English I 2019
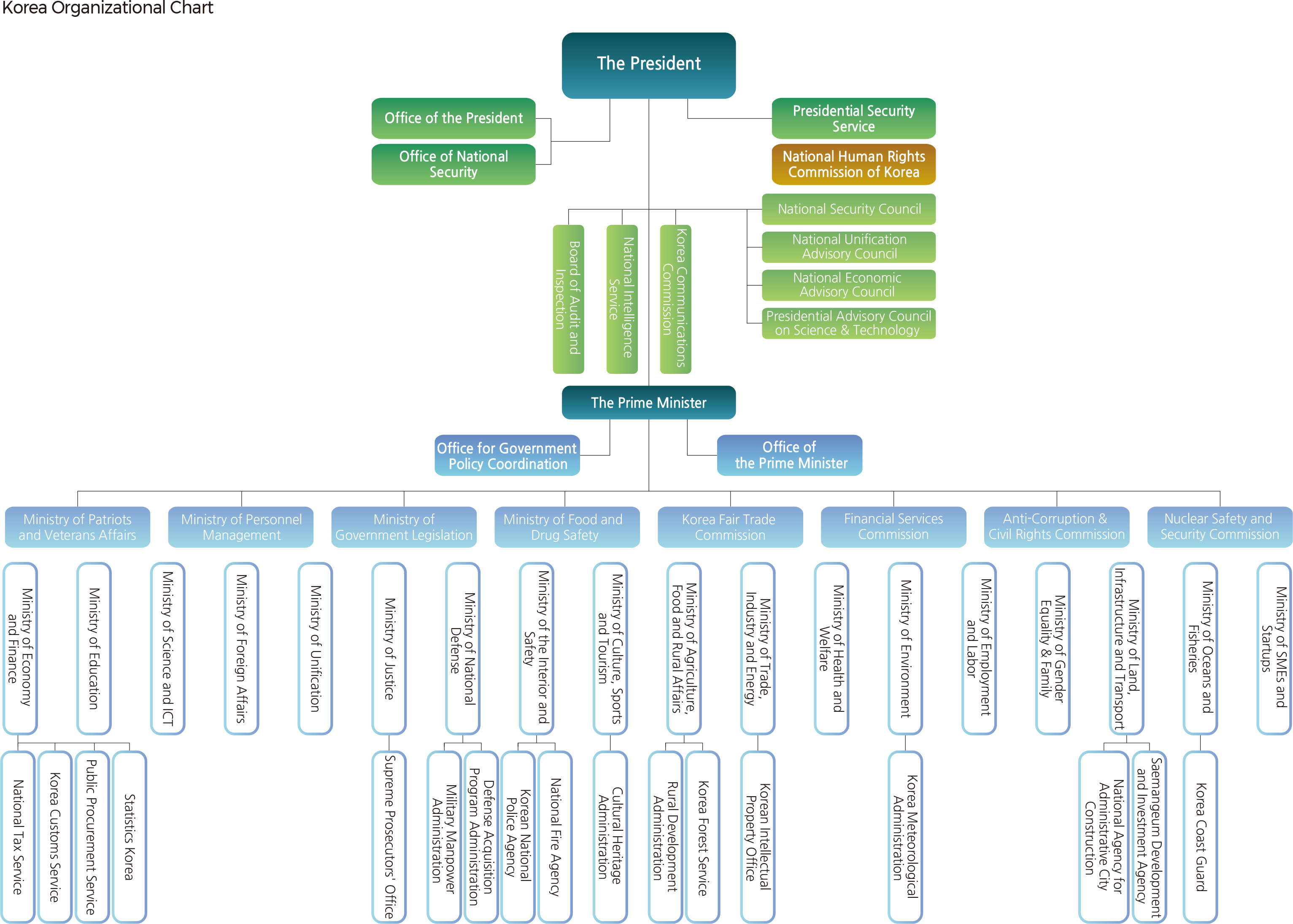
In accordance with the Constitution of the Republic of Korea, the Executive Government consists of the President and the executive branch. The president of the Republic of Korea is elected to a five-year term. On May 10, 2017, the 19th President, Moon Jae-in, took office. Article 66 of the Constitution of the Republic of Korea defines the position of the President as follows:
(1) The President shall be the Head of State and represent the State vis-a-vis foreign states.
(2) The President shall have the responsibility and duty to safeguard the independence, territorial integrity, and continuity of the State and the Constitution.
(3) The President shall have the duty to pursue sincerely the peaceful unification of the homeland.
(4) Executive power shall be vested in the Executive Branch headed by the President.
The State Council shall deliberate on important policies that fall within the power of the Executive Government. The State Council shall be composed of the President, the Prime Minister, and other members who shall be appointed by the President on the recommendation of the Prime Minister. The Prime Minister shall be appointed by the President with the consent of the National Assembly. The executive ministries shall be established under the control of the President, and the ministers shall be appointed as members of the State Council.
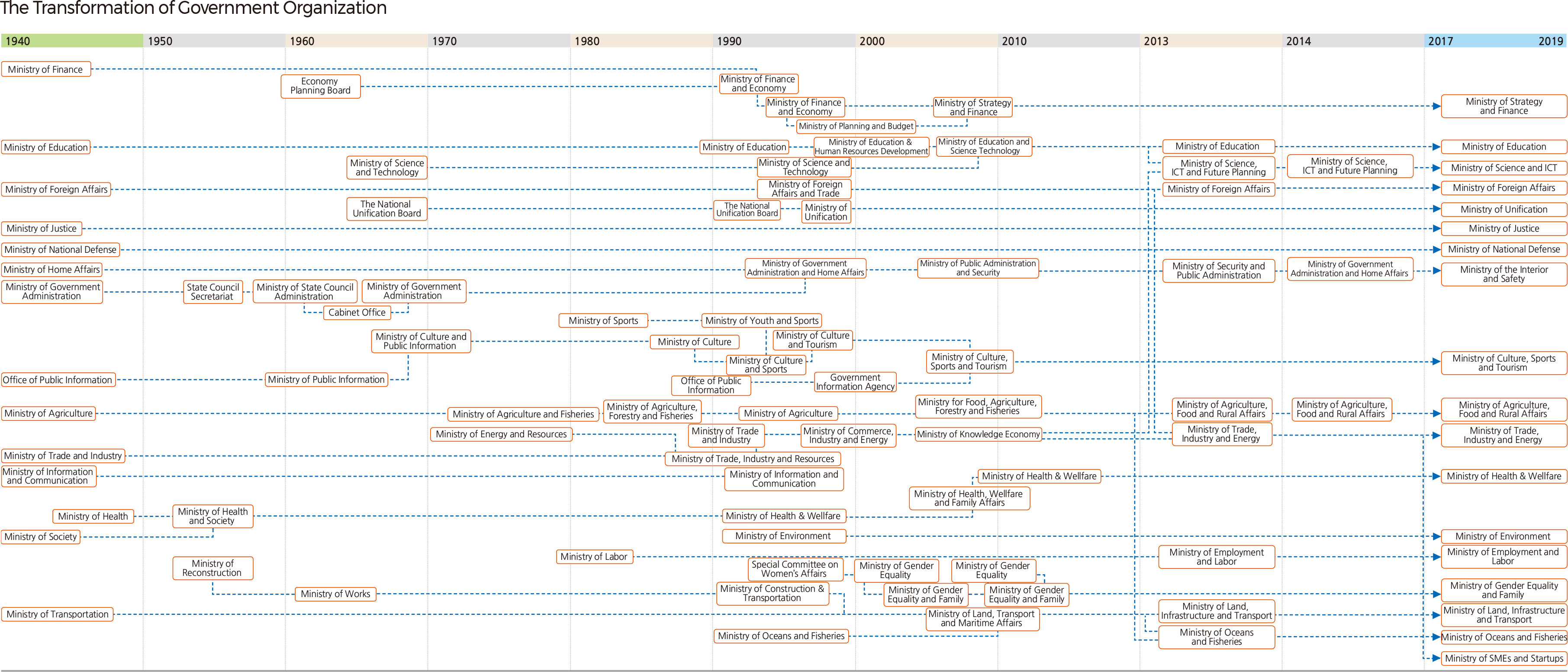
In addition, The Board of Audit and Inspection shall be established under the President's affiliation to examine the final accounts of revenues and expenditures of the State, audit the accounts of the State and such organizations as prescribed by the laws, and inspect the works performed by government agencies and the duties of their employees. The current executive branch consists of 18 executive ministries, 5 ministries, and 17 agencies in accordance with the Government Organization Act (Enforcement Date: June 8, 2018; Act No. 15624). |