Comprehensive Edition 2022
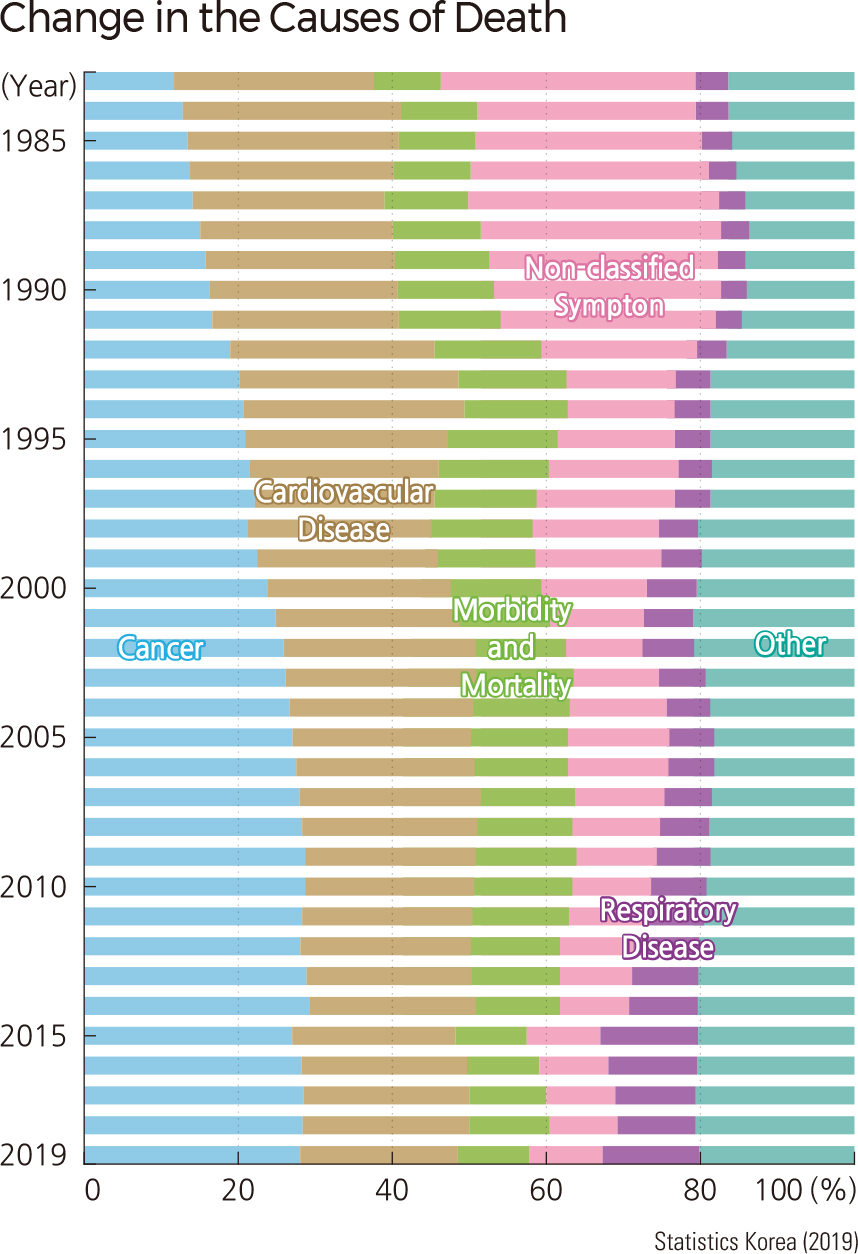
The expansion of modern medical science in Korea has paralleled economic growth over the last half century. With an abundance of well-trained medical personnel, high-tech equipped medical facilities, and a systemically maintained health screening system, life expectancy in Korea is among the highest compared with other nations around the world. Through the introduction of a universal health insurance system, all citizens enjoy the benefits of health insurance. Medical expenses have increased, however, due to an aging population and health span (the number of years that one lives in good health) that is shorter than it is for other OECD countries.
Access to medical care has greatly increased because general clinics have become more evenly distributed nationwide. In contrast, general hospitals continue to be preferentially located in large metropolitan areas. Most medical institutions in Korea are private, comprising around 94% of health institutions, the lowest among OECD countries.
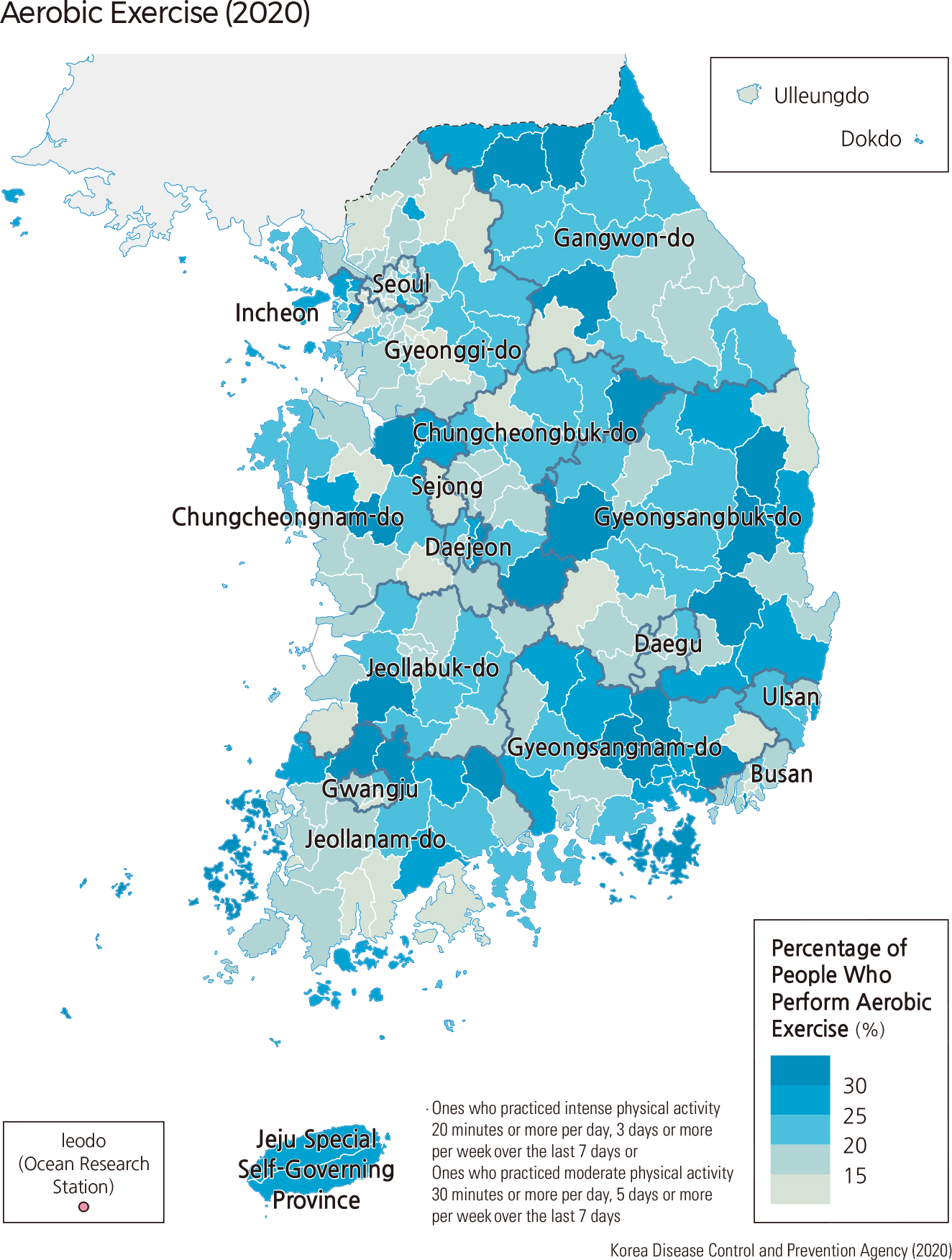
There is a growing awareness of the importance of diet and exercise for maintaining general health and well-being. An emphasis on creating greenspace and walkable, bike-friendly communities helps to foster environments that encourage routine exercise. The geographic patterns of obesity and participation in aerobic exercise are in part reflective of local opportunities for outdoor pursuits. Another factor in obesity rates is the shift toward a Western-style diet, especially among young people, which unfortunately tends to increase rates of obesity.
|