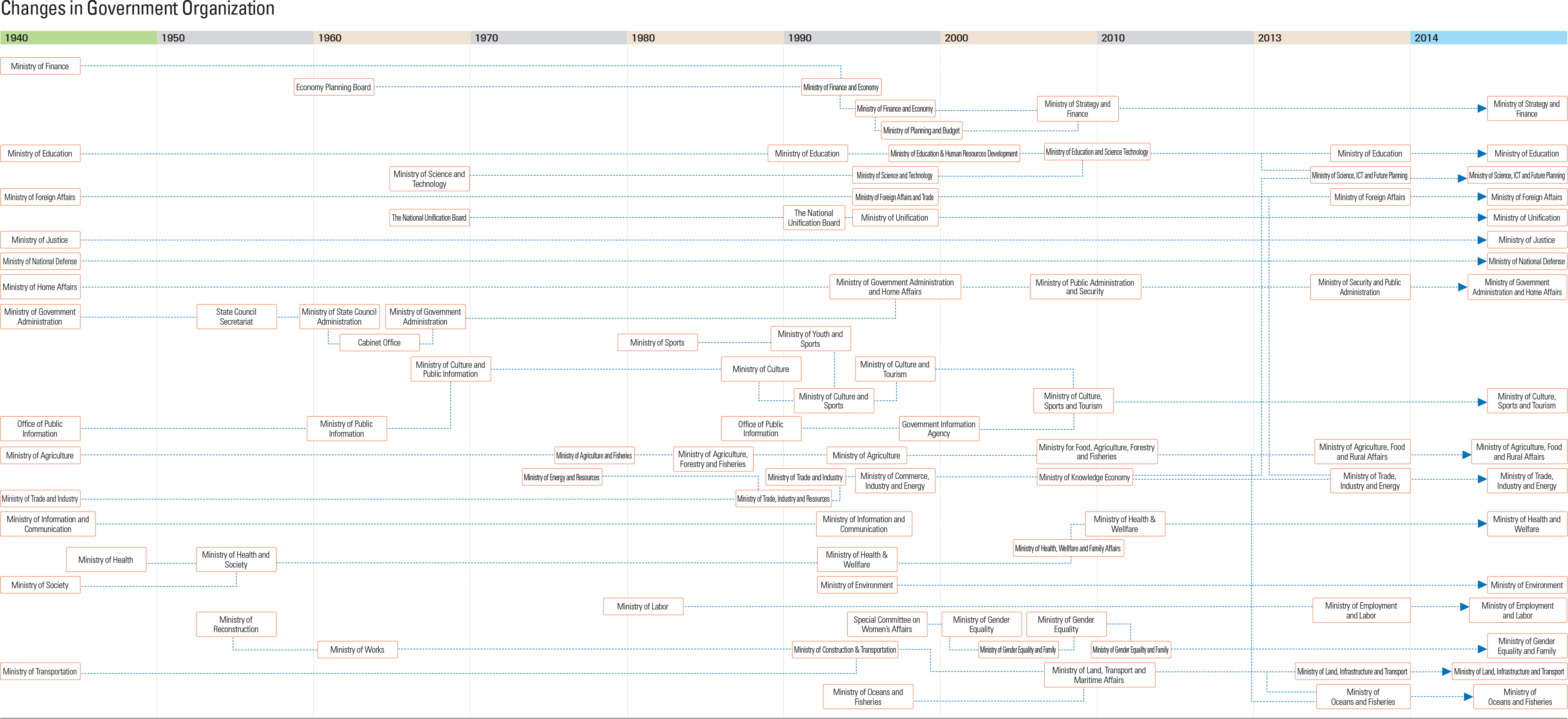
In 1948 the Government Organization Act specified that the Korean government should be divided into 11 executive ministries: Home Affairs, Foreign Affairs, Justice, National Defense, Finance, Education, Agriculture and Forestry, Commerce and Industry, Transportation, Social Affairs, and Postal Services. It also called for the formation of four nonexecutive ministries – Government Administration, Government Legislation, Planning, and the Bureau of Public Information – along with the formation of three committees: Inspection, Examination, and General Accounting. Since its inception in 1948, the structure of the Korean government has changed through the subsequent decades.
The election of President Park Guen-hye in 2013 ushered in what was called “A New Era of Hope and Happiness.” During the launch of the new administration in February, 2013, four key policy objectives were announced: Economic Revival (3 strategies, 42 goals), the People’s Happiness (4 strategies, 64 goals), Cultural Enrichment (3 strategies, 10 goals), and the Laying of the Foundation for Peaceful Unification (3 strategies, 13 goals). The Park government has also promoted an efficient governmental system which can support what it terms as a “creative economy,” and this has served as a guiding theme for economic revival, especially through the convergence of science and information and communications technologies. The New Era has also established that public safety is a matter of the highest priority in domestic affairs. The current government has been organized into 17 Executive Ministries, 3 Ministries and 17 Offices according to the revised Government Organization Act amended in 2014 (Act no. 12844).
● Ministry of Strategy and Finance: This ministry administers “the establishment of mid- and longterm strategies for national development, formulation, overall control and coordination of economic and financial policies, formulation, execution and performance management of budgets and funds, currency, foreign exchange, National Treasury, government accounting, internal tax system, customs, international finance, management of public institutions, economic cooperation, State property, private investment, and national debts.
● Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning: This ministry takes charge of “the formulation, overall control and coordination of policies on science and technology, research, development and promotion of science and technology and cooperation therein, training of science and technology personnel, research, development, production and utilization of nuclear energy, planning of national informatization, protection of information, information culture, fusion and promotion of broadcasting and communications, management of radio waves, information and communications industry, postal service, postal money orders, and postal transfers.”
● Ministry of Education: This ministry is in charge of “policies on the development of human resources, school education, lifelong education, and sciences.”
● Ministry of Foreign Affairs: This ministry oversees “diplomacy, economic diplomacy, diplomacy for international economic cooperation, coordination of duties regarding international relations, treaties and other international agreements, protection of and support for Korean nationals abroad, formulation of policies on overseas Koreans and research and analysis of international circumstances.”
● Ministry of Unification: This ministry is in charge of “policies on unification, and dialogue, exchanges and cooperation between the South and North, education on unification, and other duties on unification.”
● Ministry of Justice: This ministry takes care of “prosecution, enforcement of sentences, protection of human rights, control of entry and departure into from Korea, and other legal matters.”
● Ministry of National Defense: “The Minister of National Defense shall administer military administration, military command and other military duties,” and the Ministry is in charge of “enlistment, mobilization, and other duties of military administration.”
● Ministry of Government Administration and Home Affairs: This ministry assumes responsibility for “the formulation, overall management and coordination of policies on security and disaster, systems of emergency preparedness and civil defense, general affairs of the State Council, promulgation of Acts, subordinate statutes and treaties, government organization and prescribed number of public officials, personnel management, ethics, services and pension of public officials, awards and decorations, government reformation, administrative efficiency, electronic government, protection of personal information, maintenance of government buildings, local government systems, support for business, finance and taxation of local governments, support for underdeveloped regions, mediation of disputes among local governments, elections and referendums.”
● Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism: “The Minister of Culture, Sports and Tourism shall administer duties concerning culture, arts, video, advertisement, publishing, publications, sports, tourism, publicity of State affairs and Government announcements.
● Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs: This ministry oversees “agriculture, livestock farming, foods, farmland, irrigation, promotion of food industry, development of farming villages and distribution of agricultural products."
● Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy: This ministry supervises “commerce, trade, industry, trade relations, trade negotiations, overall management and coordination of trade negotiations, foreign investment, policies on the research and development of industrial technology, energy and underground resources.”
● Ministry of Health and Welfare: This ministry is in charge of “health, sanitation, prevention of epidemics, medical administration, pharmaceutical administration, relief of the needy, support for self-sufficiency, social security, children (including infant care), elderly persons, and disabled persons.”
● Ministry of Environment: This ministry is devoted to “the conservation of natural and living environment and the prevention of environmental pollution.
● Ministry of Employment and Labor: This ministry oversees “overall employment policies, employment insurance, development and training of occupational capability, standards for working conditions, workers’ welfare, coordination of labor-management relations, industrial safety and health, industrial accident compensation insurance, and other duties concerning employment and labor.”
● Ministry of Gender Equality and Family: This ministry focuses on “the planning and consolidation of policies on women, improvement of women’s status, such as promotion of women’s rights and interests, juveniles and families (including duties concerning multi-cultural families and children for healthy family projects).
● Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport: This ministry controls “the formulation and coordination of comprehensive plans for national land, conservation, utilization, and development of national land and water resources, construction of cities, roads and houses, coasts, rivers reclamation, overland transportation, railroads, and aviation.”
● Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries: This ministry oversees all matters “maritime policies, fisheries, development of fishing villages, distribution of marine products, maritime transportation, harbors, marine environment, ocean surveys, development of marine resources, research and development of marine science and technology, and adjudication on cases of maritime safety.”