English III 2021
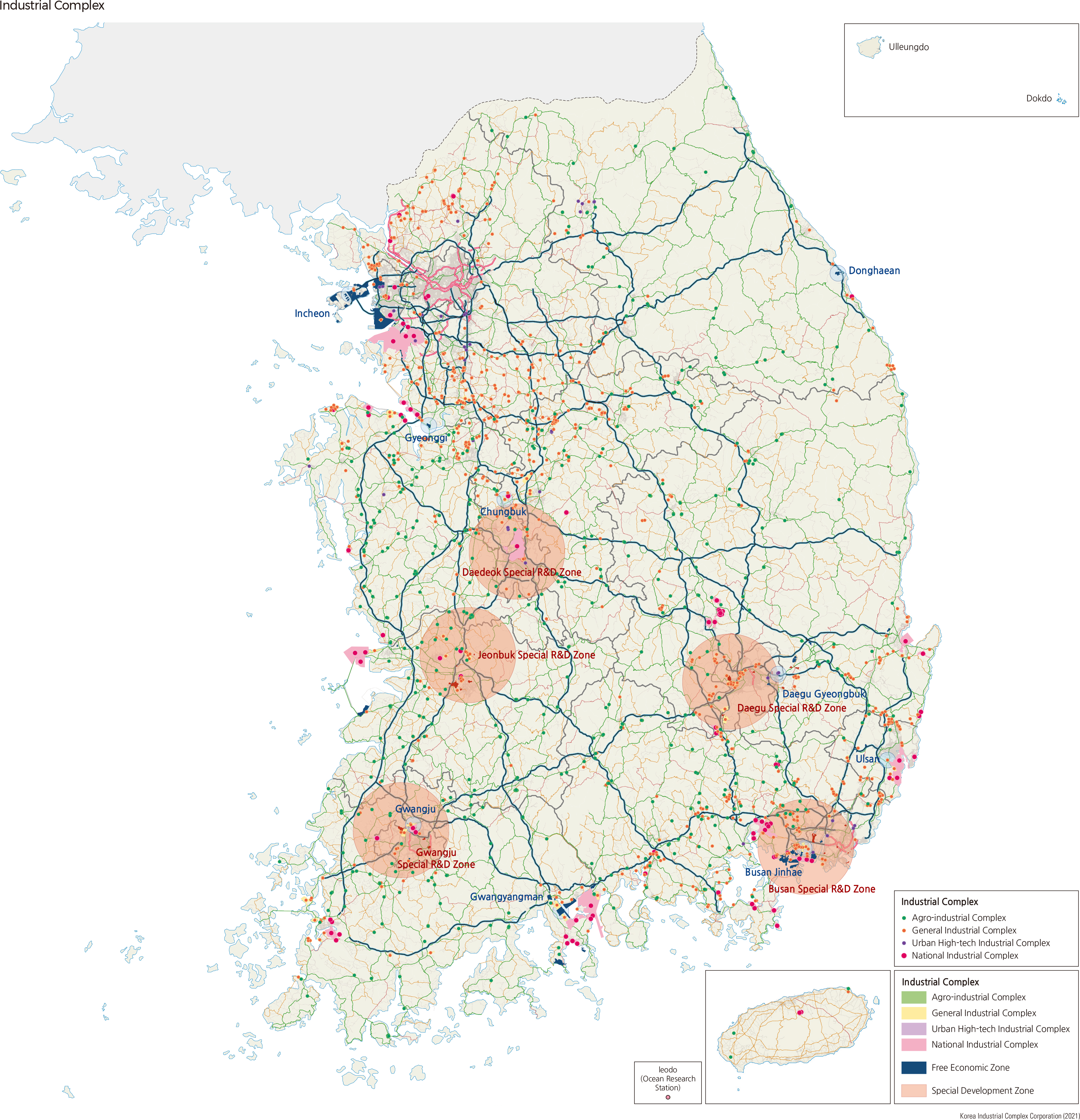
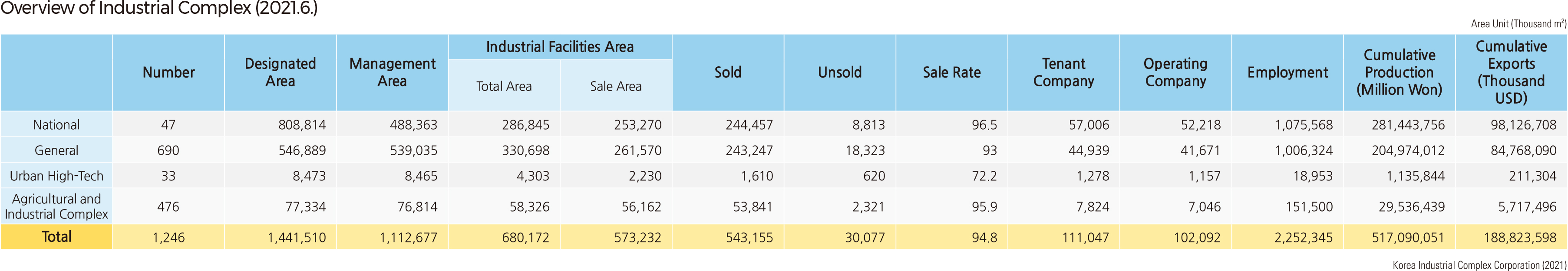
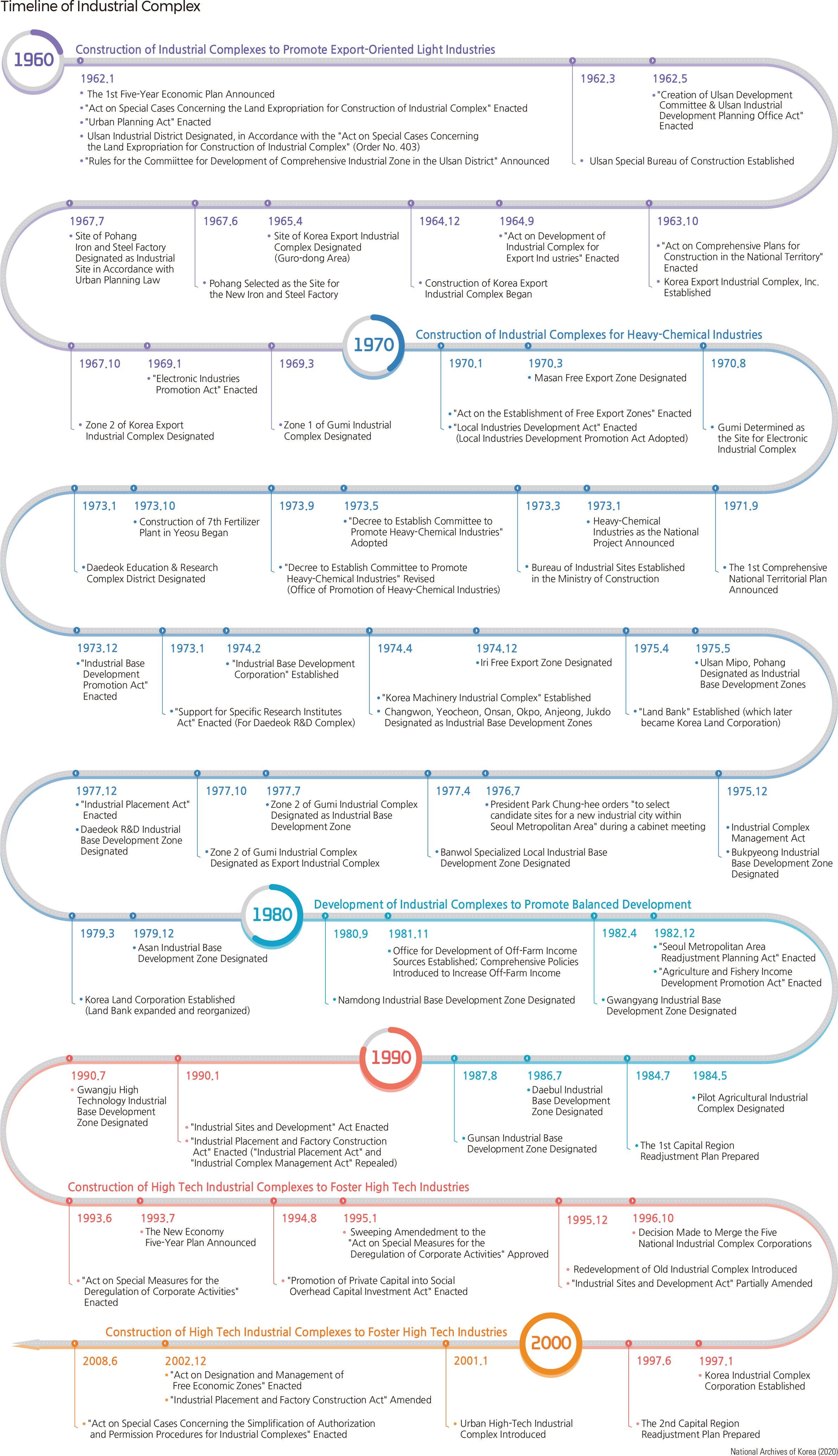
The development of industrial complexes began with the designation of the Ulsan Industrial District in 1962 and the construction of the Guro Industrial Complex in 1966. In the late 1960s, industrial complexes were built in the provincial capital, such as Gwangju, Daejeon, Jeonju-si, Cheongju-si, Daegu, and Chuncheon-si. In the early 1970s, industrial complexes were established in small and medium-sized cities like Iksan (former Iri), Wonju-si, and Mokpo-si with the introduction of the local industrial development incentive zone system. In the late 1970s, specialized industrial complexes were built to foster the heavy and chemical industries: chemical (Ulsan, Onsan, and Yeosu), light industry (Biin, Gunsan), steel (Pohang, the lower Nakdonggang), electronics (Gumi), and shipbuilding (Busan, Ulsan, and Geoje). Since 1980, the government has pursued the balanced development of the country. In 1984, agro-industrial complexes were first introduced, and many agro-industrial complexes were designated in the late 1980s. The government introduced the Urban High-Tech Industrial Complex System in 2001. Various industrial complexes, such as venture business complexes, software promotion complexes, and information and communication industrial complexes, have been constructed along with the governmental strategies to make the knowledge-based industry a new growth engine.
The Free Trade Zone (FTZ): The Free Export Zones (FEZ) were first established in the 1970s. Masan FEZ (1970) and Iksan FEZ (1974) were first designated. In 2000, the Act on Designation and Management of Free Trade Zones renamed the FEZ the Free Trade Zone (FTZ). Currently, four types of FTZs are distributed in 13 cities. The industrial complexes are managed by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. Seven industrial complexes are located at Gunsan, Gimje, Daebul, Yulchon, Donghae, Ulsan, and Masan. The airports, hinterland and logistics terminals and logistic complexes are managed by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport. Incheon International Airport is designated as the Airport and Hinterland FTZ. However, no FTZ has been designated as the Logistics Terminals and Logistic Complex yet. The Ports and Hinterland types are managed by the Minister of Oceans and Fisheries. Five ports, including Incheon Port, Pyeongtaek/Dangjin Port, Pohang Port, Busan Port, and Gwangyang Port, are in this group. The benefits provided to companies include property tax reduction, customs exemption and refund, and corporate tax and income tax reduction.
Foreign Investment Zone (FIZ): In 1994, the Foreign Business Complex was introduced to promote the domestic investment of foreign companies. In 1999, the Foreign Investment Zone (FIZ) was developed to promote foreign investment. In April 2017, a service-type FIZ was first established for the knowledge-based service industry, such as R&D in Mapo-gu, Seoul. As of 2020, there are 28 complex-type FIZs, 78 individual-type, and three service-type. Local tax reduction for up to 15 years and customs exemption for five years from the declaration of import of capital goods are available for foreign companies within a FIZ.
Free Economic Zones (FEZ): Incheon FEZ, Busan-Jinhae FEZ, and Gwangyang Bay FEZ were first designated in 2003. Currently, there are nine FEZs in Korea. Foreign-invested companies and development project operators in the FEZ are exempted from customs duties, acquisition tax, and property tax according to laws such as the Special Act on Designation and Management of Free Economic Zones and the Restriction of Special Taxation Act.
INNOPOLIS (Special R&D Zone): INNOPOLIS Daedeok was launched in 2005, followed by INNOPOLIS Gwangju (2011), INNOPOLIS Daegu (2011), INNOPOLIS Busan (2012), and INNOPOLIS Jeonbuk (2015). Since 2017, InnoTown, a town-type R&D Special Zone, has been implemented, including crucial technology centers housed in universities, research institutes, and public enterprises. In 2019, six InnoTowns in Ansan-si, Gimhae-si, Jinju-si, Changwon-si, Pohang-si, and Cheongju-si were designated. In 2020, an additional six InnoTowns were established in Gumi-si, Gunsan-si, Naju-si, Ulju-gun, Hongneung-gun, and Cheonan-Asan-si.
International Science & Business Belt: This industrial complex aims to form a science-based innovation cluster through the breakthrough promotion of basic science by connecting research bases and technology belts at Sejong Special Self-Governing City, Daedeok Research Complex, and Daejeon Industrial Complex. The comprehensive plan was finalized in 2009, and the construction of three base districts began in 2016: the Sindong District (Heavy ion accelerator), the Dungok District, and the Doryong District (Institute for Basic Science). Exemption and reduction of income tax, corporate tax, and property tax, and additional financial support from local governments are available for companies in this industrial complex.
High-Tech Medical Complex: This complex consists of a medical R&D hub for developing new drugs and advanced medical devices to foster the medical industry as a new national growth engine. In 2008, a special law was designated. In 2009, Sinseo Meditech District in Daegu for synthetic new drugs and IT-based medical devices and Osong High-tech Medical Complex in Chungcheongbuk-do for new biologic drugs and BT-based medical devices were selected. |