Comprehensive Edition 2022
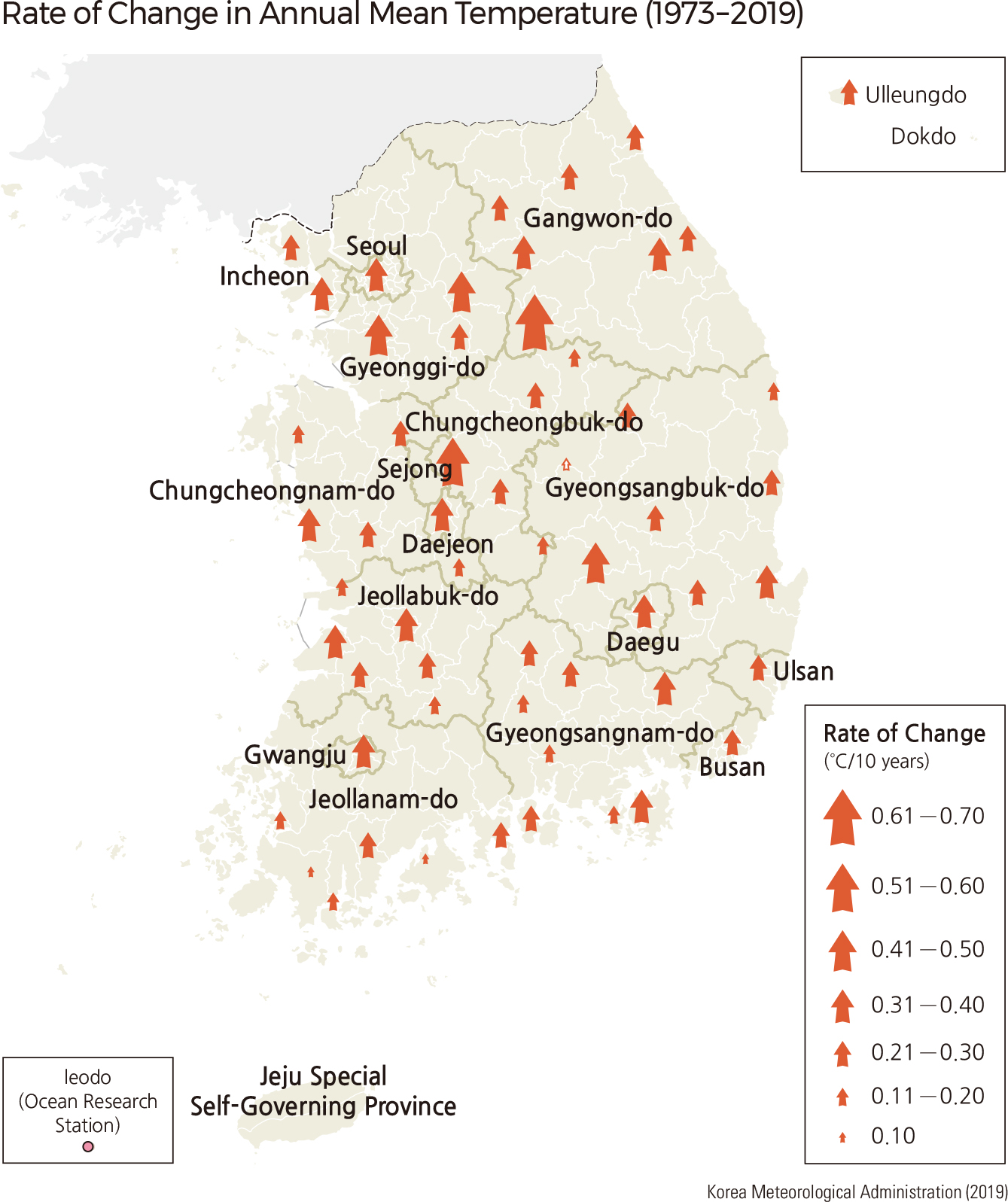
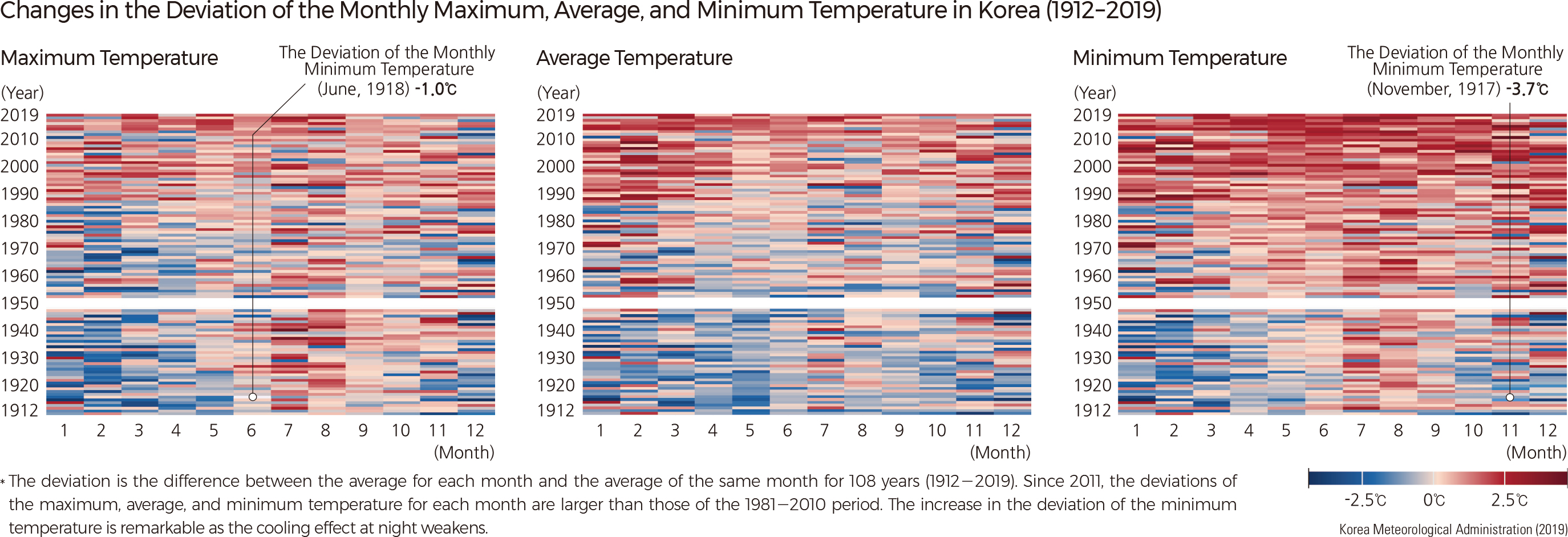
A detailed network of climate monitoring stations in Korea provides a nice data set for assessing climate change. Over the past decade, the broad trend across northeast Asia has been for warmer spring, summer, and fall seasons, whereas winters have been cooler, especially in the continental interior. On the Korean Peninsula, mean annual temperatures have increased at rates averaging 0.27°C/decade, with a maximum warming rate of 0.61°C/decade. Summer temperatures have increased by 0.6–1.1°C over the past decade compared to the long-term average. In general, cities have warmed more than rural areas.
Precipitation on land has decreased in recent years, while precipitation over the ocean has increased. The disparity in precipitation between land and ocean is most evident during the summer months. The decline in rainfall on land starts in winter and lasts through spring and summer, contributing to water shortages in East Asia in spring.
The annual mean temperature of the Korean Peninsula is expected to rise steadily throughout the 21st century. According to the Trewartha climate classification, the southern coast of the Korean Peninsula, including Jejudo, is classified as a humid subtropical climate region. As global warming accelerates, the boundary of the subtropical climate region is projected to move gradually to the north.
The annual mean number of tropical nights is expected to increase substantially by the late 21st century. According to some estimates, many areas of the peninsula, excluding the major mountain highlands, will have a much greater annual number of tropical nights than today. Later, as climate change becomes more intensified, it is anticipated that areas with tropical nights will expand to include the mountain highlands. It’s also expected that there will be an increase in the number of days affected by heat waves in the lowlands. The number of heavy precipitation days is also projected to increase in most regions, with frequency and rainfall amounts varying widely, depending on time, region, and scenario. |