English I
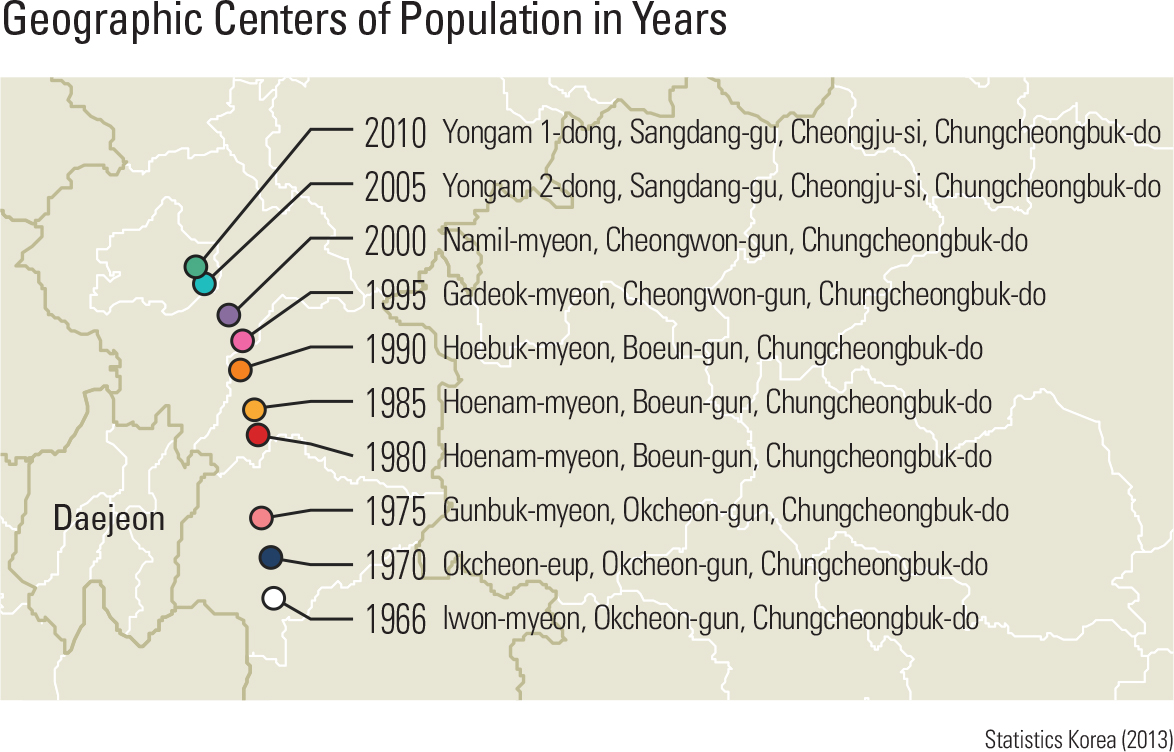
Population affects the characteristics of a nation’s politics, economy, culture, and infrastructure. The key characteristics of the population of a country or region include population distribution, population structure, and population migration. Population distribution is the population sizes of regions at a particular time. Population structure is the composition of the population of a region that denotes particular demographic attributes, including such important variables as age, sex, income, and household composition. Migration is the population movement between regions over a particular time period. Changes in population distribution come from natural increase and decrease (births and deaths) and migration. Natural increases and decreases of the population are monitored with statistics on total fertility and mortality rates. Migration, on the other hand, is affected by the geographical distribution of the political, economic, social, cultural, and spatial characteristics. Such influences function as determining factors for population influxes and outflows between regions; as a result, the socio-spatial process of migration takes place. Population migration includes regional in-migration and out-migration domestically and international migrations. Domestic migration is classified as the migration between urban and rural areas, between city and city, and among rural areas. In general, economic, demographic, and geographic factors jointly affect migration patterns. page_2 |