Comprehensive Edition 2022
Seoul has experienced a rapid increase both in population and land area in modern times. During the Joseon Dynasty (1392–1897), Seoul was surrounded by a fortress wall and consisted of Hanseong and five -bus, which together formed the political and administrative center with its inner and outer districts (Seongjeosimni). The outer districts stretched about 4 km beyond the city wall. By the end of the 19th century, the city’s population hovered above 200,000. From the end of the Joseon Dynasty through the period of Japanese colonial rule, the city’s boundaries grew as railroads and streetcar routes were constructed. A massive residential area was built to house Japanese immigrants and farmers who migrated to the city during this period. Following its liberation from Japan, Seoul’s population was close to 900,000 and grew to 1,700,000 before the Korean War as overseas Koreans returned home.
Seoul has modified its administrative areas eight times since the confirmation of the first urban plan in 1936, resulting in the expansion of urban districts. Starting with the organization of the seven -gus in 1943, Seoul’s population increased sharply before industrialization, and the rise in population density accelerated as industrialization rapidly grew after the 1960s. The concentration of the population resulted in the development of the outskirts of the city, and the opening of subways further facilitated urban expansion. The land area of Seoul has been 605 km² since 1995. Seoul takes up 0.6% of the national territory and is composed of 25 autonomous -gus and 424 administrative -dongs as of 2019.
Like Seoul, six other metropolitan cities have had increases in population and expanded their administrative areas. In 1995, metropolitan cities, serving as hub cities in the local area, were reorganized by integrating surrounding areas and became directly-controlled municipalities.
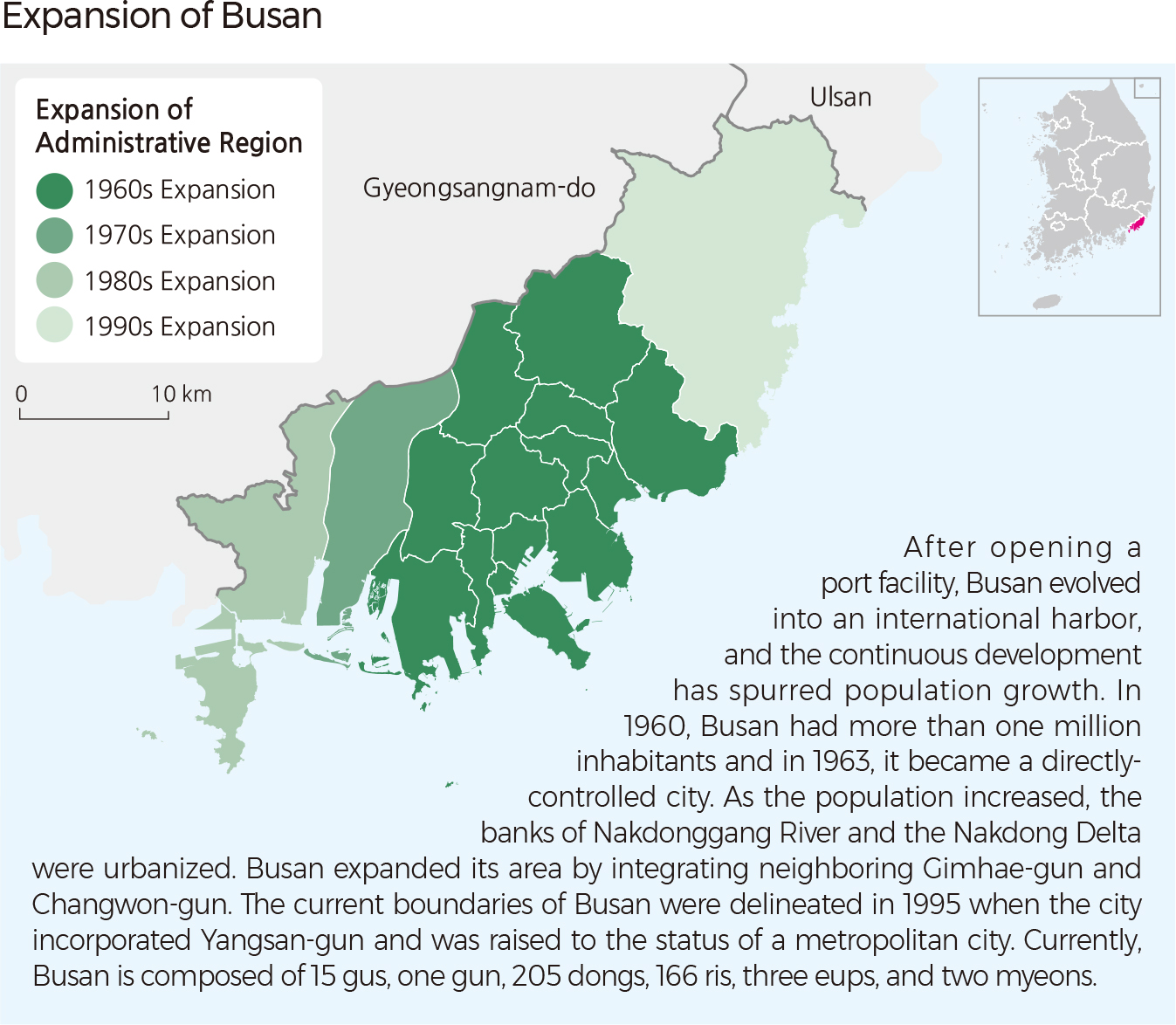
<map> Expansion of Busan After opening a port facility, Busan evolved into an international harbor, and the continuous development has spurred population growth. In 1960, Busan had more than one million inhabitants and in 1963, it became a directly-controlled city. As the population increased, the banks of Nakdonggang River and the Nakdong Delta were urbanized. Busan expanded its area by integrating neighboring Gimhae-gun and Changwon-gun. The current boundaries of Busan were delineated in 1995 when the city incorporated Yangsan-gun and was raised to the status of a metropolitan city. Currently, Busan is composed of 15 gus, one gun, 205 dongs, 166 ris, three eups, and two myeons.
<map> Expansion of Daegu In 1981, Daegu was elevated to a directly-controlled city, merging with Dalseong-gun, Chilgok-gun and a part of Gyeongsan-gun. After becoming a metropolitan city in 1995, the city grew significantly in size. Currently, Daegu is composed of seven gus, one gun, three eups, six myeons, and 130 dongs.
<map> Expansion of Incheon As the gateway city to the capital region, Incheon was elevated in status to a directly-controlled city in 1981 and became a metropolitan city by integrating Ganghwa-gun and neighboring remote areas in 1995. Incheon is composed of eight gus, two guns, one eup, 19 myeons, and 133 dongs.
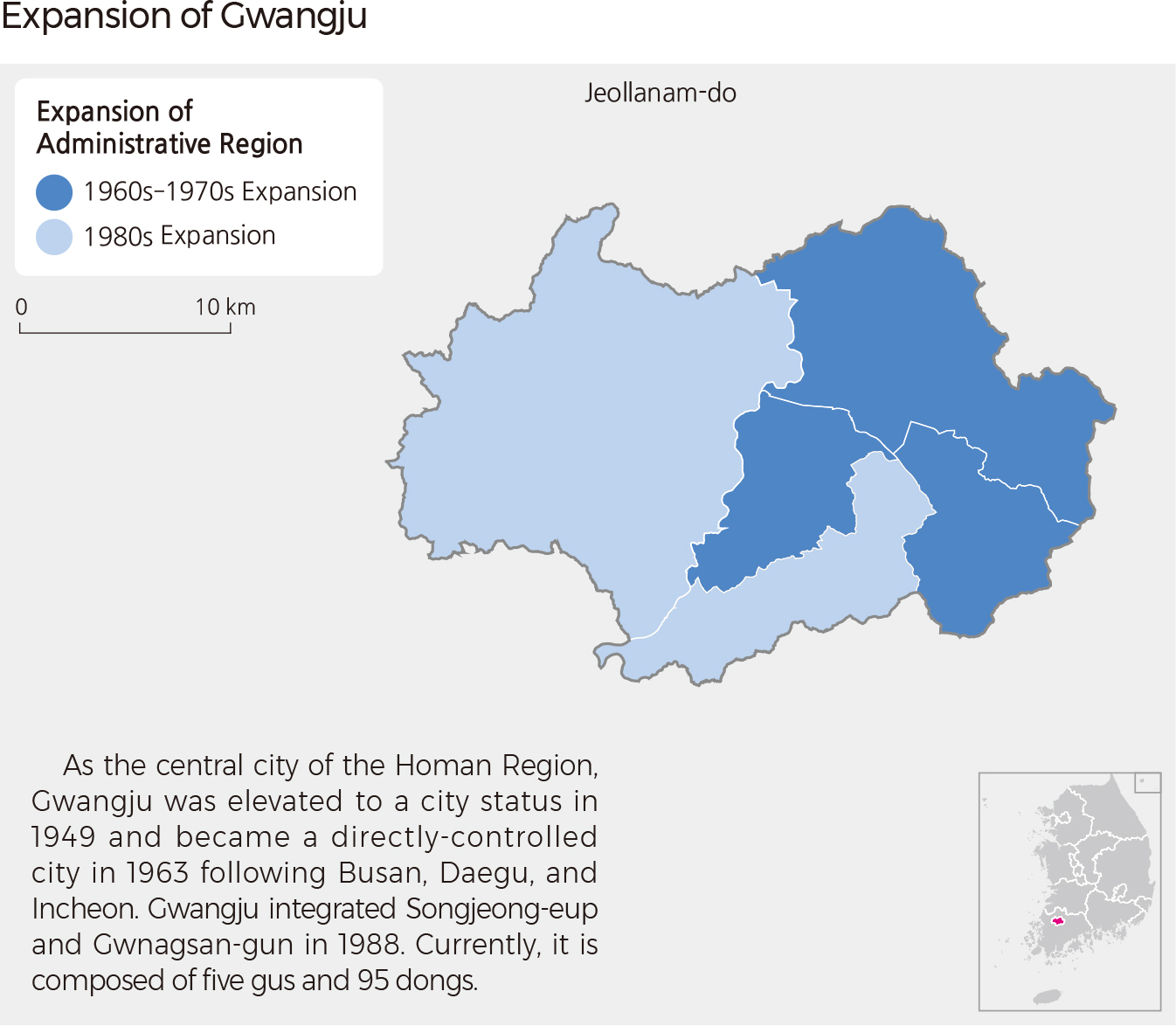
<map> Expansion of Gwangju As the central city of the Homan Region, Gwangju was elevated to a city status in 1949 and became a directly-controlled city in 1963 following Busan, Daegu, and Incheon. Gwangju integrated Songjeong-eup and Gwnagsan-gun in 1988. Currently, it is composed of five gus and 95 dongs.
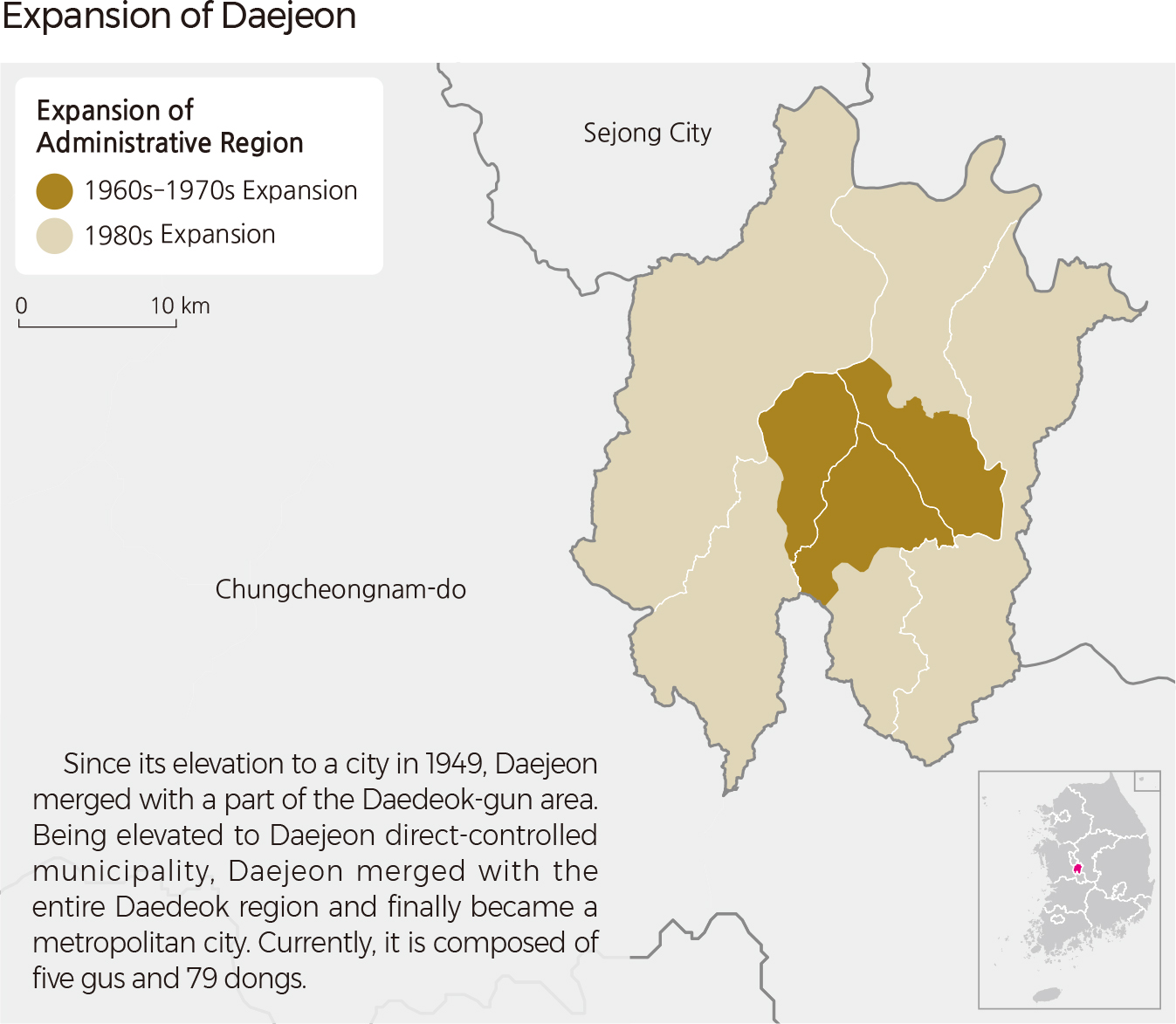
<map> Expansion of Daejeon Since its elevation to a city in 1949, Daejeon merged with a part of the Daedeok-gun area. Being elevated to Daejeon direct-controlled municipality, Daejeon merged with the entire Daedeok region and finally became a metropolitan city. Currently, it is composed of five gus and 79 dongs.
<map> Expansion of Ulsan With the establishment of nearby industrial complexes, Ulsan has enjoyed rapid growth. In 1962, it was elevated to city status. In 1995, it was integrated with Ulsan-gun and finally elevated to metropolitan city status. Ulsan is composed of four gus, one gun, 44 administrative dongs, and 12 eups and myeons in its administrative region system. |