English III
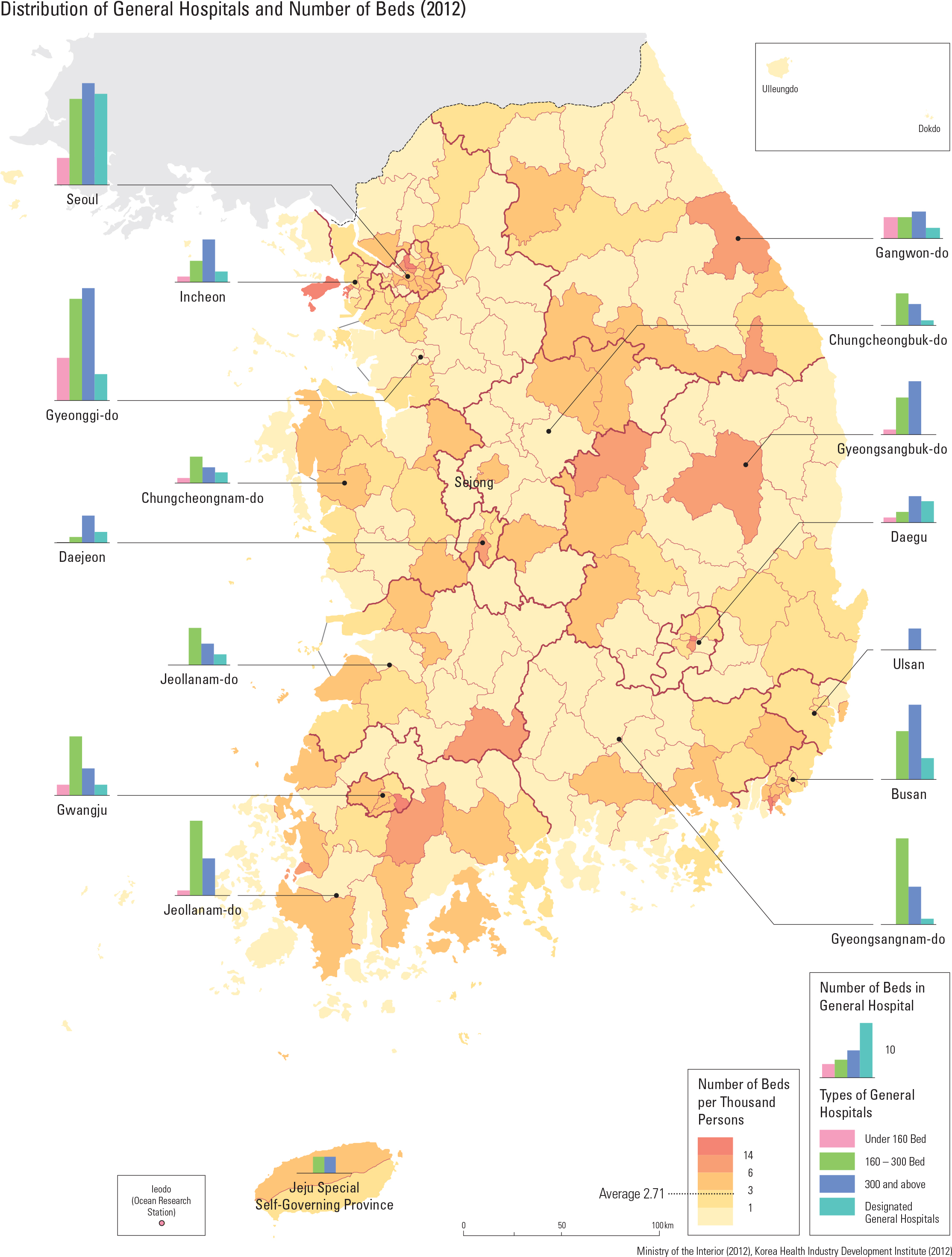
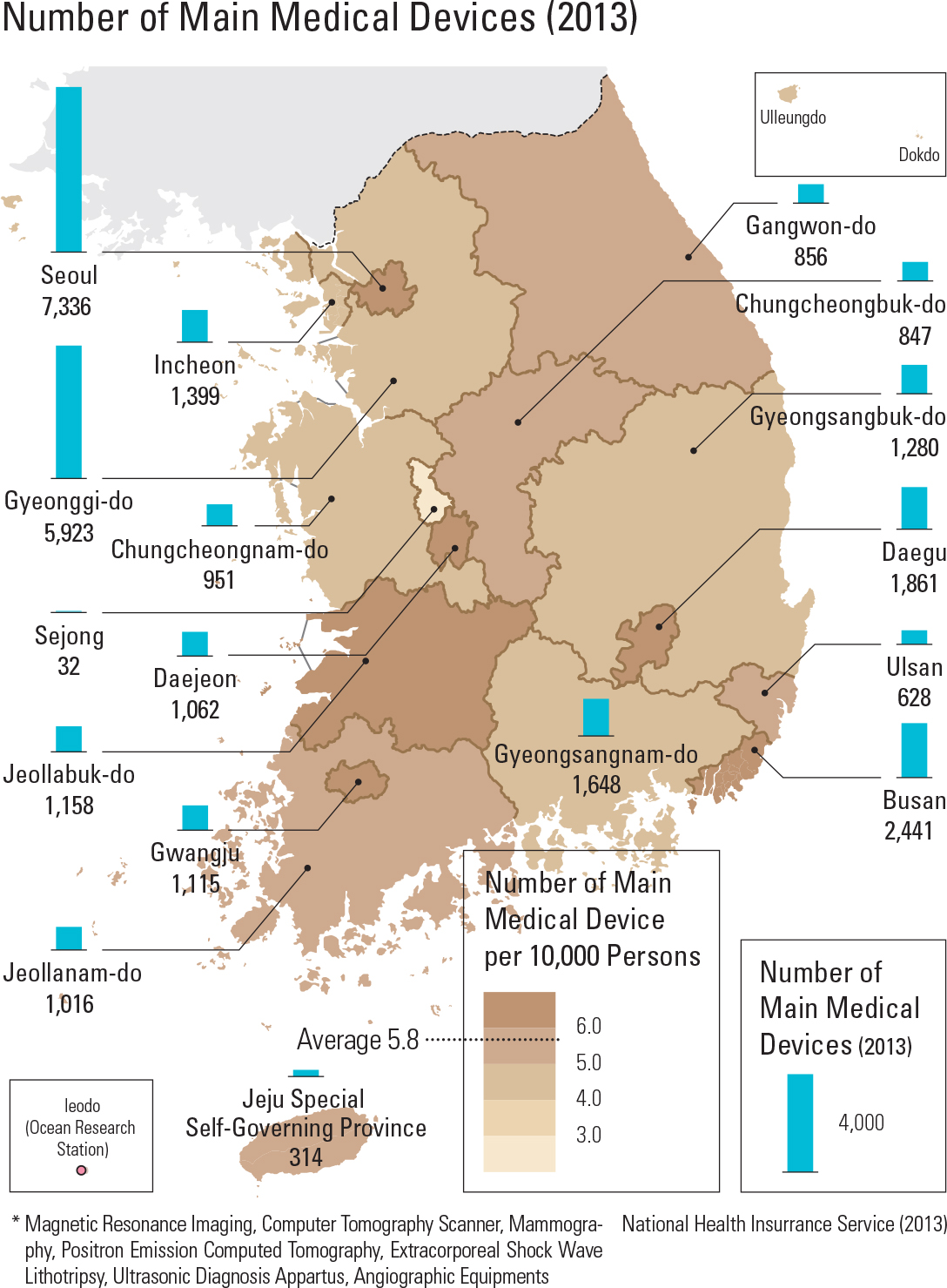
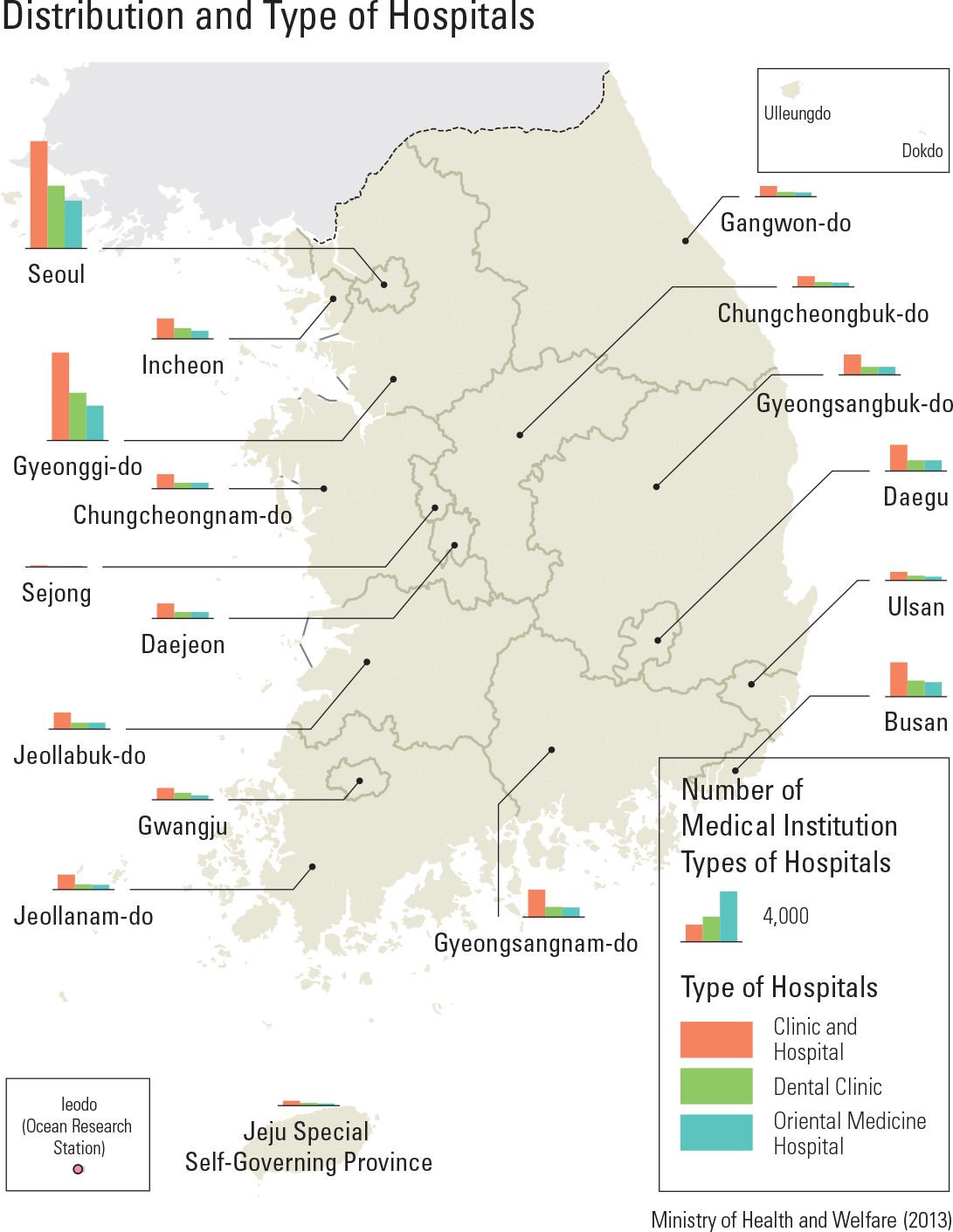
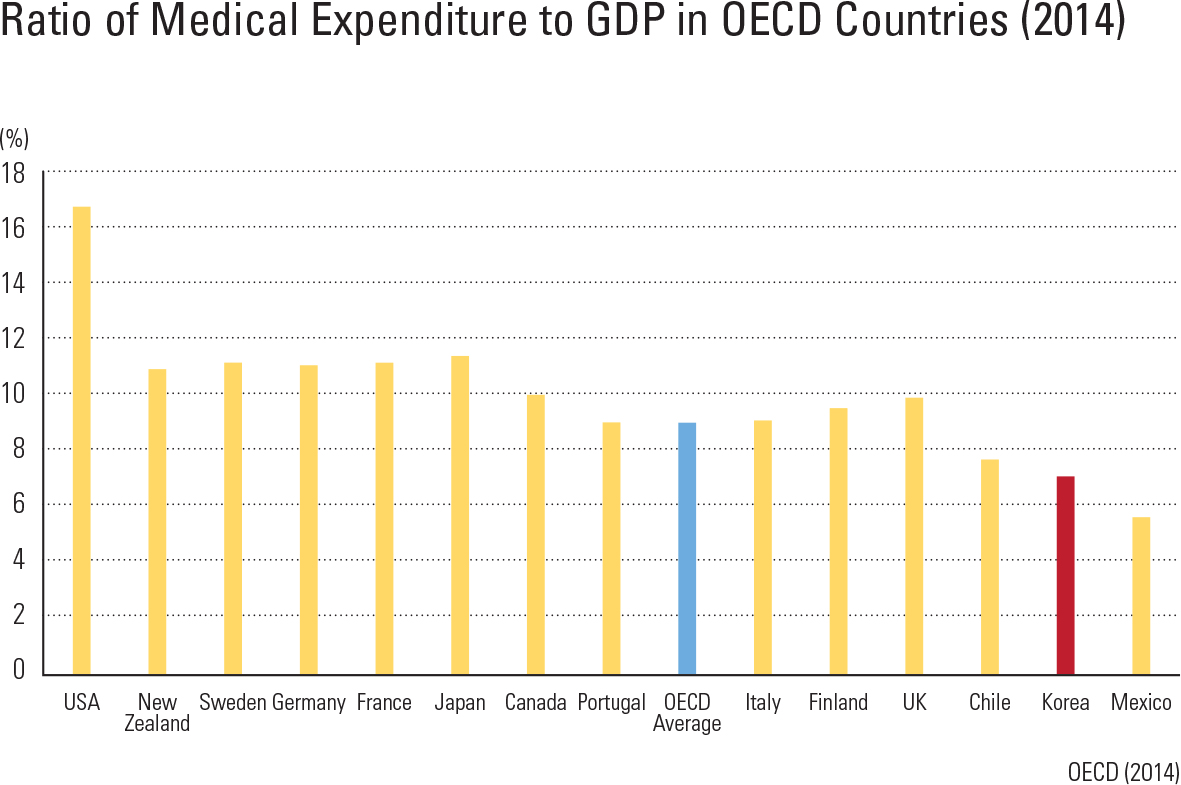
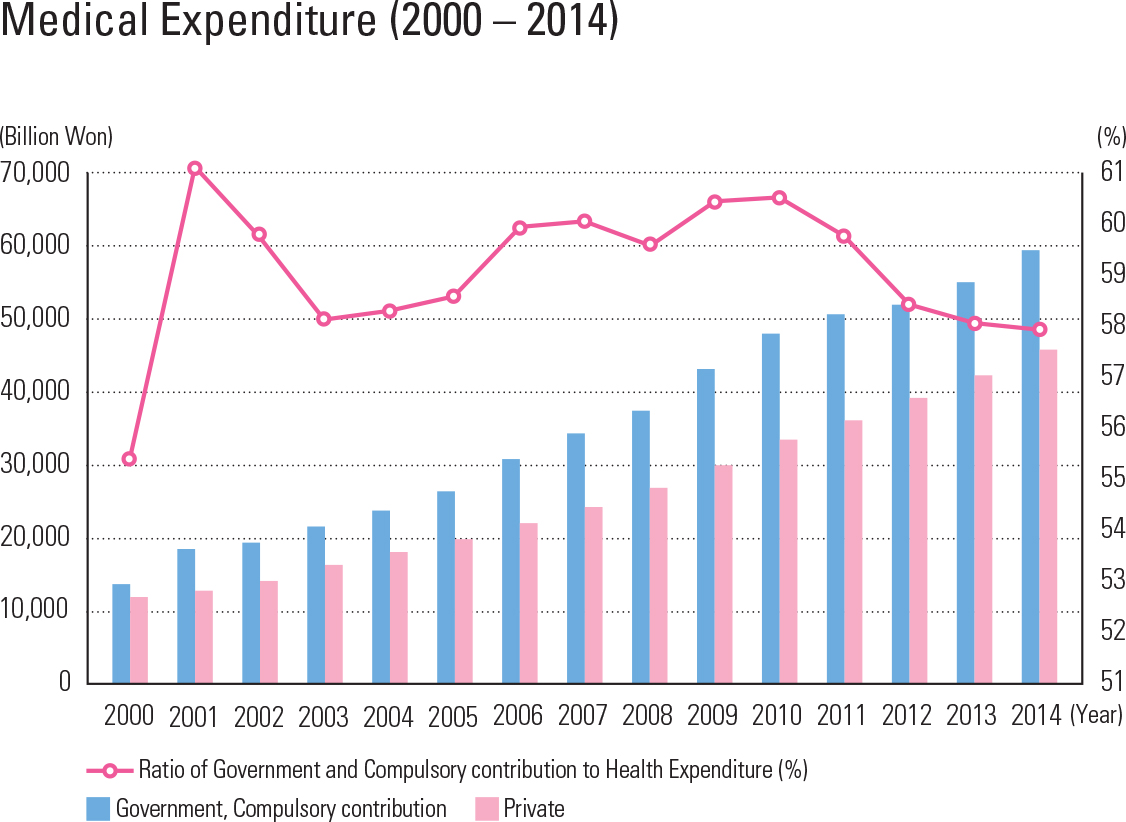
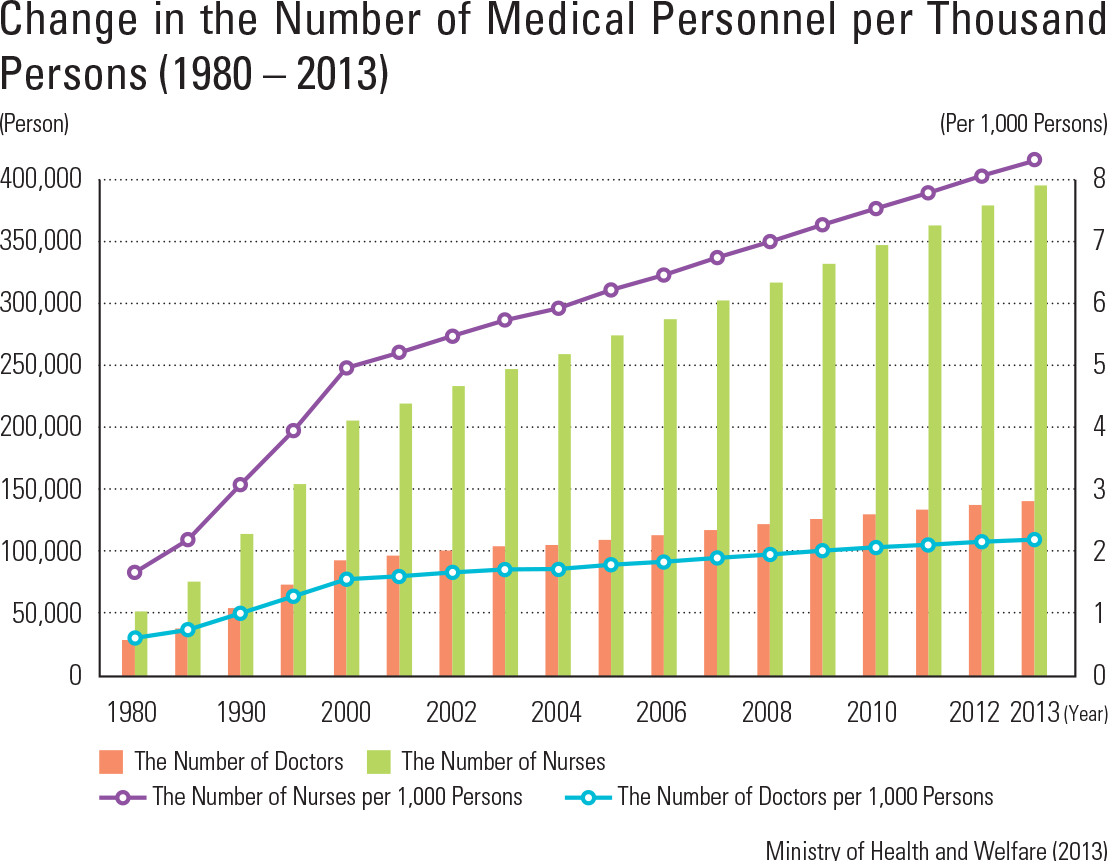
Korea’s medical expenditure per GDP is about 7 percent, lower than that of major countries of the OECD. However, medical expenditure has constantly increased as a result of an aging pop- ulation and the increased interest in health care. Medical expenditure is classi ed into two catego- ries: expenditure of government and compulsory contribution, and the private financial resources of private insurance and personal expenses. In the case of medical expenses, public financial resources have steadily increased, but have begun to decline recently. An important issue for Korea is how to balance demands for increased health care spending with demands for scal sustainabil- ity by the government. Korea is very famous for well-trained medical personnel. The number of medical doctors and nurses is steadily increasing, and excellent med- ical personnel are being educated at all levels in colleges and universities, but the number of doctors and nurses per 1,000 people is relatively lower than that of other OECD countries. Korea’s medical institutions are largely divid- ed into clinics, hospitals, and general hospitals, depending on the size of the institution. Mild dis- eases are treated at widely distributed clinics and hospitals by specialized doctors. Serious illnesses or diseases are treated at the higher medical insti- tutions, such as a general hospital. As many dental clinics are also widespread, access to dental clin- ics is good, too. Oriental medicine hospitals and clinics provide medical services based on oriental medicine. Medical access has greatly increased because general clinics and hospitals are evenly distributed nationwide, while general hospitals are mainly distributed in metropolitan cities.
page_2 |