English III
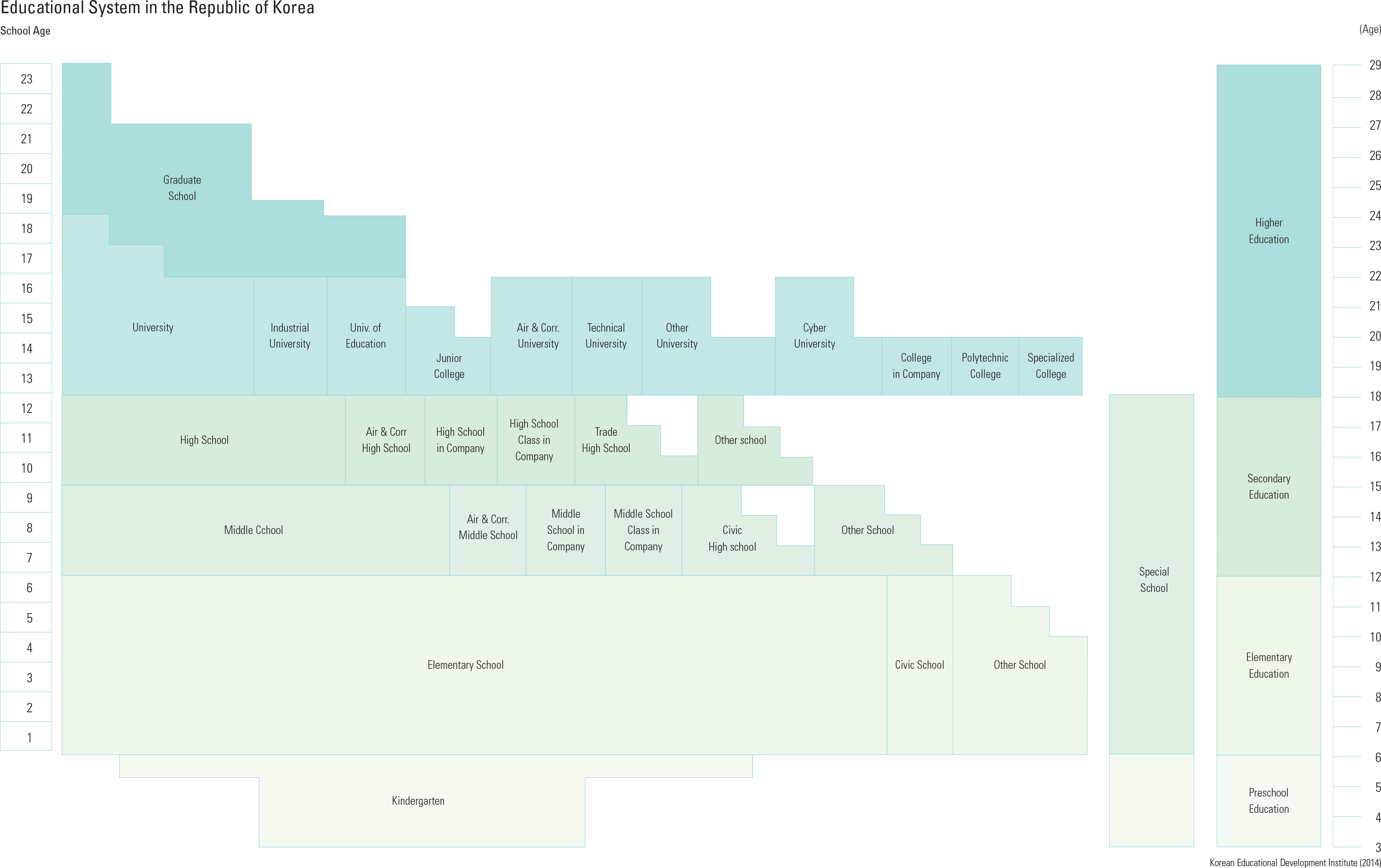
Education has become the most important inter- est and concern for modern Koreans. Education is closely related to all aspects of society at all lev- els, such as family planning, population structure, household expenditure, residence selection, and city planning. In addition, a high level of enthusi- asm for education and the high level of education spending, including private education expendi- tures, are conspicuous characteristics of Korean society. As with many countries, where modern educa- tion begins at the birth of the nation-state, Korean education has undergone significant changes through its modernization process. The Korean school system is composed of elementary edu- cation for kindergarten and elementary school, secondary education for middle and high school, and higher education for college and related lev- els. Most Koreans acquire at least six years of elementary education and another six years of secondary education, and the proportion entering higher education institutions, including college, is among the highest in the world. Each education level is offered by various educational institutions. Elementary and second- ary education is provided by public educational institutions established by the state, along with a variety of private educational institutions. Various schools have been established for special purpos- es in accordance with the characteristics of stu- dents. At the high school level, more choices such as college prep, vocational, and technical high schools are available. Higher education is based on four-year universities and two-year commu- nity colleges. There are also technical colleges covering various professions. Recently, online and extension colleges and degree programs have been developed. Masters and doctoral degrees are offered by many graduate schools, and many stu- dents also pursue graduate study abroad.
page_2 |