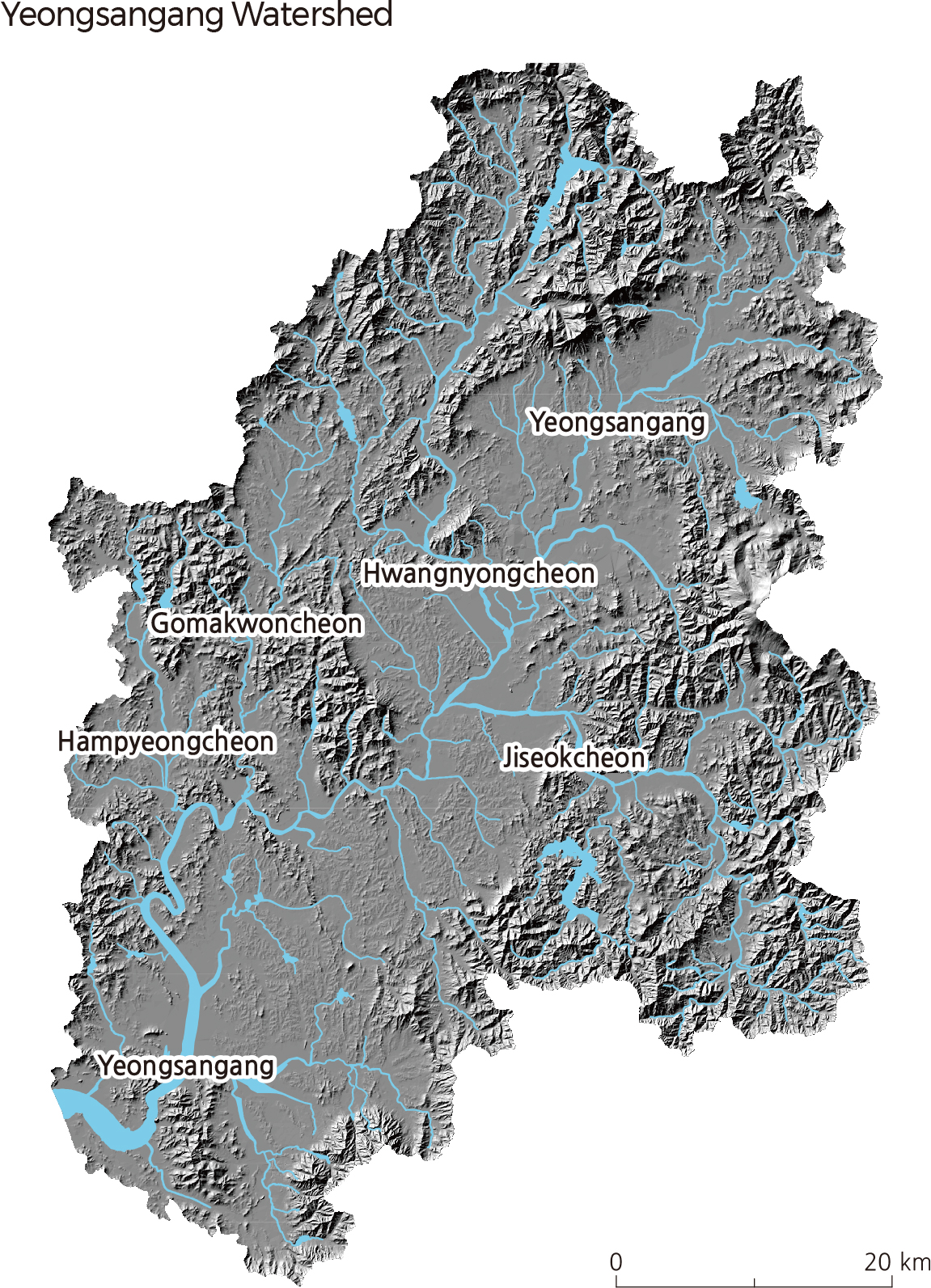
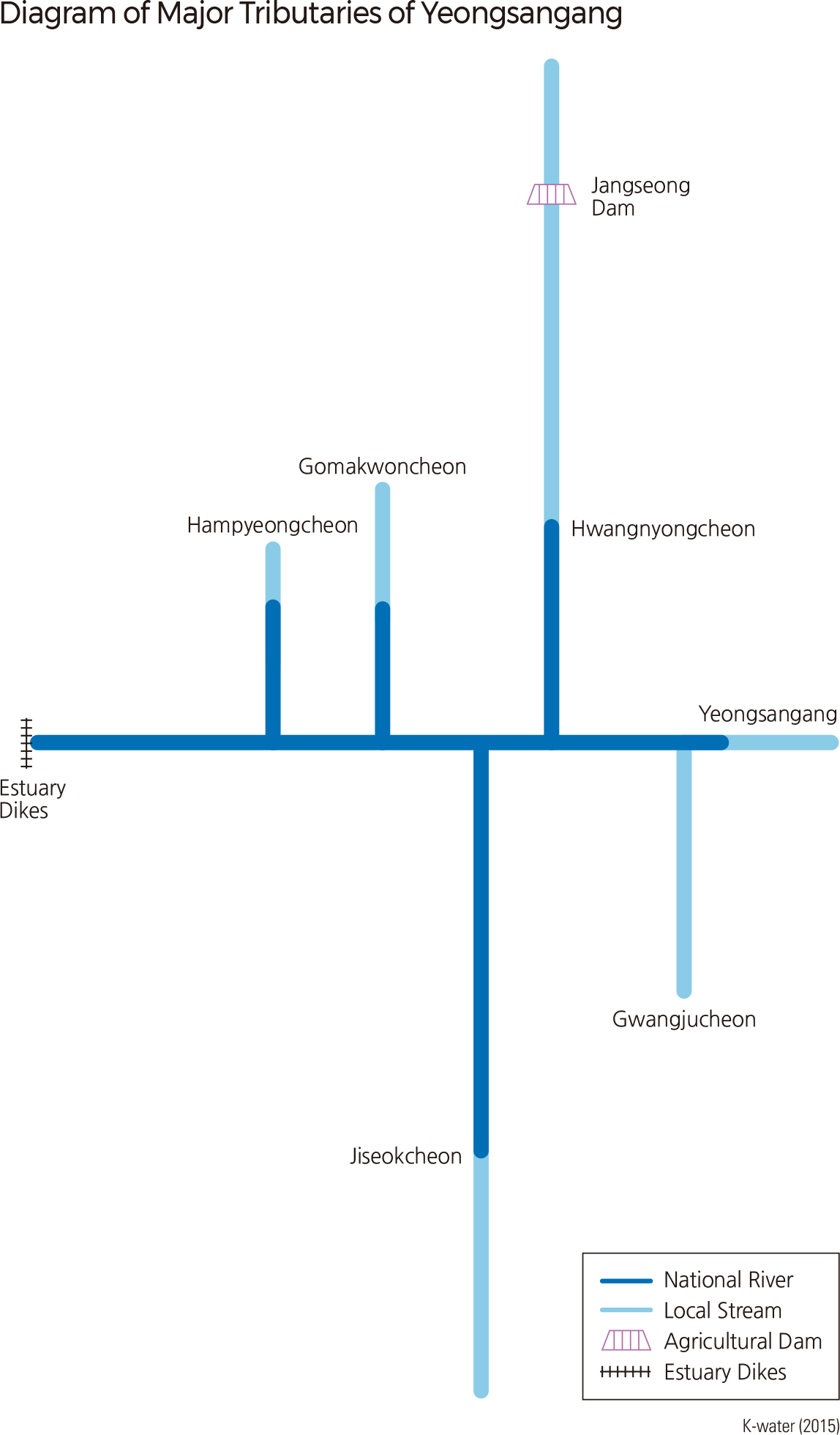
Yeongsangang is located in the southwestern region of the Korean Peninsula. It is 129.5 km long with a drainage area of 3,467 ㎢ and has a watershed that lies mainly in Jeollannam-do, Jeollabuk-do, and Gwangju. It originates in Yongso of Gamagol in Yongyeon-ri, Yong-myeon, Damyang-gun, Jeollanam-do, runs through the Naju Plains, and finally reaches the Yellow Sea at an estuary dike. The dike was constructed in 1981 to prevent seawater from flowing upstream at high tide. Hwangryonggang, Jiseokcheon, Gomakwoncheon, and Hampyeongcheon are some of the streams that flow into Yeongsangang. |