English I 2019
The National Assembly is the legislative body of the Republic of Korea and is composed of members who are elected by the people to whom sovereignty belongs. On their behalf, the National Assembly enacts laws which are the foundation of state operation, deliberates, finalizes the budget, and makes important policy decisions.
The National Assembly has the legislative power to propose and pass constitutional amendments and to enact and revise laws. It deliberates and decides upon budget proposals and settles governmental accounts, and controls state affairs by auditing the overall administration of the state and inspecting specific issues. Furthermore, it has the right to approve the President’s appointment of key public officials, such as Chief Justice of the Supreme Court, President of the Constitutional Court, Prime Minister, and Chairman of the Board of Audit and Inspection, and the right to ratify major international treaties on behalf of the people. Moreover, it also actively engages in parliamentary diplomacy, which helps elevate the nation’s interests as well as its international profile.
There are 300 statutory members of the National Assembly. Two-hundred and fifty-three members are elected from single-member constituencies, and the remaining 47 gain office through a proportional representation system. With a term of four years, the cycle of the current 20th National Assembly runs from May 30, 2016, to May 29, 2020.
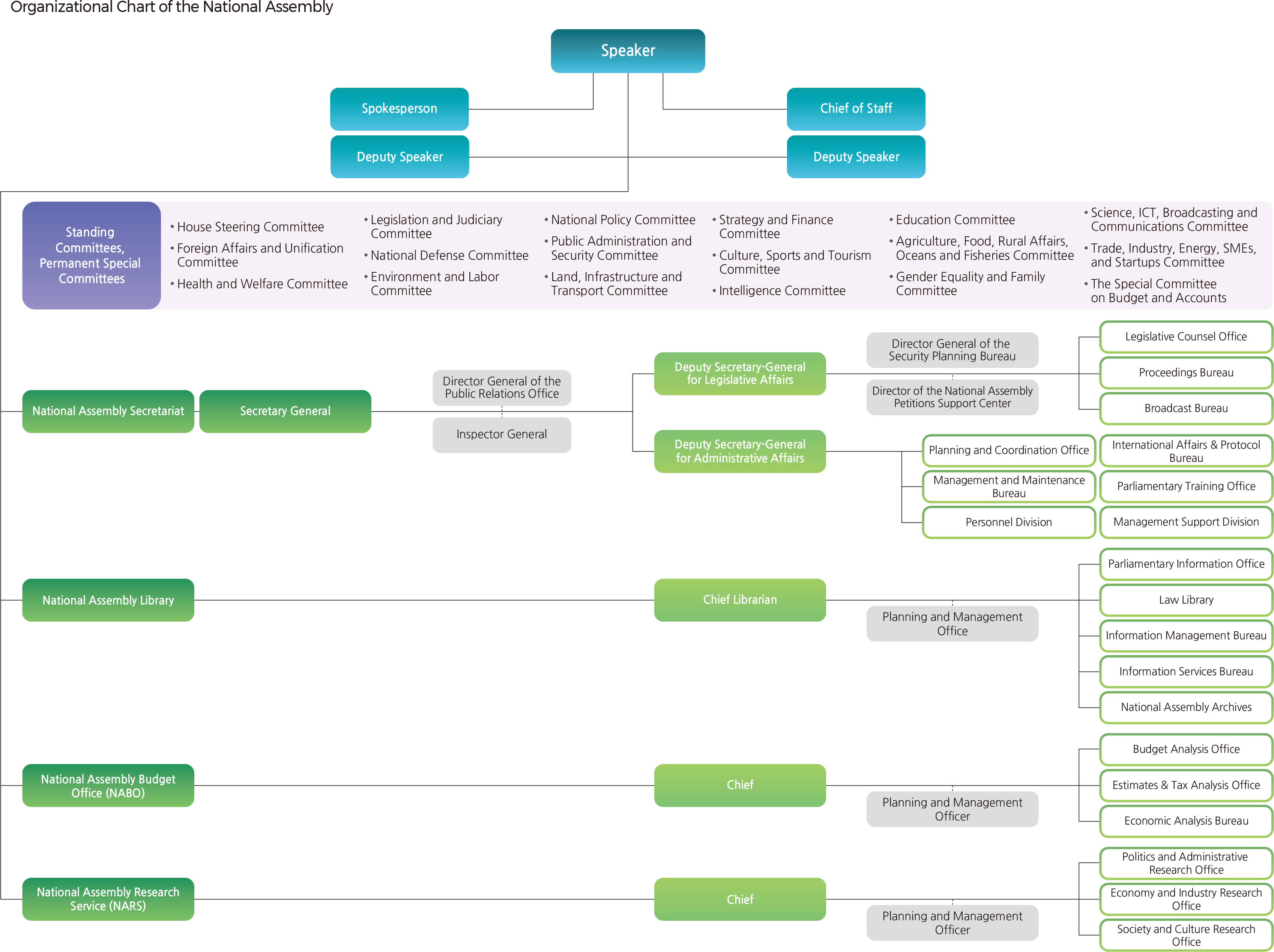
The National Assembly has one Speaker and two Deputy Speakers. They are elected at the plenary session through secret voting, and each serves a two-year term. As the leader of the legislative body, the Speaker represents the National Assembly, presides over the plenary session, and oversees the administration of the National Assembly. To maintain impartiality during the proceedings, the Speaker is not allowed to affiliate with any political party during his or her term of office. In case the Speaker is unable to carry out his or her duties within their term, a Deputy Speaker reserves the right to act in his or her place.
The National Assembly holds regular and extraordinary sessions. The regular session convenes on the first day of September every year and may not exceed one hundred days. Extraordinary sessions convene on the first day of February, April, and June (even-numbered months with the exception of August, October, and December) every year and may not exceed thirty days.
There are seventeen standing committees and one permanent special committee (Budget and Accounts) that examine bills prior to deliberation at the plenary session. Additional special committees may also be installed to deliberate on particular items. All members of the Assembly, with the exception of the Speaker, shall become a member of a standing committee for a two-year term according to their respective fields of expertise and interest.
Negotiation groups expedite the proceedings of the National Assembly as organizations to facilitate modern party politics. Any party with twenty or more Assembly members can form a negotiation group. In addition, twenty or more members who do not belong to a negotiation group may join together to set up a separate negotiation group. The composition of committees, formation of inter-parliamentary councils, and the number of speakers as well as the length of speech in meetings are determined by the proportion of members in each negotiation group.
The National Assembly Secretariat, National Assembly Library, National Assembly Budget Office (NABO), National Assembly Research Service (NARS), and support staff for representatives are components of the legislative support organizations that professionally and effectively support the authority and function of the National Assembly.
The function of the Secretariat is to support the overall parliamentary activities of lawmakers and to take care of the administrative work of the National Assembly. The Secretariat supports major legislative and parliamentary activities from supporting the smooth running of meetings, assisting the deliberation on legislative bills, and overseeing the budget and settlement of accounts and the inspection and investigation of state administration, to providing support for parliamentary diplomacy, handling civil complaints, and promoting National Assembly Broadcasting Station (NATV) services and the National Assembly as a whole.
The National Assembly Library was established to facilitate the legislative activities of lawmakers by collecting, managing, and providing necessary information regarding various pending issues and legislation. The general public also has access to the materials collected, even at night and on Sundays.
The National Assembly Budget Office (NABO) is a legislative support body specializing in financial matters that was established to promote parliamentary financial activities, including assistance in deliberating on the budget and settlement of accounts based on professional and impartial research and analyses.
The National Assembly Research Service (NARS) is an inde- pendent legislative and policy research institute established within the National Assembly to strengthen its capacity in legislation and policy development. It conducts studies, research, and analyses on legislative and policy issues in an impartial and professional manner. NARS also collects, manages, and distributes related materials, and undertakes studies and analyses on legislative trends and cases at home and abroad in the respective fields to hand them over to Assembly Members and Committees.
Each member of the Assembly is entitled to have eight advisors to facilitate their parliamentary activities. The scope of their work ranges from support for legislative activities in terms of policy formulation to political affairs concerning communication with voters. |