English III
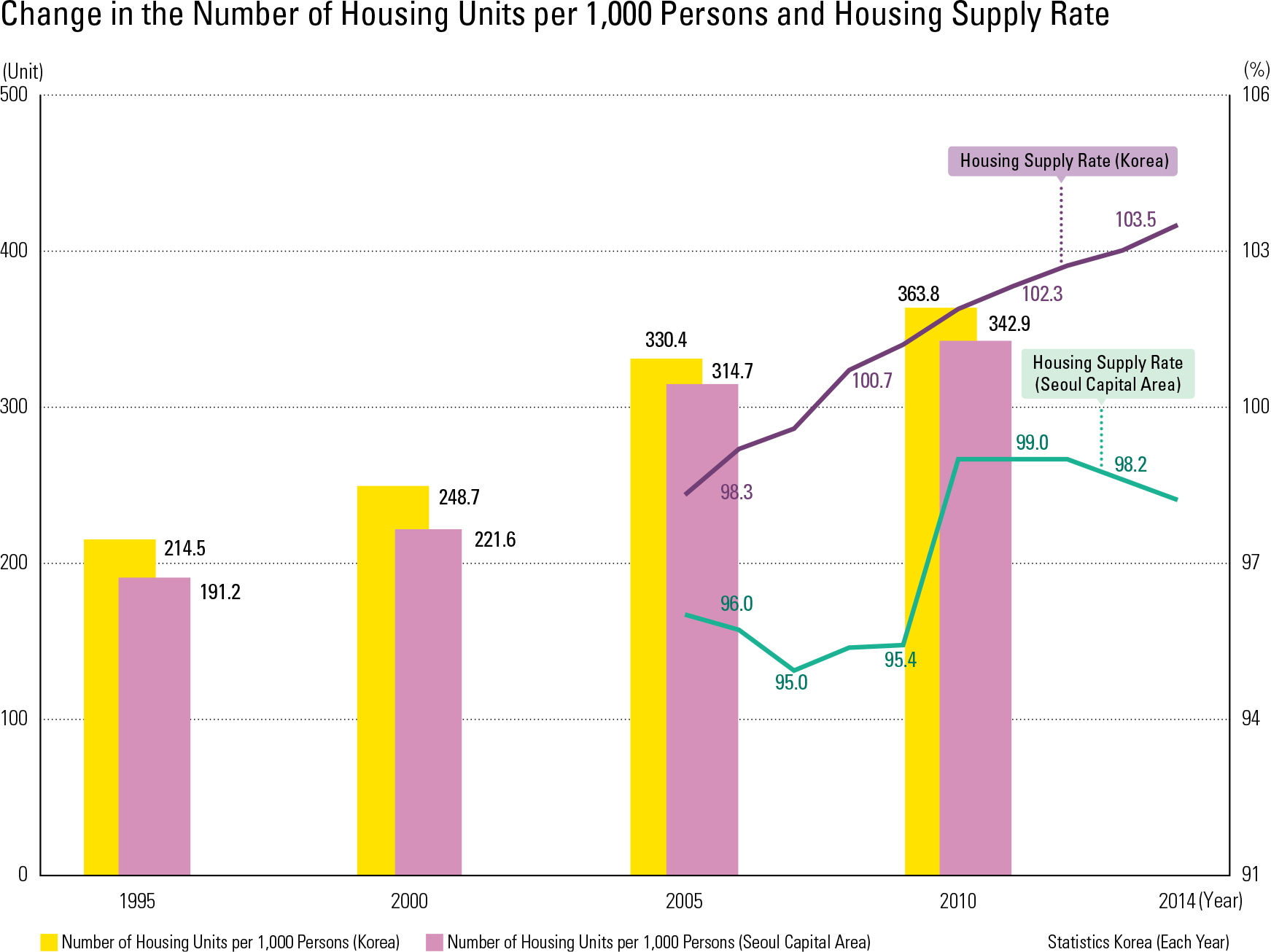
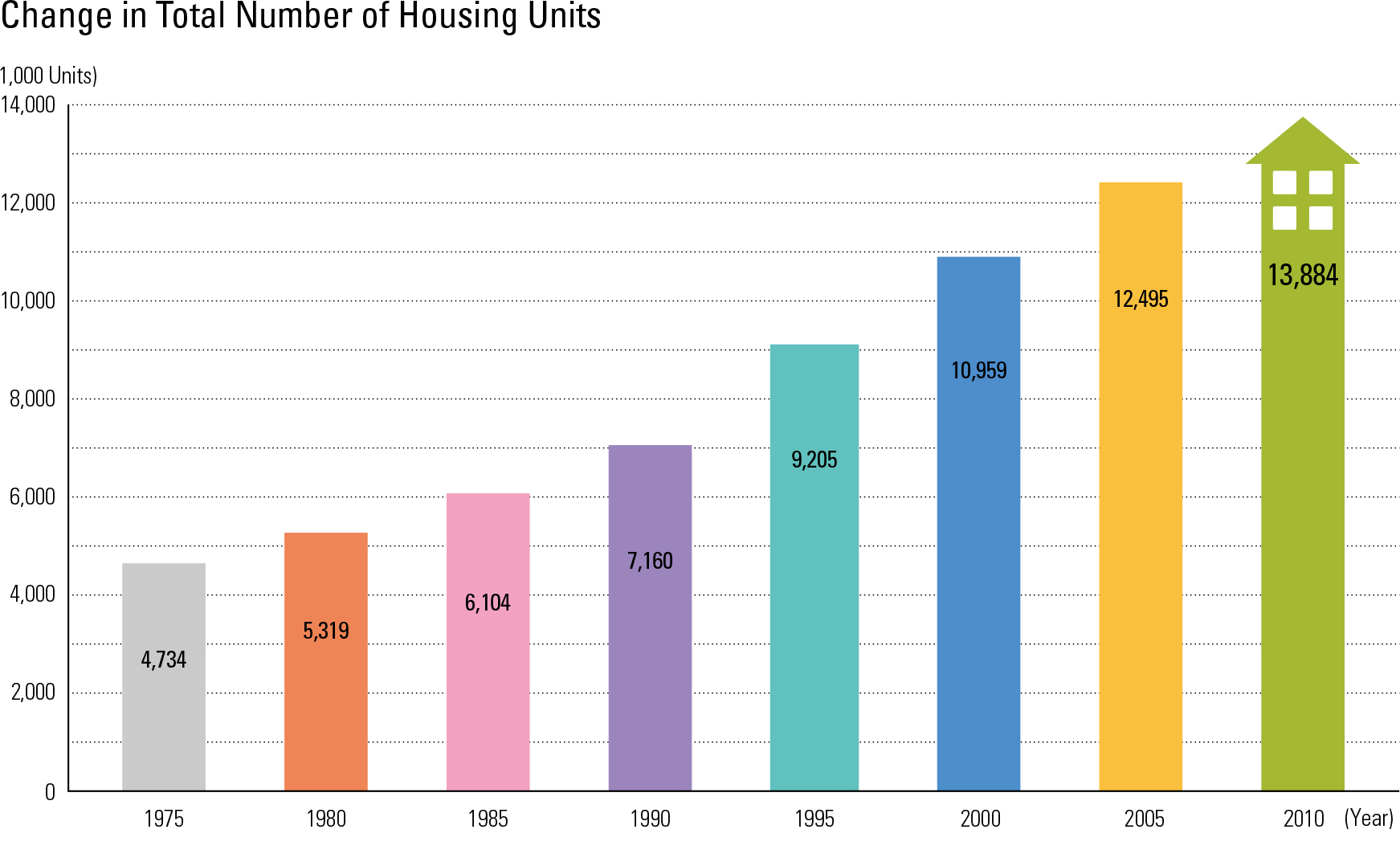
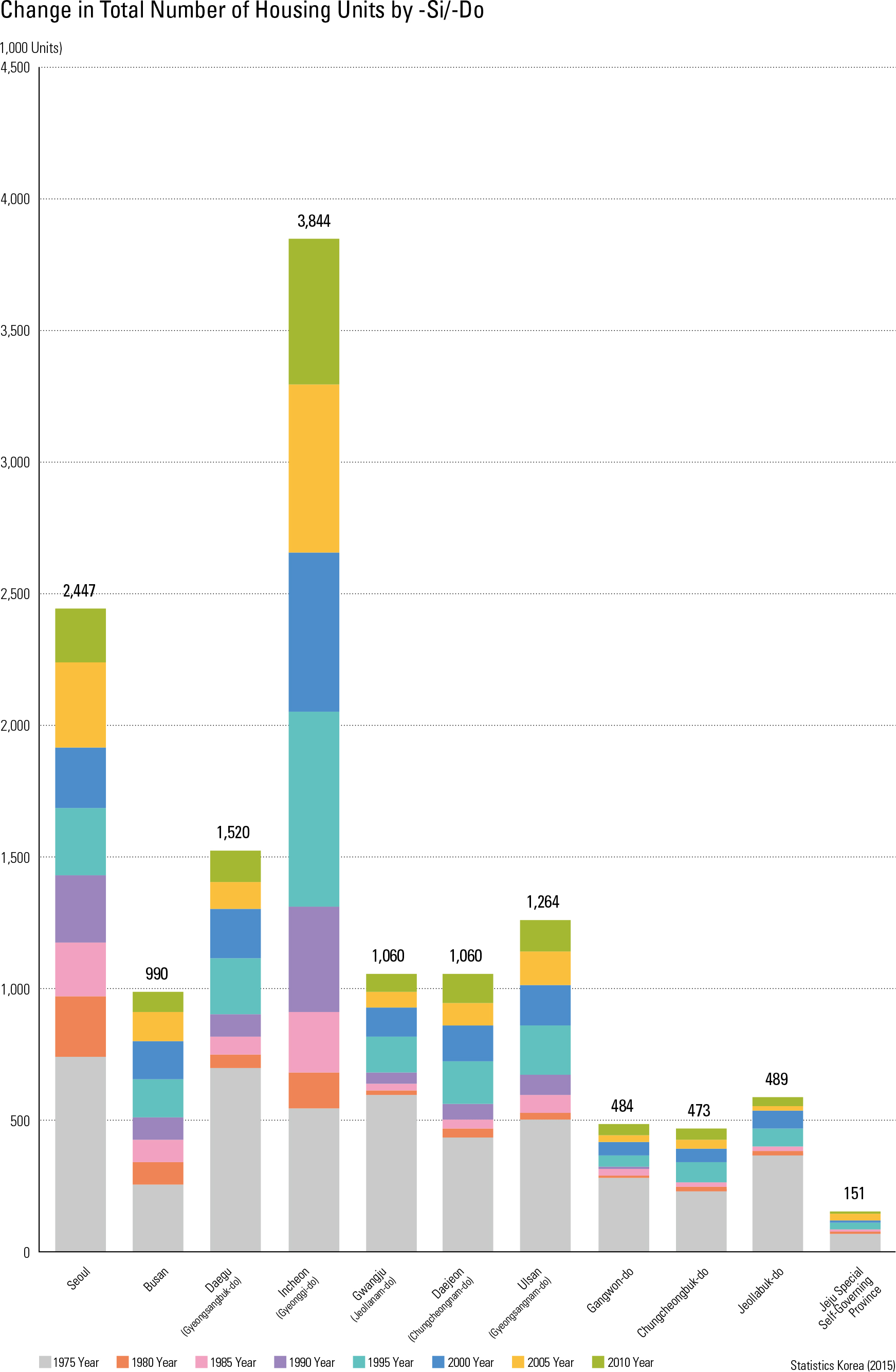
After the end of the Korean War (1950 – 1953), the Korean government started housing projects as a part of post-war reconstruction efforts. Until the 1960s, strategic investment priorities were placed on rebuilding industries. Government investment in housing was therefore very small, reaching only 2.4% of GNP during the 1962 – 1966 period and 3.0% during the 1967 – 1971 pe- riod. During these periods, housing developments were mostly led by the private sector, and only about 13% of housing development was support- ed by the public sector. In the 1970s, the Korean government began to invest more heavily in hous- ing, and established a series of necessary policies and laws. For example, the Housing Construction Promotion Act was enacted in 1973, and the Act promoted provision of “national housing” using the funds from government-owned banks or local governments. Priority to purchase was granted to people who never owned a home before, and this purchase-priority policy was maintained for more than thirty years. In addition, the national and lo cal governments contributed to the improvement of the urban environment, with land improvement projects and residential land development proj- ects. As a result, housing conditions in the Seoul Metropolitan Area and other metropolitan cities improved significantly from the perspective of total housing stock as well as homeowner ratios. In 1975 there were 4.734 million housing units in total. The number of total housing units in 2010 was 13.884 million, which is about a three-fold increase since 1975. In the Seoul Metropolitan Area, the number of housing units per 1,000 per- sons was only about 137 in 1975. It surpassed 200 in 2000, and reached 364 units by 2010 (a 2.7-fold increase from 1975), indicating that three out of every ten people own a house. Regarding the total number of housing units, the Seoul Metropolitan Area had 6.291 million houses in 2010 (45.4% of the national total). With such dramatic increases in housing supply, the housing supply ratio in the Seoul Metropolitan Area in 2010 was 99%, and, nationally, it was greater than 100%
page_2 |