English I 2019
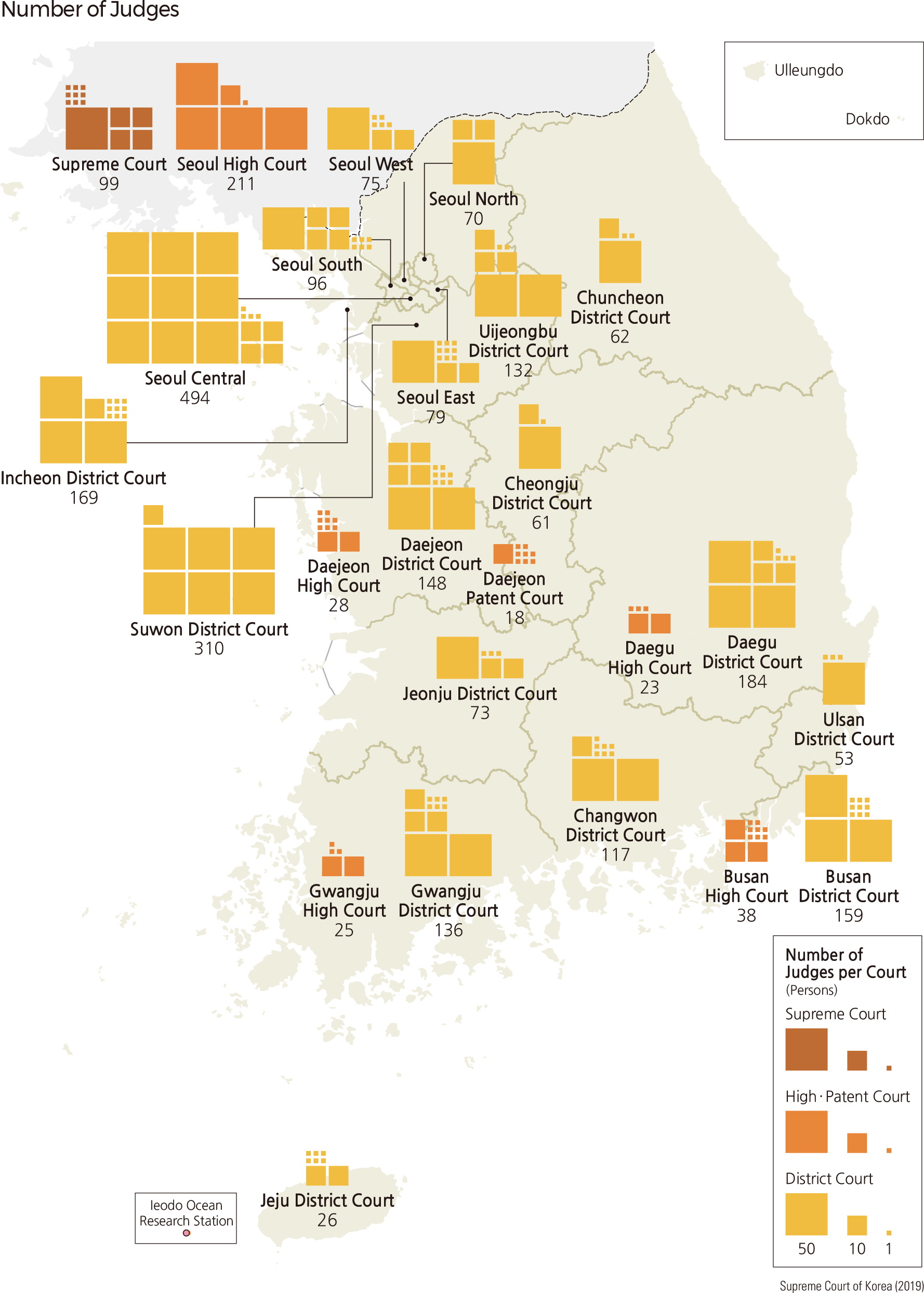
Previously, judges were appointed from among the candidates who passed the bar exam and completed training at the Judicial Research and Training Institute. A new judge appointment system is in place, in which judges are appointed from among those who have a judicial career of three or more years of experience, depending on the new appointment period. Judges recently appointed are lawyers who have passed a legal education eligibility test after completing one of 25 law schools nationwide under the Law School System introduced in 2009. As of 2018, the number of judges appointed is 2,886.
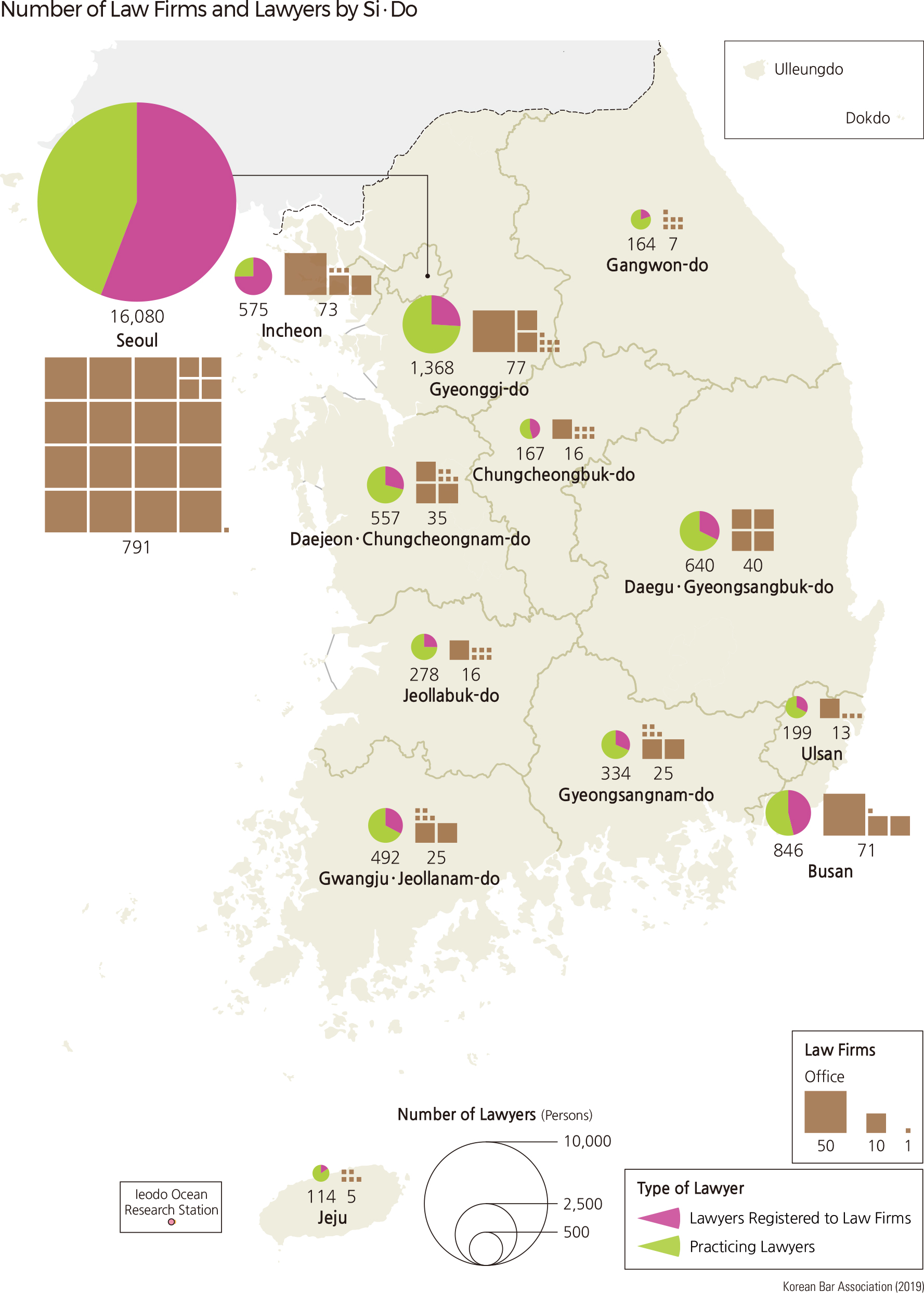
The prosecution, an executive organization responsible for criminal cases, is closely related to the courts. Therefore, the prosecution has an organization composed of the Supreme Prosecutor’s Office, Higher Prosecutor’s Office, District Prosecutor's Office, and Branch Prosecutor’s Office, in accordance with the court system. The spatial distribution of lawyers who defend the defendants in criminal cases or conduct litigations on behalf of the parties in civil lawsuits and administrative litigations are closely related to the number and size of the respective courts. Lawyers and law firms are concentrated in the Seoul metropolitan area where many courts are located.
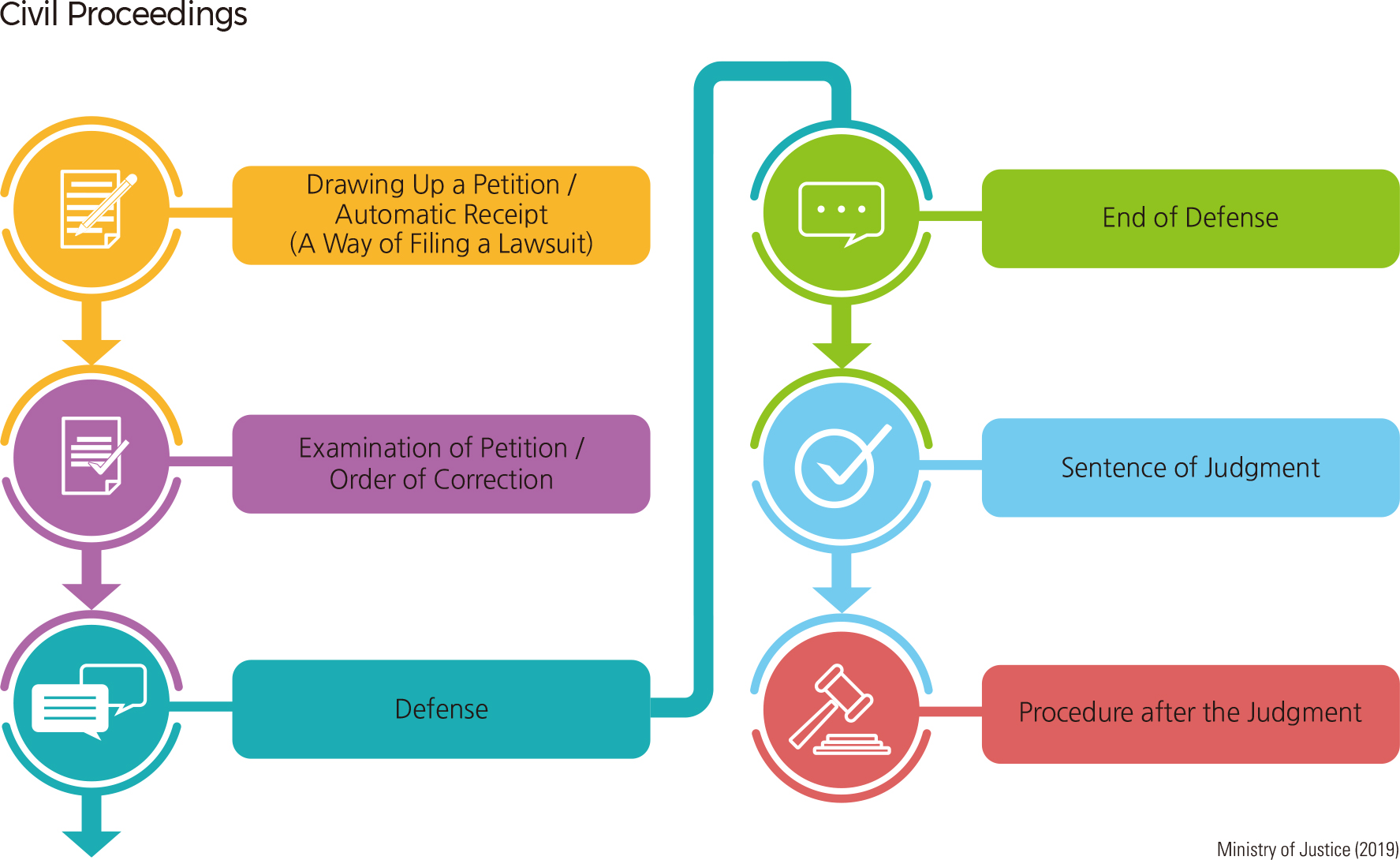
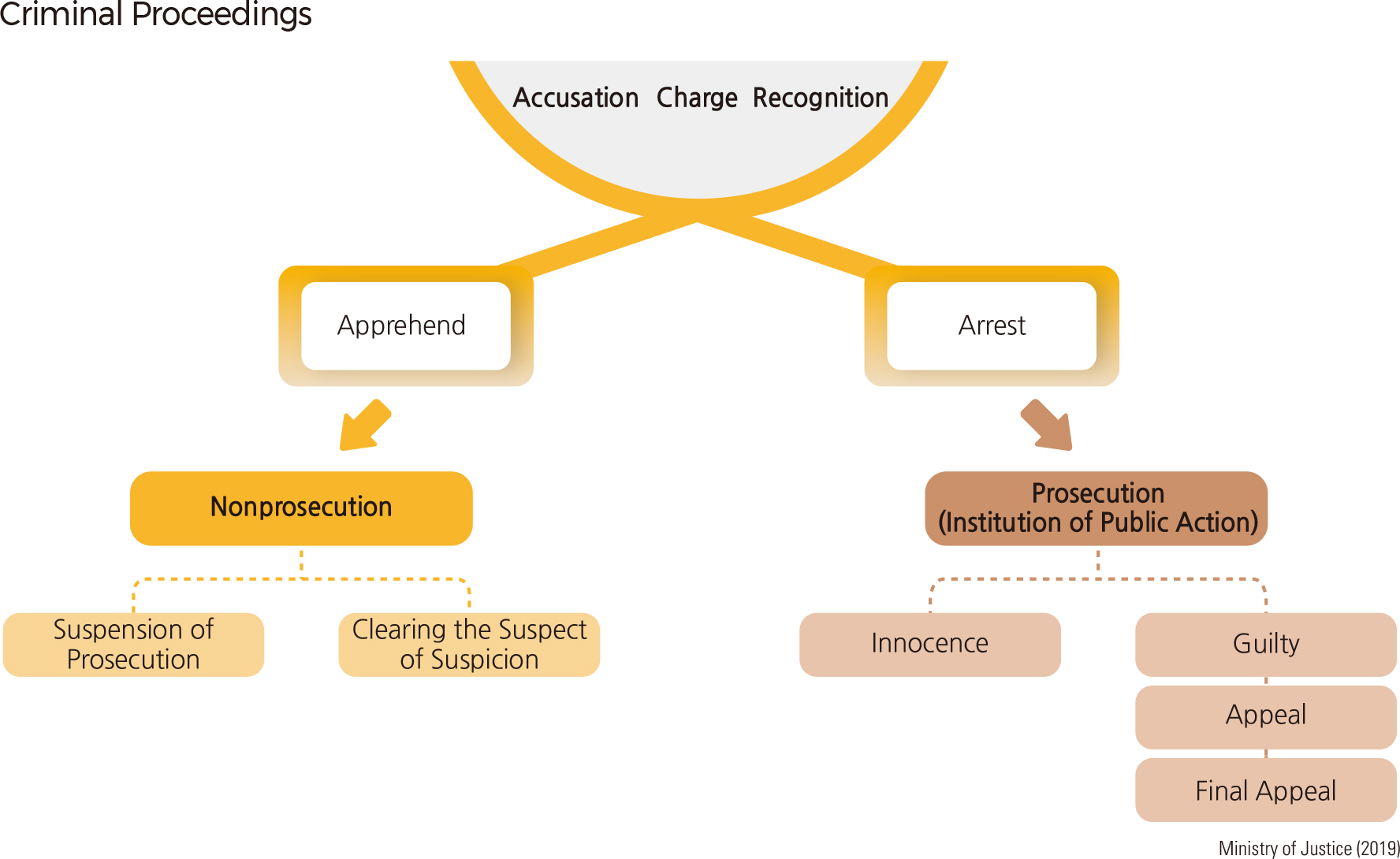
Most court trials are civil and criminal trials. Civil trials handle disputes regarding property rights and juristic relations of everyday life. The law describes in detail the trial procedure for not only the trial and subsequent levels of appeal, but also the trial procedures for small claims cases, the procedures for civil conciliation, civil execution proceedings, property description and property inquiry, and the procedures for provisional attachment and injunction. Criminal trials determine guilt or innocence of the accused under indictment and impose a punishment in the case of a guilty verdict. With respect to criminal trials, the law describes in detail the procedures of investigation, prosecution, trial, appeal, and a summary trial.
The courts are a national organization that exercises the power to administer and supervise extra-judicial matters such as immovable and movable properties, secured claim registration, and family relations registration. District courts and branches of district courts provide the registration service because registration is, unlike simple works of administrative, civil affairs, a quasi-judicial process wherein the complex interests of different groups are interwoven. District courts have a registration office as an affiliated organization to handle part of the administration of registration within their jurisdiction. A registration office handles commercial, real-estate, and ship registrations, and issues registration certificates, authentication certificates of seal, and date-fixed stamps on private documents.
The courts are responsible for the administration of the family-relation registration that replaces the patriarchal family system. Family-relation registration, is the system that registers citizen’s status individually to the family-relation registration record and officially certifies the record. It is completely different from the patriarchal family system that classified a citizen’s status relation by the head of the family. Family-relation registration (previously patriarchal family registration work) is administrated nationally, and the Supreme Court is appointed to act as the responsible unit to handle family-relation registration. The Supreme Court delegates the authority of registration to the head of administrative units (si/gu/eup/myeon), for the citizen’s convenience. |